* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cost-effectiveness: An Engineers`s Real Job
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
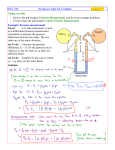
Cost-effectiveness: An Engineers's Real Job Problem 3.138* Created By: Patrick Thomas Problem •A pitot-static probe to measure the velocity distribution in a water tunnel at 20o C. •U-tube manometer that uses a liquid of specific gravity 1.7. •Maximum velocity= Vmax= 2.3 m/s. •U-tube manometers to choose from are 8, 12, 16, 24, and 36 inches, with increasing cost (respectively). Which U-tube manometer should be purchased? Assumptions • Incompressible flow p 0 • One-dimensional flow • Steady flow Important Formulae • The Pitot Formula: ( p ps ) V 2 0 1 2 p0 p s 1 V 2 2 • Hydrostatic Relationship for Manometer p down pup z • Specific gravity Specific Weight Spec.g liquid 1.7 water liquid 1.7 water 1696.6 kg m3 Calculations • Using the rearranged Pitot Equation, we can solve for the pressure difference: p0 p s 1 V 2 2639 Pa 2 • With the pressure difference and specific weight, we can solve for the displaced liquid using the hydrostatic equation: pdown pup z 2639 Pa (16643.646)z z .1586m 6.24in Discussion Although an 8 inch manometer would suffice, I suggest purchasing a 12 inch manometer (for a factor of safety of 2). Relation to Biofluids • The pitot-static probe measures slow moving fluids well. • Thus, the pitot-static probe would make a great blood pressure measurement device. • The pitot-static probe runs into problems when the flow is not laminar, however.