* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the Amaral PPT-slides here
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
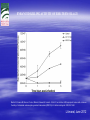
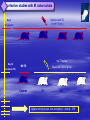
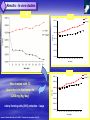
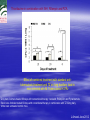
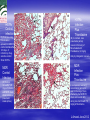
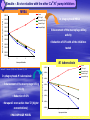
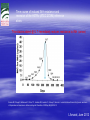
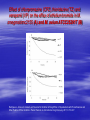
ISN THIORIDAZINE CURES MDR/XDR TB INFECTIONS. Targetting the human macrophage for enhanced killing of intracellular mdr/xdr mtb: a new concept for therapy of MDR/XDR TB. Leonard Amaral (Portugal) Eduardo Abbate (Argentina) Noton Dutta (USA) Stephen H Gillespie (UK) Jette E Kristiansen (Denmark) Chuck Sohaskey (USA) Zarir F Udwadia (India) Dick van Soolingen (Netherlands) Martin J Boeree (Netherlands) Paulo Ferrinho (Portugal) Eduardo Gotuzzo (Peru) Marta S Martins (Ireland) Rubin Thanacoody (UK) Jakko van Ingen (Netherlands) Miguel Viveiros (Portugal) Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Causative agent of Tuberculosis (TB) Emergence of Multi-Drug Resistant strains (MDR-TB) Resistance to at least isoniazid (INH) + rifampicin (RIF) Emergence of Extensively-Drug Resistance strains (XDR-TB) WHO; Weekly Epidemiol Record; 2008 Progression of Resistance TOTALLY DRUG RESISTANT Mtb Remains to be defined Multi-Drug Resistant M. tuberculosis New approaches - Phenothiazines Purpose of the studies In vitro, ex vivo and in vivo studies Macrophage model Role of efflux pumps PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS IS CAUSED BY THE STEADFAST HUMAN PATHOGEN MYCOBATERIUM tuberculosis. IT IS AN INTRACELLULAR INFECTION OF THE PULMONARY MACROPHAGE (ALVEOLAR II CELL) L Amaral, June 2012 WHEREAS AN INFECTION BY Mtb IS INTRACELLULAR, ACTIVE TUBERCULOSIS IS WHEN THE BACTERIUM BREAKS OUT OF ITS MACROPHAGE PRISON AND IS EXPELLED TO THE OUTSIDE IN MICRODROPLETS OF SPUTUM. ACTIVE TB IS INFECTIOUS! L Amaral, June 2012 DEFINITION OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBLE Mtb SUSCEPTIBLE TO ISONIAZID (INH) AND RIFAMPIN (RF). MULTIDRUG RESISTANT Mtb (MDR-TB) RESISTANT TO INH AND RF. EXTENSIVELY DRUG RESISTANT Mtb (XDR TB) RESISTANT TO INH, RF, STREPTOMYCIN, ANY FLUOROQUINOLONE, AND TO INJECTAB LE ANTI-TB DRUGS (AMIKACIN, KANAMYCIN AND CAPREOMYCIN). L Amaral, June 2012 TDR-TB 5 CASES OF TDR-TB IN ONE MUMBAI HOSPITAL 2012. IS THERE A PROBLEM? Udwadia ZF. Totally drug resistant tuberculosis in India: who let the djinn out? Respirology. 2012. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 22564108. W.H.O 2009 SHORT GLOBAL REPORT L Amaral, June 2012 PROBLEM: WHAT IS MEANT BY NEW CASES OF TUBERCULOSIS? ANSWER: NEW CASES OF ACTIVE TB L Amaral, June 2012 GLOBAL TUBERCULOSIS: FACTS 2007 (W.H.O. 2009 Report). 2 TO 3 BILLION INFECTED WITH Mtb. 10.5 MILLION NEW CASES. OVER 2 MILLION DEATHS. 511,000 NEW CASES OF MDR TB. XDR TB ????? TDR-TB ????? L Amaral, June 2012 MORTALITY PRODUCED BY: MDR-TB 20 TO 80 % within 2 years. MDR-TB co-infected with HIV/presenting w/AIDS 80 to 100 % within 1 year depending on area where therapy is given. XDR-TB > 80% within 6 months or sooner if co-infected with HIV/presenting with AIDS. TDR-TB ????? L Amaral, June 2012 THERE ARE NO SAFE AND EFFECTIVE DRUGS AGAINST MDR/XDR/TDR-TB, EXCEPT FOR ----------. L Amaral, June 2012 ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS FOR A PERFECT ANTI-MDR/XDR/TDR-TB DRUG! 1. HAVE ACTIVITY AGAINST ALL FORMS OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANT STRAINS. 2. HAVE ACTIVITY WHERE THE MDR/XDR TB STRAIN RESIDES: THE HUMAN PULMONARY MACROPHAGE! 3. HAVE NO TOXICITY. 4. NO RESISTANCE TO THE DRUG CAN BE MADE BY MUTATION OF MDR/XDR/TDR Mtb. L Amaral, June 2012 HISTORY OF PHENOTHIAZINES 1890 MB inhibits mobiliby of bacteria; kills malaria and syphilis causing organisms (Guttmann & Ehrlich). 1890’s Makes cats and humans lethargic (Bodini). 1957 Methylene blue (MB) dye. Chlorpromazine (CPZ) derived from MB by Rhone-Polenc: first neuroleptic. 1975 CPZ In Vitro activity against Mtb (Molnar). 1966 Thioridazine (TZ) derived from CPZ. 1996 In vitro activity of TZ against all forms of antibiotic resistant strains of Mtb (Amaral et al). L Amaral, June 2012 Develop new anti-TB drugs effective against intracellular MDR/XDR-TB. Phenothiazines Amaral et al; others TZ • Mellaril® DERIVATIVES • less toxic than CPZ • Drowsiness (most common) Schnetzler & Carrel (TZ) Charpentier • Serious side-effects (toxicity) (CPZ) • Gradually replaced by TZ Guttman & Erhlich • Wide gamut of in vitro antimicrobial activity. 1891 1953 1964 2004-2008 PHENOTHIAZINES Thioridazine (TZ) Chlorpromazine (CPZ) L Amaral, June 2012 The antimycobacterial activity of thioridazine derivatives against drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis: in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo studies TZ Unidade de Micobactérias and UPMM Instituto de Higiene e Medicina Tropical Universidade Nova de Lisboa Lisbon, 4th November 2008 Amaral L et al..Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1996) 38, 1049-1053 L Amaral, June 2012 HOWEVER, IN VITRO CONCENTRATIONS ARE CLINICALLY IRRELEVANT SINCE THE MAXIMUM CONCENTRATION OF THESE COMPOUNDS THAT CAN BE ACHIEVED IN THE PATIENT IS 0.5 mg/L OF PLASMA! L Amaral, June 2012 Experimental outline Screening of TZ derivatives (22) Mutagenicity Assay (Ames test) Toxicity in lymphocytes (Trypan blue exclusion method) Non-toxic and non-mutagenic Studies derivatives In vitro S. aureus / MRSA (model) MIC and MBC – microdilution method M. tuberculosis / MDR-TB MIC and MBC – BACTEC 460TM Ex vivo Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Infection studies in macrophages (phagocytosis assay) In vivo Toxicity assays (Balb/C) – TZ and derivatives Infection studies – TZ and derivatives Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) TZ derivatives + TZ • Synthesis: Prof. György Hajós (Chemistry Institute of Budapest, Hungary); Chemical manipulation of the parent compound (TZ) Amaral L, Martins M and Viveiros M. (2007). Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 7(3):257. In Vitro Growth inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Thioridazine derivatives. Compounds MIC 50 (mg/L). Thioridazine 10 Isoniazid 0.08 #1550 >20 #1686 20 #1687 20 #1532 20 #1688 20 #1689 20 #1819 >20 #1820 >20 #1821 >20 #1867 5 #1868 20 #1869 >20 #1870 10 #1871 >20 #1872 20 #1873 >20 #1874 >20 #1875 5 #1929 >20 L Amaral, June 2012 ENHANCED KILLING OF MYCOBACTERIUM tuberculosis by 0.1 mg/L of DERIVATIVES OF THIORIDAZINE. Martins M, Schelz Z, Martins A, Molnar J, Hajös G, Riedl Z, Viveiros M, Yalcin I, Aki-Sener E, Amaral L.. In vitro and ex vivo activity of thioridazine derivatives against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007;;29:338-40. L Amaral, June 2012 INTRACELLULAR ACTIVTY OF NON-PHENOTHIAZINES L Amaral, June 2012 ENHANCED KILLING ACTIVITY OF XDR-TB BY SILA 421 Martins M, Viveiros M, Ramos J, Couto I, Molnar J, Boeree M, Amaral L. SILA 421, an inhibitor of efflux pumps of cancer cells, enhances the killing of intracellular extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB). Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;33:479-82 L Amaral, June 2012 IN VIVO STUDIES L Amaral, June 2012 Toxicity assays - TZ • Animal model: Balb/C females (25 gms) mg TZ/kg/day E 25 50 100 200 400 • daily inoculations • daily weighing √ In all the concentrations tested no toxicity was obtained √ Concentrations selected for treatment: 100, 400 and 1200 mg TZ/Kg/day F 1200 Infection studies with M. tuberculosis Infection with TB (1×106 CFU/mL) Day 0 I.P. injection mg TZ/kg/day Day 30 NO TZ Except the Control group Treatment (TZ) Control 100 400 • Organs removal (lungs, liver and spleen) – plating – CFU 1200 Results - In vivo studies Lungs Liver Control 1,00E+10 1200mg TZ 1,00E+08 CFU/mg 1,00E+06 1,00E+04 1,00E+02 1,00E+00 1,00E-02 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 Time (days) Spleen Control 1,00E+10 1,00E+08 (equivalent in the human to 1,00E+06 1200 mg/Kg/day) CFU/mg Mice treated with TZ 1200mg TZ 1,00E+04 1,00E+02 • colony forming units (CFU) reduction – lungs 1,00E+00 1,00E-02 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 Tim e (days) Amaral L, Martins M, Viveiros M. (2007). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 59:1237. 210 240 270 300 CONFIRMATION OF MOUSE WORK van Soolingen D, Pando RH, Orozco H, Aguilar D, Magis C, van Ingen J, Amaral L, Boeree M. Thioridazine shows promising activity in a murine model of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis. PloS One 2010;5. pii: e12640. Thioridazine in combination with INH, Rifampin and PZA. Effect of combined treatment with standard antituberculosis treatment and TZ on lung bacillary load in mice infected with M. Tuberculosis H37Rv Grey bars: Animals treated 60 days with conventional therapy: Isoniazid, Rifampicin and Pyrazinamide Black bars: Animals treated 60 days with conventional therapy in combination with TZ 32mg daily White bars: untreated control mice. L Amaral June 2012 H37Rv Control infection (A) Extensive lung consolidation (arrows) is visible in control animals after 120 days of infection by drugsensitive control Strain H37Rv. MDR Control Infection (C) Control mice after 120 days of infection with MDR strain show extensive pneumonic areas (arrow) H37Rv Infection Plus Thioridazine (B) In contrast, less pneumonia (arrow) is seen in the lung of Mice treated with Thioridazine 32 mg/kg daily by intragastric cannula. MDR Infection Plus Thioridazine In comparison, less lung consolidation (arrow) is seen in the lung of mice infected by the MDR-TB strain and treated daily during two months with 70 mg/kg of thioridazine L Amaral June 2012 Thioridazine cures XDR TB L Amaral June 2012 L Amaral June 2012 CURE OF XDR-TB (SECOND STUDY) Abbate E, Vescovo M, Natiello M, Cufré M, García A, Gonzalez Montaner P,Ambroggi M, Ritacco V, van Soolingen D. Successful alternative treatment of extensively drugresistant tuberculosis in Argentina with a combination of linezolid, moxifloxacin and thioridazine. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011 Dec 1.[Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 22134348. MECHANISM OF ACTION L Amaral June 2012 Mechanism of action of TZ and its derivatives inside the macrophage? Questions raised… Concentration of the compound inside the macrophage? • macrophage can concentrate 100 times the phenothiazines inside lysosomes / phagosomes • Ca2+ / K+ pumps inhibitors • Inhibitors of Ca2+ transport (calmodulin) and influx/efflux dependent on energy • Clinical concentrations 0.1 mg/L processes 10 mg/L However… Inhibition of macrophage • MIC TZ (TB/MDR-TB) = 20 mg/L • MBC TZ (TB/MDR-TB) = 30 mg/L intracellular pumps? cellular Other studies… Search Journal home > Archive > Article > Abstract go Advanced search Article Nature 416, 291-297 (21 March 2002) | doi:10.1038/416291a; Received 12 December 2001; Acce January 2002 • Killing activity of phagocytic cells (Neutrophils) Killing activity of neutrophils is mediated through activation of proteases by K + flux Emer P. Reeves1,2, Hui Lu1,2, Hugues Lortat Jacobs3, Carlo G. M. Messina1, Bolsover4, Giorgio Gabella5, Eric O. Potma6, Alice Warley7, Jürgen Roes8 an Anthony W. Segal1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. • Correlated with K+ 7. 8. availability Centre for Molecular Medicine, University College London, 5 University Street, London WC Centre for Molecular Medicine, Department of Physiology, University College London, 5 Un Street, London WC1E 6JJ, UK Centre for Molecular Medicine, Department of Anatomy , University College London, 5 Univ Street, London WC1E 6JJ, UK Windeyer Institute of Medical Sciences, University College London, 5 University Street, Lon 6JJ, UK Institut de Biologie Structurale, 41 rue Horowitz, 38027 Grenoble, France Ultrafast Laser and Spectroscopy Laboratory, Materials Science Centre, University of Gron Nijenborgh 4, 9747 AG Groningen, The Netherlands Rayne Institute, St Thomas' Hospital, Lambeth Palace Road, London SE1 7EH, UK These authors contributed equally to this work. Correspondence to: Anthony W. Segal 1 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addre A.W.S. (e-mail: Email: [email protected]). Top of page Abstract • Dependent upon transport processes affected by agents that inhibit Ca2+-activated K+ pumps • Rise of Ca2+ and K+ associated with the killing activity of phagocytic cells Other Ca2+/K+ pump inhibitors Ca2+/K+ pump inhibitors Verapamil • • Ca2+ channel blocker; inhibits plasma Ouabain Reserpine indirect effects on the K+ pumps of mammalian cells membrane mediated transport of K+ into the macrophage preventing access to Ca2+ • Inhibition of efflux pumps of bacteria and eukaryotic cells • direct effects on the K+ pumps of mammalian cells Results – Ex vivo studies with the other Ca2+/K+ pump inhibitors MRSA Control Bacterial concentration (bacteria/mL) 1,00E+10 In phagocytosed MRSA: TZ 0.1 mg/L 1,00E+09 Reserpine 80 mg/L 1,00E+08 Ouabain 80 mg/L 1,00E+07 Verapamil 80mg/L • Enhancement of the macrophage killing 1,00E+06 activity 1,00E+05 1,00E+04 • Reduction of CFU with all the inhibitors 1,00E+03 tested 1,00E+02 1,00E+01 1,00E+00 0 2 4 6 M. tuberculosis Hours post-infection Control 1,00E+07 TZ 0.1 mg/L Martins M & Amaral L (2006). Res. J. Microbiol. 1(3): 203. In phagocytosed M. tuberculosis: • Enhancement of the macrophage killing activity • Reduction of CFU • Verapamil: more active than TZ (higher concentrations) • MACROPHAGE MODEL Bacterial concentration (bacteria/mL) Reserpine 80 mg/L 1,00E+06 Ouabain 80 mg/L Verapamil 80 mg/L 1,00E+05 1,00E+04 1,00E+03 1,00E+02 1,00E+01 1,00E+00 0 1 2 3 Days post-infection Martins M, Viveiros M, Amaral L. (2008). In Vivo 22(1): 69. K+ Ca2+ A Na+ ATP B Ca2+ H+ K+ Ca2+ Ca2+ K+ Ca2+ H+ K+ Ca2+ H+ C H+ ATP K+ ATP ATP Ca2+ Ca2+ K+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ K+ Ca2+ Ca2+ ATP K+ Ca2+ H+ ATP Ca2+ K+ H+ K+ ATP K+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ K+ H+ Ca2+ H+ H+ H+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ G H+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Amaral L, Martins M, Viveiros M. (2007). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 59:1237. F K+ ATP D E K+ H+ ATP K+ ATP Na+ Ca2+ K+ ATP Ca2+ H+ ATP Ca2+ Ca2+ H+ ATP K+ K+ Ca2+ H+ ATP Ca2+ H+ H+ Ca2+ Ca2+ H+ L Amaral, May 2011 The Role of efflux pumps in MDR-Mtb Laboratory demonstrations of induced efflux activity by bacteria. L Amaral, June 2012 Time course of induced INH resistance and reversion of the H37Rv (ATCC 27294) reference strain. Thioridazine added @ IL 7 immediately reduces resistance to INH (arrow) RE Viveiros M, Portugal I, Bettencourt R, Victor TC, Jordaan AM, Leandro C, Ordway D, Amaral L. Isoniazid-induced transient high-level resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Sep;46(9):2804-10. L Amaral, June 2012 Automated EB method for bacteria Ethidium Bromide (EB) transport of fluorescent substrates (EB) through the cell envelope of living bacterial cells common substrate of bacterial efflux pumps emits weak fluorescence in aqueous solution (outside cells) and becomes strongly fluorescent when concentrated in periplasm Viveiros M et al, Int J Antimicrob Agents. 31(5):458-62, 2008. Spengler G et al, Anticancer Research 29: 2173-2177, 2009. Detection of Efflux Activity by Real-time Fluorometry PKI Detection of efflux activity on a real-time basis Separate detection of accumulation and efflux of ethidium bromide (EtBr) Identification of compounds with efflux pump inhibitory activity – efflux pump inhibitors (EPIs) Ethidium bromide (EtBr) Rotor-Gene 3000TM (Corbett Research) rotor spins tubes at 500 rpm filter set (rotates for each channel) lens LED light source (rotates for each channel) sensitive PMT (photomultiplier) detector Effect of chlorpromazine (CPZ), thioridazine (TZ) and verapamil (VP) on the efflux of ethidium bromide in M. smegmatismc2155 (A) and M. avium ATCC25291T (B) Rodrigues L, Aínsa JA, Amaral L and Viveiros M. Inhibition of Drug Efflux in Mycobacteria with Phenothiazines and Other Putative Efflux Inhibitors. Recent Patents on Anti-Infective Drug Discovery, 2011; 6:118-127. Average quantification of the relative expression level, by RT-qPCR, of the genes that code for efflux pumps in M. tuberculosis. Relative expression level ± SD Strains mmpl7 Rv1258c p55 efpA mmr Rv2459 H37Rv INH (R) 0.44 1.99 0.82 0.34 0.44 0.50 H37Rv INH (I) 10.56 15.26 6.96 8.00 9.95 22.63 401/06 INH (C) 34.30 22.63 18.38 16.00 24.25 9.19 401/07 INH (C) 17.15 14.93 9.85 6.96 9.19 27.86 401/08 INH (C) 4.16 7.80 11.31 8.57 2.29 2.64 Machado D, Couto I, Perdigão J, Rodrigues L, Portugal I, Baptista P, Veigas B, Viveiros M. and Amaral L . Contribution of efflux to the emergence of isoniazid and multidrug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS One 2012; 7(4): e34538. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034538 CONCLUSIONS • • • • • • • THIORIDAZINE HAS IN VITRO ACTIVITY AGAINST ALL STRAINS OF Mtb. THIORIDAZINE ENHANCES INTRACELLULAR KILLING OF MDR/XDR Mtb. THIORIDAZINE CURES THE MOUSE OF AN MDR Mtb INFECTION. THIORIDAZINE CURES THE HUMAN OF AN XDR-TB INFECTION. DUAL MECHANISM OF ACTION: A) INHIBITION OF K+ EFFLUX OF MACROPHAGE PERMITTING ACIDIFICATION OF PHAGOLYSOSOME. B) INHIBITION OF EFFLUX PUMPS OF Mtb THAT BESTOW MDR PHENOTYPE. BY-PASSES ANY MUTATIONAL RESPONSE MADE BY Mtb THAT WOULD LEAD TO RESISTANCE. THIORIDAZINE IS CHEAP, RELATIVELY SAFE WHEN PATIENT IS MONITORED FOR CARDIA FUNCTION, AND SHOULD BE CONSIDERED FOR THERAPY OF XDR/TDR Mtb INFECTIONS. May 2011 Special Issue of PRI: Thioridazine MDR/XDR TB ADDITIONAL BENEFITS OF THIORIDAZINE INHIBITS ESSENTIAL GENES OF Mtb (Dutta NK, Mazumdar K, Dastidar SG, Karakousis PC, Amaral L. New patentable use of an old neuroleptic compound thioridazine to combat tuberculosis: a gene regulation perspective. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov 2011;6:128-138.) IMPROVES QUALITY OF LIFE OF THE XDR-TB PATIENT (Udwadia ZF, Sen T, Pinto LM. Safety and efficacy of thioridazine as salvagetherapy in Indian patients with XDR-TB. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2011;6:88-91. KILLS DORMANT Mtb (Sohaskey C. Latent tuberculosis: is there a role for thioridazine? Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2011;6:139-46. Review. ). ANTICIPATED SHORT TERM USAGE FOR MDR/XDR/TDR-TB INFECTIONS WILL DO NO HARM (Thanacoody RH. Thioridazine: the good and the bad. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov 2011;6:92-98. Review.). ISN RESEARCH TEAM L Amaral, May 201