* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy: Conservation and Transfer
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
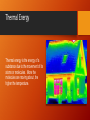
Energy: Conservation and Transfer Matter • Anything that takes up space and has mass Mass • The amount of matter in an object • The gram is the metric unit for mass Physical Properties of Matter Observable characteristics that can change without changing their chemical composition. • Like the Commutative property in math. • Example: Shredded paper, cut up fruit, lava States of Matter • Condensation • Solid • Liquid • Gas • Plasma • Melting Point – The temperature at which solid matter turns to liquid. • Boiling Point – The temperature at which liquid matter experiences the same pressure as the atmospheric pressure. • Freezing Point – The temperature at which liquid matter turns to solid. Chemical Property A change in matter that produces new substances. Examples: • Ability to burn • Wood to ash • Ability to rust/ react with oxygen • Metal to rust • Ability to form a new substance with chemical composition different than the original substance. • Digestion of food Conduction • Conduction is the transfer of heat from one molecule to another through a substance. Metals are considered good conductors since they can speedily transfer heat. Stone is also a moderately good conductor, but wood, paper, air, and cloth are poor heat conductors. Convection Transfer of heat from one place to another by the movement of fluids or gases. Radiation • The energy radiated by solids, liquids, and gases in the form of electromagnetic waves as a result of their temperature. Transfer • to convey or remove from one object, place, person, etc., to another. Electromagnetic Waves • Electromagnetic waves are formed when an electric field (shown as blue arrows) couples with a magnetic field (shown as red arrows). • When you listen to the radio, watch TV, or cook dinner in a microwave oven, you are using electromagnetic waves. Thermal Energy Thermal energy is the energy of a substance due to the movement of its atoms or molecules. More the molecules are moving about, the higher the temperature. Convection Cell • Moving body of fluid due to the rise of heat and fall (gravity) of cool gases until the heat is no longer heated. (Ex. Current/cycle) • Convection cells are responsible for making macaroni rise and sink in a pot of boiling water. One of the forces that contributes to lava erupting from a volcano is convection. •