* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download View/Open
Economic model wikipedia , lookup
Icarus paradox wikipedia , lookup
Schools of economic thought wikipedia , lookup
History of economic thought wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral economics wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Royal Economic Society wikipedia , lookup
Development economics wikipedia , lookup
Economics of digitization wikipedia , lookup
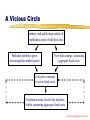
Crisis and Transition The Economics of Scholarly Communication John Houghton [email protected] Centre for Strategic Economic Studies Victoria University www.cfses.com Context of the ‘Crisis’ National Innovation Systems: Prosperity depends as much, if not more, on the knowledge distribution power of the system as it does on its knowledge production power Dynamics of the context: Funding pressures & accountability Increased publication incentive & output IT revolution - transforming production, distribution & consumption of content Price increases (decline of AUD) Centre for Strategic Economic Studies Australian Research Libraries % 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 1986 1987 1988 Serials Expenditure 1989 1990 1991 Monograph Expenditure 1992 1993 1994 Serials Purchased 1995 1996 1997 1998 Monographs Purchased Centre for Strategic Economic Studies Economics of Information Information is the product of the codification of knowledge - knowledge is a ‘public good’, but information is not Information is ‘non-rivalrous in consumption’ social returns are maximised through expansion of access & dissemination Information is an ‘experience good’ - value in authorship & branding, as well as content Centre for Strategic Economic Studies Economics of Content Creation (1) Dysfunctional institutional incentives: Promotion, tenure & funding linked to publication Encouraging more published output Multiplying titles & raising aggregate fixed costs Centre for Strategic Economic Studies Economics of Content Creation Payments by authors (2) (submission/publication fees): Disincentive to publish & reduced dissemination Publication by means not merit High transaction costs, not worth the effort Incentive for publishers to lower the bar Payments to authors (pay for content): Demand & supply would keep payments low High transaction costs Simply raises publisher costs Centre for Strategic Economic Studies Alternative Publication Mechanisms Key elements for success (not just communication) Value in selection & filtering (eg. peer review) Dangers in alternative article filtering strategies Differences between humanities & natural sciences Dangers where authors & readers are not the same Dangers in applied fields (eg. medicine) Must meet the needs of authors and readers Centre for Strategic Economic Studies Economics of Production Increasing returns & concentration Knowledge economy will create a proliferation of materials, firms & activities Ease of access via internet will drive down rents at the delivery level Rents will migrate up the value chain to those with genuinely scarce factors & competitive advantages Is that authors or publishers? Centre for Strategic Economic Studies Economics of Distribution A library costs crisis? Must consider whole of system costs Acquisitions practices reinforce publisher business models & contribute to the crisis Price signals have rarely reach consumers Very low price elasticity of demand Centre for Strategic Economic Studies A Vicious Circle Authors seek publication outlets & publishers seek to build their lists Publisher portfolios grow, increasing their market power New titles emerge, increasing aggregate fixed costs Unit prices increase to cover fixed costs Circulation/reads of each title declines, further increasing aggregate fixed costs Centre for Strategic Economic Studies What Can Be Done? Reduce costs, ensure prices reflect value in use or change what the market will bear Market distorting approaches: National site license Consortial purchasing Market conforming approaches: Transmit price signals to consumers Trial alternative mechanisms & encourage new entrants (but beware of fixed costs) Create an effective structure of incentives Centre for Strategic Economic Studies In Summary… System dysfunction & technological change Resolving the crisis: Reform system of incentives Establish alternative publishing models Counter publisher market power Foci for attention: Tackle the basic problems Think through the design of alternatives Find out what users actually needed Centre for Strategic Economic Studies