* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alternator
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
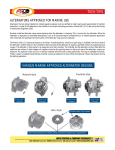
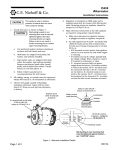
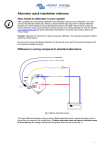
Tutorial: Physics Topic: Alternator Prepared by: RNDr. Ondřej Jeřábek Projekt Anglicky v odborných předmětech, CZ.1.07/1.3.09/04.0002 je spolufinancován Evropským sociálním fondem a státním rozpočtem České republiky. Alternator General information: Alternator is rotary electric machine Changes rotary energy ( kinetics energy ) or mechanical energy to electric energy Output capacity is led to electrical system Alternator works on electrical induction principle Voltage is induced in conductor, if conductor and magnetic field move to each other Extent of induced voltage depends on magnetic field rate and conductor movement speed ( engine revolutions ) Alternators are synchronous machines According to their rotor’s type they further divide to: With plain rotor- turbo-alternators – driving machine is mostly steam turbine (in steam power plant) speed turns 3000 min-1, as network freqeuency 50 Hz Low-acting alternators are driven by low-acting machine (mostly by water turbine). Speed turn is whole number ratio of 3000 min-1, as network frequency 50 Hz It makes mechanically connected set with driving machine. Driving machine and alternator are on the same shaft. Alternator with rectifier is designed so that accumulator is charged when combustion engine runs idle It is important advantage for city traffic Accumulator durability charged by alternator with rectifier is longer than accumulator durability charged by dynamo Alternator is excited directly of accumulator immediately after ignition start Alternators produce electricity in the same way as direct-current generators Rotating magnet rotates – rotor inside stationary fit windings on iron cores - stator Electrical current is produced by rotor movement caused by mechanic energy There are mostly sets of stator windings in stator that are moved round slight amount of 180° Rotor magnetic field can be caused by induction or permanent magnet Car alternator has the same construction as industrial alternators Car alternator produces 3- phase electrical current Alternating current must be rectified before entry to car network Diodes are used to rectifying of alternating current Diodes are fixed to diode bridge To limitation of voltage values , alternator output direct current is controlled by Zener diode Alternator advantage comparing with dynamo is mainly its low weight Find out alternator on the Internet: a) Alternator´s rotor and stator b) Find out on the Internet alternator wiring diagram wired to electrical circuit Describe main alternator components that you found out on the Internet Describe and explain alternator wiring to electrical circuit JAN, JAN, JAN, JAN, Zdeněk; ŽDÁNSKÝ, Bronislav ; Zdeněk; ŽDÁNSKÝ, Bronislav ; Zdeněk; ŽDÁNSKÝ, Bronislav ; Zdeněk; ŽDÁNSKÝ, Bronislav ; ČUPERA, Jiří ČUPERA, Jiří ČUPERA, Jiří ČUPERA, Jiří . . . . Automobily 1. Brno : Avid, 2004. 211 s. Automobily 2. Brno : Avid, 2004. 120 s. Automobily 3. Brno : Avid, 2004. 220 s. Automobily 4. Brno : Avid, 2004. 350 s. Translation: www.seznam.cz www.slovnik.cz JANATA, Petr. Handy slovník technický anglicko-český a česko-anglický. Plzeň: Nakladatelství Fraus, 2000. ISBN 80-7238-075-3 Lingea LEXIKON 5, Technický slovník anglicko-český a česko-anglický. 2010.