* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recontruction and the “Wild” West 1865-1890
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
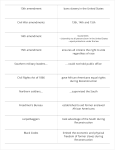
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction: Remaking the South 1865-1877 Goals: (1) What did Reconstruction mean? (2) Was the South really reconstructed? Problems of Reconstruction Social: How do we help/protect freedmen and their rights? Economic: How do we rebuild the South? How do we pay for it? Political: What do we do with/to the Southern states? How do we bring them back into the Union? Presidential Reconstruction (Two possible plans) Lincoln’s Plan 10% of voters swear oath of loyalty States must draft new constitutions that abolish slavery Forgiving and nonpunitive Johnson’s Plan 50% of voters must swear oath of loyalty States must draft new constitutions that abolish slavery Radical Reconstruction (Wade-Davis Bill [1864] and Reconstruction Acts of 1867-1868) South divided into 5 military districts not including Tennessee, which had ratified the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution and was readmitted to the Union Required Congressional approval for new state constitutions, which had to include a provision to allow all men, including African Americans, the right to vote Prohibited any former Confederate officials from holding office “Ironclad Oath”: required every white male to swear he had never borne arms against the Union or supported the Confederacy Required all states to ratify the Fourteenth Amendment President Johnson impeached for violating the Tenure of Office Act - found not guilty by one vote but…Congress now controlled the federal government Why did Congress go after President Johnson? He vetoed both the Freedman’s Bureau bill and the Civil Rights Act (both in 1866) and for the first time Congress overrode a president’s vetoes. The North During Reconstruction Thriving industry Increased use and development of technology Trade markets expanded Labor needs continue to grow The “New South” Sharecropping & Tenant Farming emerge Freedmen face many obstacles Segregation becomes an acceptable part of society Struggles for political control President Grant • Willingness to cooperate with Radical Republicans though he wasn’t one of them. • As general and as president, quiet and unassuming but determined. • Military experience in some ways proved a handicap in public office, as he was used to being obeyed and not having to negotiate. Grant’s Imperfections Grant expected his political appointees to carry out orders as his military subordinates had done, but his trust proved misplaced. His lack of experience in public affairs often led to the appointment of poorly-qualified persons. Military experience led him to place too much trust in people, a mistake in the political arena. His trust in the spoils system badly damaged his presidency and political reputation. Grant Administration Scandals Grant presided over an era of unprecedented economic growth and political corruption. * Fiske/Gould gold scandal. * Credit Mobilier scandal. The Gold Thing Jim Fiske and Jay Gould attempted to corner gold market in 1869 Persuaded Grant to order federal Treasury to stop selling gold. Fiske and Gould then bid price of gold upward. Treasury finally released gold and the bubble burst in 1869 (b/c of over-speculated/inflated value of gold; similar to 1929 Stock Market Crash); caused a financial panic, stock market depression, bankruptcies of Wall Street firms Congressional probe found Grant did nothing illegal but acted recklessly. Credit Mobilier Scandal Insiders of the Union Pacific Railway formed Credit Mobilier --a railroad construction company. Hired themselves to build the railroad and paid themselves huge fees (paid dividends of 348% to stockholders) Distributed shares of stock to members of Congress to avoid interference. In 1872 the charges confirmed by a Congressional investigation that censured two members & the vice president Grant’s reputation tarnished although most corruption occurred before his presidency. Successes of Reconstruction New Constitutional Amendments- 13, 14, 15…Free, Citizens, Vote!! Southern economy diversified African-Americans elected to all levels of government Failures of Reconstruction Political corruption at all levels of government Black codes and Jim Crow laws put in place throughout the country Sharecropping and tenant farming created economic inferiority for African-Americans White supremacy groups (KKK) form and are opposed (Force Act 1870 and Civil Rights Act 1871) Former Confederate leaders return to power after 1877 Poll taxes, literacy tests, grandfather clauses prevent African-Americans from voting Impacts of Reconstruction Republicans dominate the government Solid South (“Redeemers”) emerges (Democrat bloc) Civil rights are given, but not guaranteed Federal government is SUPREME over states Racial tensions surge as the nation SLOWLY rebuilds Corruption of the Grant administration filters throughout government