* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Light and Electrons!
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
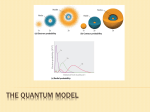
Light and Electrons! Shining “light” on light, electrons, and their properties Andy Berger 5/30/08 Periods 1 & 2 René Descartes Historical Theories Two major societies contributing to Light theory Isaac Newton Indians: (5th-6th Cent. BC) • First theories about light made by Hindu schools of Samkhya and Vaisheshika • Believed that light was one of the five fundamental subtle “elements” of nature • Developed from Indian atomism • Believed that rays of light from sun were fire atoms at high speed Greeks: (5th-2nd Cent. BC) -Empedocles concluded that the Earth is made of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water -Euclid hypothesized that a beam of light projects from the eye -Also had theories about the refraction of light Others: -René Descartes (first one to assume light acted in waves) -forerunner of light theory; believed light to be a disturbance of the plenum Historical Theories (cont’d) -Isaac Newton: proposed that light came from one source and emanated in all directions as particles -Robert Hooke: came up with Law of Elasticity -All were equally important in their contributions to the understanding of light Lots of Light!!! Robert Hooke The Basics • What is light? Definition: Light is electromagnetic radiation, that is, a self-propagated wave, or particle, depending on the viewpoint, with several properties that is sometimes seen by the human eye depending on the wavelength. Properties of light waves: 1. Amplitude 2. Wavelength(λ)-measured in nm 3. Frequency(υ)-measured in Hz Wavelengths of Light Types of light: 1.Radio Waves 2. Microwaves 3. Infrared Waves 4. Visible Light 5. Ultraviolet Light 6. X-Rays 7. Gamma Rays Classical Mechanics vs. Quantum Mechanics Classical Mechanics Quantum Mechanics -Newtonian Mechanics -Theoretical, not entirely proven -Objects that can be seen -Objects can not be seen -Traveling at “ordinary” velocities -Traveling near the speed of light -Realistic -have measurable wave-like properties -The basis of physics Light? Wave or Particle -Big dispute about whether light acts in waved or particles -Main contenders Einstein and Max Planck; Einstein for particles, Planck for waves -Both developed equations: Einstein- E = MC2 Planck- h = E/υ E = energy M = Mass C = Speed of light h = Planck’s Constant E = energy υ = frequency -Some claimed that light had to be particles because there was evidence of it going around objects; also Photoelectric Effect by Einstein helped the cause -Photoelectric Effect theorized that light has photons, or “packets” of energy -A man named Thomas Young proved, however, that light acts in waves because of his diffraction experiment in 1800 -Later, Louis de Broglie united the both theories Duality of Nature 1924- Louis de Broglie brought together the ideas of wave and particle properties of light -Came up with the equation: λ = h/mv -Duality of Nature/Light -The smaller the object, the more obvious the waves (i.e. electrons) -Basically, every object has its own wavelength and emits energy while traveling Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle – impossible to know the exact momentum and location of an electron in space simultaneously De Broglie Radial Probability -Schrödinger comes up with a way to find probability of finding an electron in space -Said that electrons moved “in a blur” -Potential energy increases as electrons move out to farther energy -Made an equation: Prob. Of position Prob. Of momentum -Theorized that 90% of all electrons could be found within a line near the third electron shell -Believed that nodes got smaller and Smaller as electrons moved farther away from nucleus Schrödinger’s Quantum Numbers -Four in total: 1st Quantum Number=n -describes size of electron cloud; has values 1…infinity 2nd Quantum Number=l -describes shape of electron region; has values 0…n-1, but depends on n 3rd Quantum Number=m -tells the orientation in space; values depend on l, m=(-l…0…+l) 4th Quantum Number=s -describes the spin; is either +1/2(clockwise) or -1/2(counter-clockwise) Total Number of Electrons in a shell = 2n2 -Potential energy increases as electrons move out to farther energy Bohr’s Model -Each orbital has a specific energy, and each electron is in a distinct energy region Nodes-space in between shells -Works only for a 1 electron system Lowest orbital Equation for “electron jumping”: E = (-2.18 x 10-18)(final 1/n2 – initial 1/n2) Electron Configurations -Idea here is showing the electrons for each shell using three rules: Aufbau Principle=orbitals of the lowest energy must be filled first Pauli Exclusion Principle=only two electrons are allowed for each orbital with opposite spin Hund’s Rule=When orbitals are equal in energy, one electron must be placed in each one with same spin, before placing a second one in each orbital -Different shells have different subshells: Ex. The p shell, where l=1, has three subshells, Px, Py, and Pz E increases Examples of Electron Configurations 1. Hydrogen 1s1 2. Boron 1s2 2s1 2Px1 2Py1 3. Zinc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4. Platinum 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d8