* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Exam 3
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Tropical rainforest wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative agriculture wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
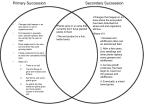
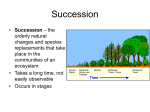
STUDY GUIDE FOR EXAM 3 Energy and Ecosystems What is biogeography? Ecological and historical biogeography: what are they? What does “ecology” mean? What are the abiotic components of an ecosystem? Know definitions of habitat, community, niche What are the relative amounts of energy following the organic and the heat paths? What is a food chain? A trophic level? What are the differences between a terrestrial and an aquatic food chain? What is an autotroph? A heterotroph? What is the difference between the detritus and the grazing food chains? What’s the concept of an energy pyramid? How do terrestrial and marine biomass pyramids differ? How is energy transferred in photosynthesis and respiration? Know the equations for both. What kind of reaction is decomposition? What is the difference between net and gross primary productivity? Why is the omnivorous human diet wasteful? What is bioaccumulation? Biogeochemical Cycles What does the term “biogeochemical cycles” mean? What are active pools? Storage pools? What are examples of active and storage pools in the carbon cycle? What are the two main pathways in the carbon cycle that cycles carbon between the atmosphere and biosphere? What are the organic and inorganic forms of carbon in the carbon cycle? What is nitrogen fixation? Why is it important? What are the biological and industrial forms of nitrogen fixation? What are legumes? What is their role in the nitrogen cycle?] How are bacteria symbiotic with legumes? What is denitrification and how is it accomplished in the nitrogen cycle? What is outgassing? Explanations for Plant and Animal Distributions What are some xerophytic plant adaptations? What are some tropophytic plant adaptations? What are some hydrophytic plant adaptations? Be able to define aerenchyma and adventitious. What are adaptations to temperature for cold and warm blooded animals? What is a bioclimatic frontier? How does it explain plant distributions? Be able to define all of the following: competition, predation, parasitism, symbiosis, commensalism, mutualism What is ecological succession? What is the difference between primary and secondary succession? Know examples of each. What is a climax community? Know the basics of evolutionary theory. What is variation? How does natural selection operate? What are the two key mechanisms for variation? What is speciation? Extinction? Dispersal? Global Biomes Definition of biome For the following biomes, know: The associated climate characteristics, some plant and animal adaptations, the distribution of that biome on the map 1. Tropical rainforest 2. Monsoon Forest 3. Subtropical Broadleaf (and Southern Pine) Forest 4. Midlatitude Deciduous Forest 5. Needleleaf (Boreal) Forest 6. Sclerophyll Forest 7. Tropical Savanna 8. Grassland 9. Desert 10. Tundra Additional terms and concepts to know about biomes: Arroyo, wash, wadi Stomata, ephemeral plants, phreatophytes (wet toes), hydraulic lift Prairie vs. steppe Why do grasslands survive fire and why is fire necessary to preserve grasslands? Alpine vs. arctic tundra Permafrost Know the relative net primary productivities of the biomes (the highest and lowest biomes) Soil What is it composed of by % volume, and what are the % volumes of the components? What is a mineral? What is parent material? How does the soil air compare to the atmosphere? Why is water a polar molecule? Wilting point, storage capacity What are the five CLORPT factors of soil formation? What is soil texture? Know the size categories for sand, silt, clay. What are colloids? Be able to use the soil texture triangle. What is surface area per unit volume and how us it related to soil particle size?(remember the loaf of bread!) What are the following soil structures: platelike, prismlike, blocky, spheroidal, structureless What is a ped? A profile? A horizon? Know the basic characteristics of the main soil horizons: O, A, E, B, C and R For each of the following Great Soil Orders, know: where it is found, what kind of climate it is associated with, the basic characteristics of soil in this order (Here is the Soil Order Song to help you remember some basics: click here.) (Table 10.1 in your textbook is also helpful for studying Soil Orders) 1. Entisols 2. Inceptisols 3. Andisols 4. Vertisols 5. Aridisols 6. Mollisols 7. Spodosols 8. Alfisols 9. Ultisols 10. Oxisols 11. Histosols 12. Gelisols Textbook Chapters. Material from the book not covered in lecture class: Chapter 8: Net production and climate, human impact on carbon cycle, geomorphic and edaphic factors, example of dune succession, succession, change, equilibrium, genetic drift and gene flow, geographic isolation, adaptive radiation, endemic species, dispersal and disjunction, read the discussion about biodiversity and endangered species on pp. 296‐298. Figures 8.7, 8.9, 8.10, 8.11, 8.23 Chapter 9: What is a savanna? What is a sclerophyll forest? Where do they occur? What are some of the important differences between deciduous and needleleaf forests? What are epiphytes? What are buttress roots? What are lianas? What are emergent canopies? Figures 9.4, 9.6, 9.7, 9.9, 9.34 Chapter 10: soil bases, acidity and alkalinity, biological processes in soil, Figures 10.5, 10.7, 10.10, 10.12, 10.13, 10.14;10.15, Table 10.1 is a good summary of soil orders,