* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Circle of Docs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
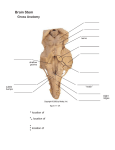
Spinal Anatomy 1. Which area of the brain is responsible for the initiation of spoken language a. Inferior frontal area b. Superior frontal area c. Superior temporal area d. Parietal area 2. The groove from the sigmoid sinus ends at the: a. Hypoglossal canal b. Jugular foramen c. Optic foramen d. Emissary veins 3. On which bone is the clivus located? a. Temporal b. Parietal c. Sphenoid d. Ethmoid 4. The internal arcuate fibers are part of which tract a. Spinothalamic b. Corticospinal c. Dorsal spinal d. Spinocerebellar 5. Which decussates in the anterior white commisure? a. Spinothalamic tract b. Faciculus gracilis c. Faciculus cuneatus d. Cerebellospinal tracts 6. Which is responsible for the detection of angular motion? a. Utricle b. Saccule c. Macula d. Cristae ampularis 7. The multifidus muscles are most pronounced in which area of the spine? a. Cervicals b. Thoracics c. Lumbars d. Sacrum 8. Which is the cause of cerebrospinal fluid flowing through the ventricles and the spinal cord? a. Vessels pumping into the subarachnoid space b. Muscles contracting c. Choroid plexus producing more CSF in the ventricles d. Cauda equina producing more CSF 9. Which is located in the posterior chamber of the eye? a. Aqueous humor b. Vitreous humor c. Lens d. Iris Anterior and posterior chambers -- aqueous humor; posterior cavity – vitreous humor 10. Which neurons are located in the cribriform plate a. Bipolar b. Unipolar c. Multipolar d. Pseudomultipolar 11. The sacral plexus lies anterior to which muscle a. Iliacus b. Superior gemellus c. Obturator internus d. Piriformis 12. Which nerve is a branch from the posterior cord of the C-5, C-6 segments a. Axillary b. Median c. Ulnar d. Radial 13. The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is derived from which of the following levels of the spine a. L-1, L-2 b. L-2, L-3 c. L-3, L-4 d. L-4, L-5 Pressure on lateral femoral cutaneous nerve: paralgia parasthetica 14. The cingulated gyrus is part of a. Thalamus b. Hippocampus c. Hypothalamus d. Limbic 15. The sympathetic nervous system is found from T-1 to L-2 and originates from a. Ventral horn b. Posterior horn c. Intermediolateral cell column d. Chain ganglia 16. The nucleus pulposus is a remnant of a. Neural groove b. Neural crest cells c. Notochord 17. Which is a continuation of the dura mater a. Epineurium b. Endoneurium c. Perineurium d. Endomysium 18. The anterior spinal artery is a branch of a. Vertebral arteries b. Middle cerebral c. Posterior cerebral d. Anterior cerebral 19. Which of the following are considered to be the sacral splanchnic nerves a. Preganglionic sympathetics b. Postganglionic sympathetics c. Preganglionic parasympathetics d. Postganglionic parasympathetics 20. Which nucleus is responsible for pain a. Substantia nigra b. Lintiform nucleus c. Putamen d. Substantia gelatinosa 21. What is the termination point for the spinothalamic tracts? a. Ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus b. Ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus c. Anterior nucleus of the thalamus d. Posterior nucleus of the thalamus 22. part of typical vertebra that corresponds to the intermediate sacral crest a. spinous process b. transverse processes c. articular pillars d. pedicles median crest – spinous process intermediate crest – pillars lateral crest – transverse 23. imbrication in the spine is most commonly seen at a. C-4 to C-7 b. T-5 to T-8 c. T-9 to T-10 d. T12 to L1 24. Which structures pass through the foramen spinosum a. Middle meningeal artery b. Maxillary nerve c. Mandibular nerve d. Ophthalmic nerve 25. Which connects to the tympanic membrane a. Oval window b. Malleus c. Incus 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. d. Stapes Which artery supply the lateral cerebrum and temporal lobe of the brain a. External carotid b. Internal carotid c. Middle cerebral d. Basilar The anterior spinal cord is served by a branch of which artery a. Basilar b. Vertebral c. Subclavian d. Carotid anterior horn of the lateral ventricles comes into contact with which nucleus a. globus pallidus b. stellate c. cingulated d. head of the caudate nucleus Which cranial nerve has its sensory ganglion lateral to the transverse process of atlas a. V b. VII c. IX d. X Bell’s palsy is caused by a lesion of which cranial nerve a. V b. VII c. IX d. X Medial deviation of the eye results from damage to which muscle a. Lateral rectus b. Medial rectus c. Superior rectus d. Inferior rectus Which develops from the metencephalon a. Cerebrum b. Thalamus c. Medulla d. Pons Which are considered to be the transducers of the ears a. Hair cells b. Utricle c. Saccule d. Semicircular canals The superior gemellus muscles and the ________ muscles are supplied by the same nerves. a. Piriformis b. Obturator internus c. Inferior gemellus d. Quadratus femoris 35. The ventral primary rami of spinal nerves innervate which muscle a. Splenius capitis b. Spinalis c. Scalenus anterior d. Iliocostalis 36. The muscles of mastication are derived from which embryological structure a. Ectoderm b. Splanchnic mesoderm c. Somatic mesoderm d. Endoderm 37. The atlanto-occipital joint is classified as a synovial ___________ joint. a. Condyloid b. Sellar c. Hinge d. Planar 38. The temporomandibular joint is classified as a __________ joint a. Synarthrosis b. Syndesmosis c. Synovial d. Symphysis 39. The radiating, expanding processes that connect capillaries or neurons are which of the following cells a. Astrocytes b. Ependymal c. Schwann d. Oligodendrocytes 40. Which nerve is a branch from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus a. Axillary b. Radial c. Ulnar d. Musculocutaneous 41. Which vertebra has a bifid spinous process a. C-1 b. C-4 c. C-7 d. T-1 C2 – C6 are bifid 42. The optic nerve synapses on which structure: a. Lateral geniculate body b. Optic tract c. Visual cortex d. Optic chiasm 43. Which artery supplies the lateral temporal lobe of the brain 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. a. Middle cerebral b. Posterior communicating c. Anterior cerebral d. Posterior cerebral The dentate ligaments attach to the a. Dura mater b. Periosteum c. Subarachnoid mater d. Pia mater The atlas axis articulation is considered to be which type of joint: a. Pivot b. Condyloid c. Planar d. Ginglymus Flexion and extension of the atlas in relation to the occiput occurs in which of the following planes: a. Transverse b. Sagittal c. Coronal d. Frontal Which ligament makes up the posterior portion of the vertebral canal a. Flava b. Nuchae c. Tectorial d. Posterior longitudinal Which nerve runs along the atlas transverse process a. Radial b. Axillary c. Supraclavicular d. Suboccipital The posterior primary rami of spinal nerves does not supply which of these muscles a. Levator scapulae b. Splenius capitis c. Splenius cervicis d. Semispinalis The anterior primary rami of spinal nerves supply which group of muscles a. Levator scapulae and rhomboids b. Spenius capitis and spenius cervices c. Longissimus and spinalis d. Multifidus and rotators Damage to the tibial nerve will result in loss of a. dorsiflexion of foot b. extension of toes c. plantar flexion of foot d. flexion of toes 52. The transverse ligament is part of which ligament a. Cruciform b. Alar c. Apical d. Posterior atlanto occipital 53. Which holds the dens in place a. Anterior longitudinal ligament b. Ligamentum flavum c. Transverse ligament d. Ligamentum nuchae 54. Which is not part of the cervical plexus a. Ansa cervicalis b. Phrenic nerve c. Greater occipital nerve d. Lesser occipital nerve 55. What is the orientation of the superior facets in the lumbar spine a. Sagittal b. Coronal c. Horizontal d. Transverse 56. Which motion in the cervical spine is most restricted from C-2 to T-1 a. Rotation b. Lateral flexion c. Flexion d. Extension 57. Neural crest cells give rise to a. Dorsal root ganglion b. Viscera c. Skin d. Thyroid gland 58. Which muscle attaches to the anterior tubercle of atlas a. Superior oblique b. Longus coli c. Inferior oblique d. Rectus capitus lateralis 59. Which cranial nerve has its nucleus of origin in the midbrain a. I b. III c. V d. VI 60. The pelvic diaphragm is primarily made up of which muscle a. Levator ani b. Coccygeus c. Piriformis d. Obturator externus 61. Which cell is responsible for detecting insignificant vibration 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. a. Pacinian corpuscles b. Organ of Ruffini c. Merkel’s discs d. End bulbs of Krause Taste buds on the epiglottis are assocated with a. X The intervertebral foramina are located inferior to which of the following structures a. Pedicle b. Articular process c. Lamina d. Transverse process A lesion in the lateral funiculus will produce a/an a. Upper motor neuron lesion b. Lower motoneuron lesion c. Extrapyramidal lesion d. Anesthesia Which of the following best describes a lower motor neuron lesion a. From the cerebral cortex to the anterior horn b. From the anterior horn to the effector c. From the affector to the anterior horn d. From the anterior horn to the cerebral cortex The spinocerebellar tracts carry which of the following a. Conscious proprioception b. Unconscious proprioception c. Vibration sense d. Two point discrimation Which is the final synapse for olfaction a. Uncus of the temporal lobe b. Inferior frontal lobe c. Superior temporal lobe d. Inferior temporal lobe On which thoracic vertebra is there both a true and an atypical rib? a. 1 b. 7 c. 9 d. 12 Which suture separates the occipital and parietal lobes a. Lambdoidal b. Frontal c. Sagittal d. Temporal The intervertebral disc is considred to be which type of joint a. Syndesmosis b. Synchondrosis c. Symphysis d. Synarthrosis