* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Ecological economics wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the environment wikipedia , lookup
Natural capital accounting wikipedia , lookup
Ecogovernmentality wikipedia , lookup
Index of environmental articles wikipedia , lookup
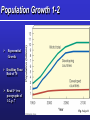
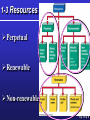
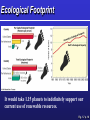
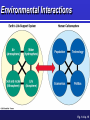
Environmental Problems, Their Causes, and Sustainability G. Tyler Miller’s Living in the Environment 14th Edition Chapter 1 What’s the use of a house if you don’t have a decent planet to put it on? HENRY DAVID THOREAU Key Concepts Growth and Sustainability Resources and Resource Use Pollution Causes of Environmental Problems Living More Sustainably 1-1 Ecology Environment Sustainable Society Environmental Science Environmental Science … is an interdisciplinary field, drawing on many diverse disciplines. Ethics Ecology Economics Chemistry Engineering Political science Biology Environmental science Atmospheric science Oceanography History Sociology Geology Anthropology Archaeology Environmental Science … is NOT the same as environmentalism. It is science, NOT advocacy. Environmental Science … can help us avoid mistakes made by past civilizations. On Easter Island, people annihilated their culture by destroying their environment. (Chapter 3 Case Study) What Keeps Us Alive? Capital Solar Natural Fig. 1-2, p. 7 LE 2-SBS Soil formation Valuation of ecosystem services Genetic resources Pollination Habitat provision Biological control Erosion control • Environmental economists have assigned monetary Climate regulation values to ecosystem services. Raw materials Recreation • Robert Costanza et al., 1997: $33.3 trillion per year! Water regulation Gas regulation Food provision Water supply Disturbance regulation Waste treatment Cultural uses Nutrient cycling From The Science behind the Story Population Growth 1-2 Exponential Growth Doubling Time/ Rule of 70 Read 1st two paragraphs of 1-2, p. 7 Fig. 1-4, p. 8 World Population Population clock Fig. 1-1 p. 5 Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Per Capita GDP Economic Development Developed Countries Developing Countries Positive Aspects Negative Aspects Globalization Social Economic Environmental Effects 1-3 Resources Perpetual Renewable Non-renewable Fig. 1-6 p. 9 Renewable Resources Sustainable Yield Environmental Degradation Tragedy of the Commons (video) The “Ecological Footprint” An ecological footprint is the area of land and water needed to produce the resources a person or population uses, plus the amount needed to dispose of their waste. Ecological Footprint It would take 1.15 planets to indefinitely support our current use of renewable resources. Fig. 1-7 p. 10 Non-Renewable Resources Energy Resources Metallic Resources Non-Metallic Resources Reuse Recycle Economic Depletion Fig. 1-8 p. 11 1-4 Pollution What is pollution? Effects of Pollution Sources Point Nonpoint Dealing With Pollution Prevention (Input Control) Cleanup (Output Control) 1-5 Environmental and Resource Problems Five Root Causes Major Problems (See Fig. 1-19 p. 12) Environmental Impact Fig. 1-13 p. 15 Environmental Interactions Fig. 1-14 p. 15 1-6 Environmental Worldviews (video) Planetary Management Stewardship (video) Environmental Wisdom What is Our Greatest Environmental Problem? Disease Overpopulation Water Shortages Climate Changes Biodiversity Loss Poverty Malnutrition Solutions Current Emphasis (Reactive) Sustainability Emphasis (Proactive) Fig. 1-16, p. 18