* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download parallel Lines and the Triangle Angle
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
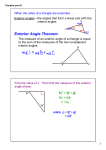
3-3 Parallel Lines & the Triangle Angle Sum Theorem M11.B.2 2.4.11.B Objectives: 1) To classify triangles and find the measures of their angles. 2) To use exterior angles of triangles. Triangle Angle-Sum The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180. m<A + m<B + m<C = 180 C A B Example: Find the missing value Find m<Z Z X 48° 67° Y Example: Find the missing value Triangle ABC, <ACB is a right angle, and CD AB. Find the values of a, b, and c (Textbook page 133 - TE) T Ex: Find the value of x, y, and z. (textbook page 132) G F J H Classify Triangles: by Angles Equiangular Acute Right Obtuse Classify Triangles: by Sides Equilateral Isosceles Scalene Ex: Classify a Triangle by its Angles & Sides 5 2 4 Vocab An exterior angle of a polygon, is an angle formed by a side and an extension of an adjacent side. For each exterior angle of a triangle, the two nonadjacent interior angles are its remote interior angles. Triangle Exterior Angle Theorem. m<1= m<2 + m<3 Example: Using the Exterior Angle Theorem