* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint 簡報
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
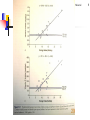
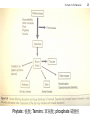
Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Vitamins Water-soluble, fat-soluble Reusable coenzymes in many metabolic reactions Generally, exercise ↑vitamin requirement ↓absorption from GI tract ↑excretion from sweat ↑turnover (degradation) ↑requirement (retention) because biochemical adaptation to training (↑ mitochondria density, muscle hypertrophy) 1 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 2 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 3 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 4 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 5 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral The roles of water-soluble vitamins in energy metabolism 6 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Assessing vitamin status Difficult to determine accurately Diagnosis of vitamin deficiency needs to COMBINE following information Blood analysis: plasma concentration and/or activity of functional enzyme(s) Dietary intake: tedious and inaccurate Clinical symptoms: unspecific Most studies showed that athletes do NOT have lower vitamin status Except with extremely low dietary energy intake or very imbalanced diet 7 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Recommended intakes of vitamins Estimated average requirement (EAR): normally distributed Amount of nutrient sufficient to meet the needs of average individual in certain age and gender Recommended daily allowance (RDA): cover 97.5% of all healthy individuals Athletes have higher requirement for vitamins, but also consume more foods/energy If energy intake match energy requirement, athletes consume reasonably balanced diet, they can get all vitamins they need from food No need for supplements 8 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 9 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Risk group for low vitamin intake Low-energy or unbalanced diet Very high energy intake (>4800 kcal/day) Consume large ‘in between meals’ and high-energy sport drinks Low in vitamins/minerals Vegetarians: B12 Vitamin loss in sweat negligible NO increased vitamin excretion in urine and feces in athletes Vitamin turnover usually unaffected by exercise Acute exercise may change plasma concentrations Mainly due to redistribution of labile pools 10 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 11 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 12 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 13 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 14 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 15 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 16 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 17 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 18 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 19 Effect of exercise on mineral requirements Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Temporary depression of free (unbound) plasma concentrations of some minerals after prolonged exercise Fe, Zn, Cu Redistribution of different tissue compartments Release of proteins from liver/neutrophils that chelate (螯合) minerals, part of acute-phase response to inflammation 20 Dietary surveys of mineral intakes in elite athletes Difficult Differences in bioavailability in various foods Not all foods have analyzed for their mineral contents Mineral contents may depend on their content in soil Plasma concentrations usually do NOT represent body pool Low iron stores Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Middle- and long-distance runners, adolescent athletes, female athletes Low Ca intake: female and adolescent athletes Low Zn, Mg intake: female athletes 21 Effect of exercise on iron requirements Iron loss in sweat Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Previous studies: can reach 0.3 mg/L Extra ~12 mg iron from food (10% absorbed) Recent studies: 6-11% iron absorbed each day lost in sweat per hour of exercise Higher sweat rate and higher iron loss in men Increased iron requirement ↑Myoglobin, red cell mass GI bleeding: irritation of stomach lining or hemorrhage of colon caused by ischemia Elite male distance runners loss 6 ml blood/day from GI during training and racing 22 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Iron Iron depletion (serum ferritin儲鐵蛋白 < 12 ug/L) common in female athletes Anemia reduce athletic performance Insufficient oxygen delivery, breathlessness, mental dysfunction, impaired temperature control, ↓immunity Periodic screening of serum ferritin in athletes Higher absorption rate for heme 血基質-iron Iron depletion without anemia ↑lactate during max exercise, ↑subjective feeling of exercise overload in elite athletes ↑performance by iron supplementation in Iron depletion without anemia Vitamin C absorption ↑ rate for nonheme-iron Anemia also result from deficiency in B6, B12, folate For nucleic acid and red blood cell production 23 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 24 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Phytate: 植酸; Tannins: 單寧酸; phosphate 磷酸根 25 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Calcium and bone health Ca intake closely related to total-energy intake Female athlete triad: amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea associated with high risk of early osteoporosis Chronically low estrogen Low body fat, low energy intake, high physical activity Eating disorder Gymnastics, swimming, long-distance running, dancers ↑Ca consumption to 120% RDA help maintain bone density and development in amenorrhea Use low-fat dairy products Sweat concentration 0.1-1.0 mM Lost 4 L sweat lost 2 mmol (80 mg) Ca 200 mg Ca intake (40% absorption) 26 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 27 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 28 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Micronutrients as antioxidants Exercise ↑free radical (unpaired electron) production Antioxidant defense system eliminate/quench free radicals Demonstrated in vivo studies Mainly through electron leakage from electron transport chain, 3-5% oxygen consumed at rest Damage to lipid, protein, DNA Prevent/reduce oxidative stress Vitamin C, E, beta-carotene Cu, Zn, Selenium: as cofactors for antioxidant enzymes Glutathione: glycine, cysteine, glutamine Polyphenols 多酚類: tea, red wine, fruits, vegetables 29 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Antioxidant and muscle damage Unaccustomed exercise or eccentric actions damage myofibers Muscle pain, soreness, stiffness, ↓range of motion, ↓glycogen resynthesis Damaged muscle tissue cause initial activation of immune system WBC attracted to damaged muscle breakdown of damaged fibers, initiate repair process Occur within fist hour after eccentric exercise, followed by infiltration of monocyte and macrophage, reaching max at 24-72 after exercise Repaired process involve production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by invading leukocytes ROS cause muscle soreness, ↑creatine kinase, oxidative damage to DNA and proteins 30 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Antioxidant mechanisms Prevent ROS formation Intercept ROS attack by scavenging Binding transition metal ion, such as Cu, Fe, to prevent initiation of free radical reactions React with chain-propagating radicals Provide favorable environment for effective functioning of other antioxidants Free radical really a bad thing? Or a signal for exercise adaptation? 31 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Vitamin C beta-carotene Vitamin E 32 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Polyphenols 33 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 34 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Regeneration of GSH Glutathione (GSH) Glutathione reductase 35 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Possible risks of high-dose antioxidant supplementation Antioxidants inhibit apoptosis (programmed cell death) In situations with high DNA damage Important defense mechanism, inhibit tumor development by eliminating new mutated cells Exercise, heavy smoking Administration of large amounts of antioxidants may prevent effective removal of damaged cells May ↑cancer risk Insufficient data to recommend antioxidant supplements for athletes Usually NO effect on exercise performance 36 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral Athletes need more antioxidants? Higher antioxidant required in athletes to reduce oxidative damage induced by exercise Dietary sources of antioxidants are preferable to single/combined supplements Based on epidemiological studies on adverse health outcomes Pro-oxidant effects with prolonged use of high-dose antioxidant supplements May need 3X of RDI Supplements may be necessary if RDI can not be met Antioxidant supplements on human performance usually negative 37 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 38 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 39 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 40 Ex Nutr c9-Vit Mineral 41