* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ICD 10 and Nephrology
Survey
Document related concepts
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
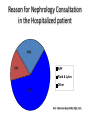
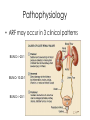
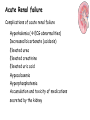
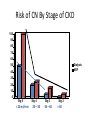
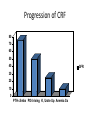
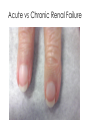
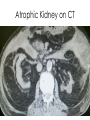
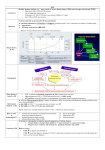
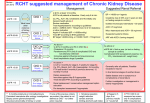
ICD 10 and Nephrology How to find ARF and CKD For Coders and Clinical Documentation Specialists Jeff Kaufhold MD FACP Nephrology Associates of Dayton Oct 2013 Summary • • • • • • • • Review of the development of ICD 10 Changes coming with ICD 10 Top 5 Clinical Documentation Issues Making the Diagnosis of ARF and CKD ICD 10 codes for renal disease RIFLE criteria for Acute renal Failure Progression of CKD and CKD stages How to differentiate Acute from Chronic ICD 9 and 10 history • ICD 9 developed by WHO • ICD 9 Clinical Modification developed for US in 1979. • CPT (clinical Procedural Terminology) codes used for ambulatory reporting. • ICD 10 developed in 1990’s • ICD 10 codes are now available in EPIC as of Oct 1 2013 • Mandatory use of ICD 10 is Oct 1, 2014. • CPT codes will continue to be used for physician practice settings/ office billing ICD 10 after Oct 1 2014 • Required for HIPAA transactions • ICD 10 CM (Diagnosis) codes Required for diagnosis of all services inpt or outpt • ICD 10 PCS (procedure) codes will be required on inpt claims • EPIC is starting the migration from ICD 9 to 10 codes now, and EPIC Premier inpt billing function includes the new ICD 10 coding structure. ICD 10 Changes Over 50% of new Dx are musculoskel, and 36 % are to distinguish R from L ICD 10 Changes • Up to 7 characters • Includes complication, severity, sequelae and other disease related parameters • Includes laterality • Includes initial or subsequent encounter code • Improved consistency of terminology • Combination codes are common i.e DM 2, controlled with renal manifestation • Has space holders for expansion ICD 10 PCS coding for inpts 0 D B 5 8 Z X Section Body system Root operation Body part Approach Device qualifier Med/Surg GI Excision Esophagus Natural No device opening, implanted endoscopi c Diagnostic ICD 9 ; 45.16 EGD with excisional biopsy, ICD 10 0DB58ZX Endoscopic esophageal excision via natural or artificial opening Most common issues in ICD 10 • Laterality – as you code, EPIC will prompt you if right or left is required • Trimester specific • Many new orthopedic codes • Specificity is increased dramatically, so physician documentation must be more specific too. Top 5 Clinical Documentation Issues • • • • • CHF Sepsis Renal Failure Pneumonia Respiratory Failure • Don’t use “Other” or accept a nonspecific diagnosis like DM, when a more specific term exists: • “DM 2 controlled with renal manifestation” ICD 10 codes • Epic is migrating codes so over next year you may search using known ICD 9 codes • Can keep your PMHx and ongoing problem list NONSPECIFIC, • But your visit diagnosis list must be as specific, detailed, and include as many modifiers/ comorbidities/severity codes as possible Common Diagnoses • ICD 9 • ICD 10 • 250.02 DM 2 no mention of controlled or complication • E11.65 DM 2 with hyperglycemia • 250.43 DM 1 with renal manifestation • E10.21 DM 1 with nephropathy AND • E10.65 DM1 with hyperglycemia Top 5 Clinical Documentation issues Condition Common issues Financial impact CHF Acute vs Chronic, systolic vs diastolic DRG 684 Renal failure without major complication or comorbidity Sepsis Sepsis, severe sepsis, SIRS, bacteremia $ 3609 Renal Failure Acute vs chronic Stage with RIFLE criteria or CKD stage With ATN is important DRG 682 renal failure with major complication and comorbidity Pneumonia Cause / specific bacteria Aspiration, simple vs complex, laterality $ 9340 Respiratory Failure Acute vs chronic, resp distress vs resp failure Quality Performance hinges on Documentation • For inpts affects the hospital quality score • For our pts affects our practice score • Lack of clear documentation results in inappropriate assignment of complication codes for expected consequence of renal disease • Improved documentation results in lower reported complication rates, • higher complexity/ comorbidity scores reflect sicker population we care for. Estimated impact on physician practice • 10 -20 % increase in denials • Differences in authorization and referral triggers • Increased scrutiny of documentation • Impact on contracting/ preferred provider status based on severity of illness as reflected in coding. ICD 10 and EPIC • ICD 10 diagnosis calculator goes live on Premier Epic Oct 28 2013 • Training modules available on Healthstream • Some codes require specific information, and a coding window will open to fill in R vs L, initial visit vs followup, sequelae. • Many codes won’t require more specificity, but for visits we should try to be as specific as possible. ICD 10 and EPIC • Many codes won’t require more specificity, but for visits we should try to be as specific as possible. • We can double click item on the problem list like DM, HTN, Other disorder of renal etc, and make it more specific, without losing / deleting associations. Make the Diagnosis of Kidney Disease • Criteria The ICD9 Code for CKD is 585.x where x = stage The ICD 9 Code for ARF is 584.9 Decreased kidney function eGFR of <60 ml/min/1.73 m2 for ≥ 3 months Abnormal urinalysis including the presence of proteinuria or hematuria Request a spot urine protein/creatinine ratio (Normal is <30 mg/g) Document an abnormal Renal Imaging Study 17 Specific details for pts with ARF and CKD • DM Type I or II, controlled or uncontrolled – Use A1c over 6.5 as uncontrolled – With renal manifestation • Hypertension – With nephropathy • CKD stages 1-5, use ESRD for pts on dialysis in the medicare ESRD program. • AKI with ATN Specific details for pts with ARF and CKD • AKI with ATN – – – – Urine findings ATN casts Oliguria Creatinine over 2.5 or > 2X baseline Were they pre-renal? • Does pt have TIN? • Look for eosinophils in blood or urine • Complications of renal failure – Anemia of CKD – Secondary hyperparathyroidism of renal origin – Protein calorie malnutrition Severe = albumin less than 3.0 Diabetes codes • E08.22 DM due to underlying condition with diabetic nephropathy • E09.22 Drug or chemical induced DM with DM CKD • E10.22 DM I with Diab. Neph • E11.22 DM II with Diabetic Nephropathy • E13.22 Other specified DM with Diabetic CKD CKD Codes • • • • • • • N18.1 CKD stage 1 N18.2 CKD Stage 2 N18.3 CKD Stage 3 N18.4 CKD Stage 4 N18.5 CKD stage 5 N18.6 ESRD N18.9 CKD unspecified CKD and DM codes • Code the DM first, then the stage: – E10.22 Type I DM with nephropathy – N18.6 ESRD • Same for Hypertensive Kidney Disease – I12 hypertensive Kidney disease – N18.4 CKD Stage 4 – If pt has heart and kidney disease, use • I13 hypertensive Heart and CKD – CHF uses I 50 codes HTN and CKD Codes • I12.0 Hypertensive CKD with Stage 5 or ESRD • I12.9 “” “” with stages 1-4 CKD • I13.10 Hypertensive Heart and CKD without heart failure, Stages 1-4 • I13.11 Hypertensive Heart and CKD without heart failure, Stage 5 or ESRD • I13.2 Hypertensive Heart and CKD with heart failure, Stage 5 or ESRD The Early NHANES III Study Analysis of Prevalence of CKD by Stage eGFR Range Population (1,000’s) Population (%) Stage Description 1 Kidney damage with normal or increase GFR ≥ 90 5,900 3.3 % 2 Mildly decreased GFR 60-89 5,300 3.0 % 3 Moderately decreased GFR 30-59 7,600 4.3 % 4 Severely decreased GFR 15-29 400 0.2 % 5 Kidney Failure < 15 300 0.1% (ml/min/ 1.73 m2) - Adapted from NHANES III (2000) 24 US Population with CKD Coresh, Selvin, Stevens. Prevalence of CKD in the US. JAMA.2007;298(17)2038. A Large National Burden in 2009 The Renal Continuum of Care Primary Care Physician At Risk Population Diabetes Hypertension Obesity CVD Nephrologist CKD ESRD 500,000+ People ~375,000 Dialysis 26,000,000+ People ~125,000 Transplant 26 Cardiovascular events by Stage of CKD NKF KDOQI guidelines www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/guidelines_ckd/toc.htm All Cause Mortality By Stage of CKD NKF KDOQI guidelines www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/guidelines_ckd/toc.htm Why Do CKD Patients Need Special Care? Renal Disease Care is Expensive ~1.5% of Patients ~10% of Federal Healthcare Costs ESRD + Late Stage Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Other Medicare ~ $30B per year Other Medicare Source: USRDS (publicly available comprehensive clinical and financial dataset reported to and used by CMS) ~375,000 ESRD + ~300,000 Stage 4 Chronic Kidney Disease 29 Timely Referral: Long-lasting benefits Late Referral patients have a 44% higher risk of mortality in the first year of dialysis compared to Early Referral patients 30 Who Should be Screened for CKD? The AT RISK Population: – HYPERTENSION – DIABETES MELLITUS – CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE – FAMILY HISTORY OF CKD 31 Screening Recommendations • Screening Should Include: – Laboratory studies to include serum creatinine and eGFR – Urinalysis to determine the presence of proteinuria – Imaging studies such as ultrasound Screening recommendations are provided in KDOQI, Guideline 1 http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/guidelines_ckd/toc.htm 32 Presence of MAU Indicates a Potential Increased Risk for CV Events Urinary Albumin (mg/day) 1,000 900 Macroalbuminuria >300 mg/day Increased CV Risk and Presence of Renal and Vascular Dysfunction 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 MAU 30-299 mg/day Increased CV Risk and Vascular Dysfunction 0 Normal Cardiovascular Risk Garg JP et al. Vasc Med. 2002;7:35-43. Eknoyan G et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42:617-622. Make the Diagnosis of Kidney Disease • Criteria The ICD9 Code for CKD is 585.x where x = stage The ICD 9 Code for ARF is 584.9 Decreased kidney function eGFR of <60 ml/min/1.73 m2 for ≥ 3 months Abnormal urinalysis including the presence of proteinuria or hematuria Request a spot urine protein/creatinine ratio (Normal is <30 mg/g) Document an abnormal Renal Imaging Study 34 How to Implement Timely Referral? • Establish CKD diagnosis and Details: – Make a specific renal disease diagnosis if possible – Identify co-morbidities • Hypertension • Diabetes • Cardiovascular Disease – Determine the severity of CKD (know the eGFR) – Identify CKD Complications • Anemia (know the Hgb) • Secondary Hyperparathyroidism (know the Ca and Phos) • Malnutrition (know the albumin) – Assess stability of Kidney Function and CKD Stage Recommendations for further evaluation are outlined in KDOQI Guideline 2 http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/guidelines_ckd/toc.htm 35 Timely Referral Decision Making • Timely Referral Guidance: – Rapidly decreasing renal function REFER – Abnormal eGFR AND proteinuria REFER – eGFR ≤ 30 ml/min/ 1.73 m2 REFER – eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2 and Cardiovascular Disease Present REFER – Uncontrolled Hypertension Present REFER 36 Reason for Nephrology Consultation in the Hospitalized patient 25% ARF 15% Fluid & Lytes Other 60% Ref: Paller Sem Neph 1998, 18(5), 524. Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative • RIFLE Criteria Helps risk stratify patients with acute renal failure. • Increased mortality seen with increases in creatinine of 0.3 to 0.5 mg/dl – 70 % increase for all inpts, – 300 % increase in cardiac surgery pts Acute Renal Failure • Definition may depend on whom you ask – Surgeon - - low urine output – Intensivist-- severe acidemia – Nephrologist-- rising serum creatinine • Frequency - depends on clinical setting – 1% of all admissions to hospital – 2-5% of all individuals during a hospitalization – 4-15% during cardiopulmonary bypass – 10-30% of all admissions to ICU Definition • ‘…a sudden and severe decrease in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) sufficient to cause increases in BUN and Scr (azotemia), Na/H2O retention (edema), and development of acidemia and hyperkalemia…’ • review of 27 studies showed no 2 used the same definition “chronic renal confusion” What’s in a name? • lack of a universally recognized definition of ARF • 2004 consensus conference – proposed the term acute kidney injury (AKI) to reflect the entire spectrum of ARF recognizing that an acute decline in kidney function is often secondary to an injury that causes functional or structural changes in the kidneys Newest Definition: Mehta CritCare 2007 • An abrupt (within 48 h) reduction in kidney function currently defined as: – an absolute increase in serum creatinine of either >= 0.3 mg/dl, – or a percentage increase of >= 50 % or a reduction in UOP (documented oliguria of < 0.5 ml/kg per h for > 6) RIFLE criteria • • • • • Risk low uop for 6 hours, creat up 1.5 to 2 times baseline Injury creat up 2 to 3 times baseline, low uop for 12 hours Failure Creat up > 3 times baseline or over 4, anuria Loss of Function Dialysis requiring for > 4 weeks ESRD Dialysis requiring for > 3 months RIFLE estimate of Mortality • • • • • • • Two studies No renal failure Risk Injury Failure Loss of Function ESRD Uchino 4.4 % 15% 29% 53.9% Hoste 5.5 8.8 11.4 26% Crit Care Med 2006; 34:1913-7, Hoste CCM 2006; 10:R73 RIFLE criteria • When markers of severity of illness are looked at excluding renal data, no difference in groups is seen. The differential for any lab abnormality is: • • • • • • • Lab error Lab error Lab error Iatrogenic Polypharmacy Real disease IN THIS ORDER! Acute renal failure (ARF) • Differential for Lab abnormality: Causes: – A rise in the BUN level can occur without renal injury, such as in GI or mucosal bleeding, steroid use, or protein loading (such as IV nutrition) – A rise in the creatinine level can result from medications (eg, cimetidine, trimethoprim) that inhibit the kidney’s tubular secretion, or an increase in creatinine production such as seen in Rhabdomyolysis. (muscle breakdown) – True Anuria is most commonly the result of an obstructed foley catheter, or an error in recording output. The worst cause of anuria is cortical necrosis. Acute renal failure (ARF) • An abrupt or rapid decline in renal function • Marked by a rise in BUN (azotemia) or serum creatinine concentration – Immediately after a kidney injury, BUN or creatinine levels may be normal • The only sign of a kidney injury may be decreased urine production • Use RIFLE Criteria to evaluate Risk. Acute renal failure (ARF) • History and Physical examination: – Nephrotoxic drug ingestion – History of trauma or unaccustomed exertion – Blood loss or transfusions – Congestive heart failure – Exposure to toxic substances, such as ethyl alcohol or ethylene glycol Acute renal failure (ARF) • History and Physical examination: – Exposure to mercury vapors, lead, cadmium, or other heavy metals, which can be encountered in welders and miners – Hypotension – Volume contraction • Vomiting/Diarrhea/Sweating/Nursing Home – Evidence of connective tissue disorders or autoimmune diseases Pathophysiology • ARF may occur in 3 clinical patterns BUN:Cr > 20:1 BUN:Cr 10-20:1 BUN:Cr > 20:1 Pathophysiology • ARF may occur in 3 clinical patterns • Suggested by labwork: BUN:Cr > 20:1 Pre-Renal or Post-Renal BUN:Cr 10-20:1 Intra-Renal BUN:Cr < 10:1 Extrinsic Production of Creatinine (rhabdomyolysis), this pattern also seen in dialysis patients) Prerenal ARF • Prerenal ARF represents the most common form of kidney injury and often leads to intrinsic ARF if it is not promptly corrected • From any form of extreme volume loss – GI, renal (Vomiting, Diarrhea, diuretics, polyuria), cutaneous (eg, burns), and internal or external hemorrhage can result in this syndrome • Systemic vasodilation or decreased renal perfusion • • • • Anesthetics Drug overdose Heart failure Shock (eg, sepsis, anaphylaxis) Approach to ARF • Pre-Renal – Most common – Due to NPO, Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, NSAIDS – Due to renal artery disease, CHF with poor EF. – Usually BUN / creat ratio over 20. – Usually creat < 2.5 Approach to ARF • Intra-Renal – Most commonly pre-renal tipping over into true renal injury. – Acute Tubular Necrosis is result (70%) – Tubulo-Interstitial Nephritis (20%) – Acute vasculitis/GN rare (5-10 %) Intrinsic Renal Failure • Intrinsic ARF – acute tubular necrosis – acute interstitial nephritis – acute glomerulonephritis – acute vascular syndromes – intratubular obstruction • BUN:Creat ratio 10-20 :1 • In Pre-renal ARF, once creat is > 2.5, there is some degree of ATN Intrinsic ARF Urinalysis • Intra-Renal – Acute Tubular Necrosis (70%) • Dirty brown casts, low UOP – Tubulo-Interstitial Nephritis (20%) • Eosinophils in blood or urine, • Potassium out of proportion to creat. • Normal BP, related to drug exposure – Acute vasculitis/GN rare (5-10 %) • Proteinuria, hematuria, RBC casts Approach to ARF • Post- Renal – Most commonly due to obstruction at bladder outlet • • • • Prostate problems Neurogenic bladder Stone Urethral stricture (esp after CABG) Acute Renal failure Complications of acute renal failure Hyperkalemia ( ECG abnormalities) Decreased bicarbonate (acidosis) Elevated urea Elevated creatinine Elevated uric acid Hypocalcaemia Hyperphosphatemia Accumulation and toxicity of medications secreted by the kidney Documentation for ARF • • • • List the ARF N17.9 Cause of the ARF (ATN N17.0) Underlying CKD with stage if present N18.X Volume status – Volume overloaded E 87.7 or dry E 86 • Electrolyte abnormalities – Hyperkalemia E 87.5 / hyponatremia E 87.1 • Acid base status – acidosis E 87.2 or alkalosis E 87.3 • Estimated GFR: < 30 ml/min means many meds need to be adjusted Transplant Specifics • Just because your patient has a transplant, they still have Chronic Kidney disease. – List the transplant – List the CKD stage for chronic allograft dysfunction – List acute allograft dysfunction if present – List the cause of their underlying CKD/ESRD – List comorbidities and complications • Are they anemic due to Cellcept use? • Did they develop NODAT? Doc talk, Precyse University, Oct 2013 PCKD specifics • PCKD Q 61.3 • Acquired cyst N 28.1 • Q 60-64 Congenital Malformations of the urinary System • Autosomal Dominant or recessive? • Liver /other cysts? One common Cause of ARF • Contrast Induced nephropathy CIN Risk Factors for Contrast Nephropathy • Age over 60 • Diabetes • Pre-Renal States – CHF – NSAIDS, ACE Inhibitors, Diuretics • Proteinuria Includes, but not limited to Myeloma. • Pre-existing Renal Disease Risk of CN By Stage of CKD 100 90 80 70 60 Dialysis ARF 50 40 30 20 10 0 Stg 5 < 20 ml/min Stg 4 20 – 30 Stg 3 30 – 60 Stg 2 > 60 CKD Stages • • • • • • Stage 1. Stage 2. Stage 3. Stage 4. Stage 5. Stage 6. Normal function with known dz GFR 60-80 GFR 30-60 GFR 15-30. GFR less than 15. ESRD on dialysis. Progression of CRF 80 70 60 50 40 GFR 30 20 10 0 PTH climbs PO4 rising K, Urate Up Anemia Sx How do you differentiate ARF from CRF. • What physical exam finding tells you the pt has Chronic Kidney Disease? • What Would you see on renal Imaging for a pt with CKD? Lindsey’s Nails Acute vs Chronic Renal Failure Atrophic Kidney on CT