* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download management - University Of Wisconsin
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
New Concepts in
Chronic Kidney Disease
Jonathan B. Jaffery, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
University of Wisconsin-Madison
New Concepts in
Chronic Kidney Disease
•
•
•
•
•
The Epidemic
Estimating GFR & Staging
Risk factors for progression
Role of Angiotensin II
Management
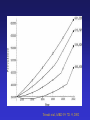
Incidence/Prevalence of ESRD in the US
USRDS, 2000
Trivedi et al, AJKD 39: 721-9, 2002
Patient awareness of CKD
Proportion of individuals who were ever told that they had weak or
failing kidneys by the level of GFR (ml/min per 1.73 m2), elevated
urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR; mg/g) and gender.
Coresh et al, JASN 16: 180-188, 2005
Estimating GFR
• Cockcroft-Gault Equation1
Ccr(ml/min)=
(140-Age)(Weight)
72(Scr)
(0.85 if female)
• MDRD Equation2
GFR(ml/min/1.73m2)=
170 (Scr)-0.999(Age)-0.176(SUN)-0.170(Alb)+0.318
(0.762 if female)(1.180 if black)
1
Cockcroft and Gault, Nephron 1976
2
Levey et al, Ann Intern Med 1999
Estimating GFR
• Modified MDRD equation
– e-GFR = 186 x (PCR)-1.154 x (Age)-0.203 x (0.742
if female) x (1.210 if African American)
• Convince the lab to do it automatically
• On-line e-GFR calculators
– http://www.nkdep.nih.gov/healthprofessionals/tools/gfr
_adults.htm
– http://www.kidney.org/kls/professionals/gfr_calculator.
cfm
CKD Staging
K/DOQI guidelines, AJKD, Vol. 39, No 2, Suppl 1, February 2002
Sample e-GFR
Serum
Creatinine
1.2 mg/dl
2.0 mg/dl
Age
Male
Female
35
73
54
70
64
47
35
41
30
70
35
26
Chronic Kidney Disease
progression risks
•
•
•
•
•
Hypertension
Proteinuria
Glycemic control
Smoking
Lipids
CKD Progression Risks
hypertension
CKD Progression Risks
proteinuria
U protein on Ccr
0
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
-2
-4
Slope ml/min/y
-6
-8
All MAP
-10
Norm BP
Hi BP
-12
-14
-16
-18
-20
U protein; g/d
Measuring proteinuria
• The ratio of protein or albumin to creatinine in an
untimed (spot) urine sample is an accurate alternative to
measurement of protein excretion in a 24-hour urine
collection.
CKD Progression Risks
glycemic control
Cumulative Incidence of Urinary Albumin Excretion {300 mg per 24 Hours (Dashed
Line) and 40 mg per 24 Hours (Solid Line)} in Patients with IDDM Receiving Intensive
or Conventional Therapy.
Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, N Engl J Med 329:977, 1993
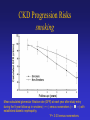
CKD Progression Risks
smoking
Mean calculated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) at each year after study entry
during the 5-year follow-up in smokers (—•—) versus nonsmokers (—
—) with
established diabetic nephropathy.
*P < 0.03 versus nonsmokers.
CKD Progression Risks
lipids
Samuelsson O et al, Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997 Sep;12(9):1908-15
ACE Inhibitors and CKD Progression
Meta-analysis
• 11 randomized controlled trials comparing
ACE inhibitors vs. other medications in
treatment of hypertension in 1860 nondiabetic
patients with CKD (S Cr=2.3).
• Results:
– ACE inhibitors lowered BP and proteinuria.
– ACE inhibitors decreased the combined risk of
progression of CKD and development of ESRD
by 30%, independent of BP lowering effects.
Jafar T, Ann Intern Med 135:73-87, 2001
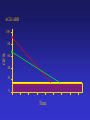
ACEi/ARB
100
GFR
80
60
40
20
0
Time
ACEi/ARB and GFR
60
50
80
40
60
30
40
20
20
10
0
0
b-Blocker
ACEi/ARB
GFR
Heart Rate
100
Chronic Kidney Disease
management
I.
Slow the progression
• Blood pressure
• Smoking
• Proteinuria
• Lipids
• Protein restriction • Glycemic control
II.
Evaluate and treat complications
• Anemia
• Osteodystrophy
III. Prepare for renal replacement therapy
• Vascular access
• Referral to Nephrology
Chronic Kidney Disease
management
• National Kidney Foundation Kidney
Disease Outcome Quality Initiative
(K/DOQI)
– The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative or
K/DOQI provides evidence-based clinical practice
guidelines developed by volunteer physicians and
health care providers for all stages of chronic kidney
disease and related complications, from diagnosis to
monitoring and management.
– http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/index.cfm
I. Slowing the progression of CKD
Hypertension
I. Slowing the progression of CKD
Proteinuria
• ACEi or ARB
• Nondihydropyridine calcium channel
blockers (verapamil and diltiazem)
– have been shown to effective in reducing
urinary albumin excretion, beyond ability to
lower blood pressure
(Bakris GL et al, Kidney Int. 2004 Jun;65(6): 1991-2002)
• Combinations?
I. Slowing the progression of CKD
Protein Restriction
• Animal studies - dietary protein restriction
significantly slows development of renal disease
• MDRD Study
• 585 nondiabetic patients with GFR 39 ml/min
randomized to either 1.1 or 0.7 gm
protein/kg/day
• Results – Reduction of protein intake minimally
ameliorated decline of GFR (1.1 cc/min/year)
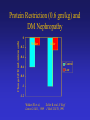
Protein Restriction (0.6 gm/kg) and
DM Nephropathy
Change GFR (mL/min/month)
0
Walker
Zeller
-0.2
-0.4
Control
Low
-0.6
-0.8
-1
-1.2
Walker JD et al,
Zeller K et al, N Engl
Lancet 2:1411, 1989 J Med 324:78, 1991
II. Managing complications of CKD
Anemia
• Diagnosis of exclusion
• Check iron stores
– TSAT (iron/TIBC) 20-50%
– Ferritin 100-600 ng/ml
• Erythropoietin replacement therapy
• Goal Hg 11-12 g/dL
II. Managing complications of CKD
Osteodystrophy
• High-turnover (osteitis fibrosa cystica) bone
disease
• Low-turnover (adynamic) bone disease
– Resistance to PTH
– Need for relatively higher PTH levels to
maintain adequate bone remodeling
– Low-turnover may have worse outcomes than
high
• Check phosphorous, calcium, intact PTH
II. Managing complications of CKD
Osteodystrophy
II. Managing complications of CKD
Osteodystrophy
• Dietary phosphate restriction
• Phosphate binders
– Calcium carbonate, Calcium Acetate
– Lanthanum Carbonate
– Sevalamer
• 1,25 Vitamin D
• Calcimimetic- not approved for pre-ESRD
III. Preparing for RRT
Vascular access
• Goal is to:
– Increase use of fistulas
– Avoid use of tunneled catheters
• Save the Veins!
• Avoid blood draws/IVs in non-dominant
arm
• NO subclavian central lines
III. Preparing for RRT
Referral
• > 50% of patients had 1st encounter with
nephrologist within 1 year of RRT
• 32% had 1st appt < 4 months before ESRD
• Patients referred late (< 4 months before
ESRD) had 72% greater mortality during
the first year of HD compared with patients
referred early (> 4 months before ESRD)
Stack AG, AJKD February 2003
Chronic Kidney Disease
summary
•
•
•
•
CKD- common final pathway
Stage using MDRD equation
Use spot urine protein:creatinine ratio
Goal is:
– Prevention
– Slow progression of disease
– Prevent and manage complications
• Control of proteinuria & blood pressure
– RAAS inhibition
• Early referral to nephrology





































![CKD talk[1].15.09 - Jacobi Medical Center](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003340080_1-9b582fb6e77d5fad41f81c427bfa5f30-150x150.png)