* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Flux - Physics
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
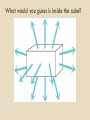
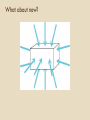
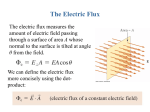
MAY THE FLUX BE WITH YOU Is that the finger??? Gauss’s Law 3.2 Happenings Wednesday – You should be finished with the Electric Field and today we start Gauss’s Law Friday – Yup, more Gauss and, oh yes, a QUIZ! Watch for a new WA on Gauss to appear suddenly. Monday … Gauss should be history so on to new stuff. (Sorry) What is the electric field at the center of the square array? A rigid electric dipole is free to move in the electric field represented in the figure.Which one of the following phrases most accurately describes the initial motion of the dipole if it is released from rest in the position shown? A) It moves to the left. B) It moves to the right. C) It does not move at all. D) It moves toward to the top of the page. E) It moves toward the bottom of the page. Consider the drawing, where the solid lines with arrows represent the electric field due to the charged object. An electron is placed at the point P and released at rest. Which of the following vectors represents the direction of the force, if any, on the electron? Gauss’s Law Let’s ask some questions of ourselves Given a distribution of charges can we figure out the Electric Field at a point in space? Yes … just add the effects of each charge (kq/d2) OK. How about the other direction – can we determine the distribution of charges if we know the Electric Field at a number of places. Sometimes. This is the topic that Gauss addressed and his answer, a mathematical theorem, is quite important in solving a certain class of problems. Last time We can use a vector to represent a small flat area: It’s length is proportional to the area. Its direction is perpendicular to the area The area need not be square, round or anything else. It must be small. Very small. Teeny Tiny small. There is an ambiguity in which of two ways the vector can point for a particular small area. What would you guess is inside the cube? What about now? How about this?? A. B. C. D. E. Positive point charge Negative point charge Large Sheet of charge No charge You can’t tell from this A Strange Statement An object entering a solid region is the same thing as a negative object leaving! Think about this….. Sphere Light Bulb Emitting N Photons per sec. Sphere Light Bulb Emitting N Photons per sec. Sphere Light Bulb Emitting N Photons per sec. This was a brief intro to Gauss’s Law. Now .. START YOUR UNITS (on G’s Law …)