* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Logan Basic Technique I
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
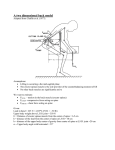
Logan Basic Technique I Study Guide Summer 2007 Midterm 1. Know the bones of the pelvis and spine, both child as well as adult. The pelvis of a child has 15 bones, adults have 4 2. Know the muscles of the spine, especially the posterior portion of the spine and spinal column, such as, all the divisions of the erector spinae, Iliocostalis Longissimus Spinalis **** LOOK IN BOOK AND NOTES TO STUDY THIS *** superficial muscles of the spine and their innervation. Knowledge of origins and insertions would be helpful. ***LOOK IN BOOK AND NOTES TO STUDY THIS*** 3. Know the IVD structure and function. Know how it receives nutrition. There are 23 IVD’s, 2 cm is lost from morning to night d/t gravity During standing, the water within the gelatinous matrix of the nucleus escapes into the vertebral body thru microscopic pores linking the casing of the nucleus and the spongy bone underlying the vertebral plateau. At night water is drawn into the nucleus and the disc regains its orginal thickness. If a constant load is applied then the loss of thickness is not linear but exponential suggesting a dehydration process proportional to the volume of the nucleus. The disc never recovers the initial thickness = AGING. This will cause joint disturbances and open athe interspace posteriorly which thes will cause osteoarthritis. Main retaining lig of spine 2 main parts: Nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus Thicker in front than in back in the lubar and cervical spines; same thickness in thorasic spine. 4. Know the significance of the following dates: a. 1916 – HB graduated from Universal b. 1927 – Vinton Logan graduates from Universal college c. 1931 – H.B. logan started teaching the logan basic tech. d. 1933 – 1st full spine x-ray 14x36 invented by warren sausser e. 1935 –Logan college was founded f. 1939 – First graduating class from logan school g. 1944 – HB died playing tennis h. 1949 – memorial here for HB. i. 1958 –Carver college merged with logan college j. 1961 – Vinton died k. 1973 – bought this campus for 1.8 mil, was a seminary l. 1979 – caggens dies and dr. mortar takes over for 8 mo m. 1981 n. 1982 – Montgomery clinic open o. 1988 – science building opened p. 1993 – george Goodman president q. 1995 r. 2004 – library was rebuilt s. 2007 – purser center was built 5. Know the ligaments of the pelvis and spine Sacrosciatic ligament is made of the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous lig. Interspinous line runs from PSIS to ASIS. LIG. OF THE SACROILIAC JT. 1.Ant. sacroiliac lig 2.Interossious sacroiliac lig.- main that holds ilium to sacrum 3. Posterior sacroiliac lig. – join S3-4 to the PSIS LIG ATTACHING SACRUM TO ISCHIUM 1. Sacrosciatic Lig. –Sacrotuberous lig (glut and biceps femoris attach, sometimes considered a muscle.) - Sacrospinous lig- sacrum and coccyx to spine of ischium. LIG OF PUBIC SYMPHYSIS 1.Superior pubic lig. 2. arcuate pubic lig. LIG OF THE LUMBOSACRAL JT. 1.Iliolumbar ligament – L4-5 to pelvis (lumbosacral lig is part of this) LIG OF LOWER SPINAL COLUMN TO PELVIS 1. Anterior longitudinal lig 2. post. Longitudinal lig 3. intervertebral disc 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. articular capsules ligamenta flava – thickest in lumbar, connects lamina supraspinous lig – causes tenderness, sp’s from C7- S1-2 tubercle Interspinous lig – runs between SP’s Intertranverse lig. 6. Know the 14 different physical findings that a patient can exhibit when he/she has suffered a sacral subluxation, both acute and chronic 7. Know the primary and secondary curves of the spine and of the body. Arch of foot – secondary Heel – Primary Knee – secondary Butt/Pelvic- primary, concave Lumbar – Secondary, compensatory Thoracic – Primary, concave Cervical – secondary, compensatory Head - primary 8. Know the gravity lines of the body. Normal spine: runs from the tip of the mastoid process through the front of the shoulder, greater trochanter, back of the patella, and about one inch anterior to the external malleolus. Normaly the line of weight likes posterior to the hip joints 9. What is the primary premise of Logan Basic Technique? The body of the lowest freely moveable vertebrae rotates towards the low side of the sacrum. 10. What is the size of the SI joint? 2 ¾ inches long (63-64mm), >1 inch (29mm) deep 11. What is the origin and insertion of the Biceps Femoris muscle? The long head of the biceps femoris attaches to the sacrotuberous ligament. Attaches to the ASIS along with the sarrtourious muscle 12. What is lumbopelvic rhythm? Rocking motion of ilium and sacrum during gait (forward leg would be PI PSIS with AI sacrum) 13. What is eccentric rotation? PSIS is posterior/ inferior during ambulation. Will be the shortened leg functionally. 14. What is concentric rotation? Anterior/ superior PSIS 15. What are the two main orthopedic tests to determine piriformis syndrome? Pace sign and Beatty sign 16. What is osteitis pubis? A disorder of the pubic symphysis characterized by pubic pain and joint disruption. It develops secondarily to inappropriate biomechanical forces 17. Describe the different Types of lumbarization/sacralization. 1A - 1 widened TP may form a jt, 1B – Both TPs 2A – 1TP forms a jt with the sacrum ; 2B – Both TPs 3A – 1 TP is fused on the sacrum ; 3B – both TPs 4 – Both 1 TP is fused and the other is a jt. ** only adjust a 1A/B, and a 2A (in prone) 18. What are the Joints of Von Luschka and where are they found? These are extra joints on the lateral aspect of the bodies. Aka uncinate or unciform processes, or uncovertebral joints. These are diarthrodial joints with synovial fluid. You can see these are white on x-rays after a sprain. 19. Describe a lumbar vertebra. 5 of them Height is greater anterior than post., no ribs attach. 20. Describe a thoracic vertebra Height is smaller ant, than post. Rib or ribs are attached to it. 12 of them 21. Describe a lower cervical vertebra These are typical vertebrae. C3-7. 22. Describe an upper cervical vertebra C1-C2. Atlas and axis. During rotation the atlas drops vertically 2-3 mm. these are atypical vertebrae. 23. Describe the iliopsoas muscle. 3 PARTS: Psoas major – from TP’s of lumbars – lesser trochanter of femur. Psoas minor – from side of T12 and IVD – pectin pubis and iliopectineal eminence Iliacus – from sup 2/3 of iliac fossa, crest, iliolumbar lig, and upper lateral sacrum to the lesser trochanter with some fibers into the femur. 24. Describe the Sartorius muscle Longest muscle in the body. From ASIS to the medial knee (pens anserine) 25. What is the superficial back line of fascia and describe its pathway. A fascia plane that starts at plantar toes and runs up with calcaneus,Achilles tendon, condyles of femur, HS, Ischial tuberosity, Sacrotuberous ligament, sacrum, sacrolumbar fascia/erector spinae, occipital ridge, galia aponeurotica/scalp fascia, and frontal brow ridge. 26. What is the most common wedged vertebra? L5 27.Describe ankylosis. Ligaments being reinforced to prevent or decrease vertebral rotation. Can be slight to complex. Fixation can progress from affecting the muscles to affecting the length of ligaments to eventually deposition of calcium in the ligaments and adjacent muscles. It obstructs normal restoration of the spine by holding the vertebrae in their distorted position. If normalized where the need for calcium in ligaments and muscles are no longer required, the body can withdraw it. 28Who are/were the presidents of Logan College and when did they serve? 1935-1944 Hugh B. Logan 44-61 Vinton Logan 61- 79 William Caggens 1979 Morter for 8 mo 1980 -1992 Haggen 1993- George Goodman 29Where are the ashes of H.B. and Vinton Logan? 30Who was the Science Building originally named for? Robert Price 31Who is the new auditorium/lecture hall named for? Purcer 32Who is the Wellness Center named for? William Harris 33Who is the administration building named for? 34What was the name of the old large classroom/clinic/men’s dormitory on the Normandy campus. Keystone hall 35What was trailer town and who lived there? It was student housing for logan’s 2 campus. The students and staff lived there. 36What was the name of the organization formed to promote Logan Basic Technique and encouraged H.B. Logan to found Logan College? Universal health basic technique