* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Resources: Books
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
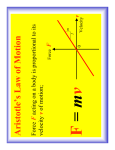
Exercises on Forces Newton’s laws of motion Law 1: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Law 2: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Law 3: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Demonstrate Experiment Title: To demonstrate Newton’s laws of motion Diagram: Method: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Results: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Calculations: Conclusion _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Errors _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers From the second law it is stated that a ____________________ is proportional to the change in a body’s _________________. Derivation of f = ma Line one: For a body of mass m, changing from a velocity v to one of u: From Newton’s second law As this is the formula used to define the unit of force, the Newton, a value of 1 can be given to k. A force is anything which causes or tends to cause an ________________________. F = ma The momentum of a body is the product of a body’s __________ and ____________. P = mv STS Newton’s first law: In the absence of air a spacecraft travelling in space will do so without engines until a force is applied to stop it. An apple falling from an apple tree will continue to fall until ____________________________________________. Newton’s second law: Is seen in the use of seat belts. When a person is thrown forward the belt expands slightly. This extends the time over which the person is slowing down. This decreases the _____________________ and with it reduces the ____________ on the person. Newton’s third law: With rockets the large force created towards the rear of the rockets creates an ____________, but _____________, __________ force causing the rocket to move _____________. Friction is a force which tends to oppose ______________. It occurs when a body slides or tries to slide along another. It occurs in all states of matter. It is both beneficial and problematic: e.g. S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers Questions S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers Conservation of momentum The conservation of momentum states that _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ The momentum of a body is the product of a body’s __________ and ____________. P = mv STS The above law applies to situations which involve collisions. It applies in situations such as the take off of a rocket. Before take off, the total momentum is ________. Afterwards the momentum of the rocket ________________ is matched by the momentum of the ________________________________. It does not apply to systems that are not closed e.g. tennis where some momentum is absorbed by the player’s arms. S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers Questions S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers Moments The moment of a force about an _________ is equal to the magnitude of the ______________ multiplied by the perpendicular _____________ from the axis to the line of action of the force. Formulae: _________________________ Unit: _________________________ It is a ______________________ quantity. The moment of a force tells us about its ability to make something _____________. e.g. when we use a door, the handle is as far from the hinges as is reasonable. Therefore if you apply a small force a large distance from the fulcrum (the turning point) it results in a large moment or turning effect. A lever is a rigid body which is free to ___________ about a fixed point. A crow bar is an example of a lever that makes maximum use of a force to move a heavy body. Diagram A couple is created by two parallel forces with the same magnitude acting in opposite directions. An obvious example is in the handlebars of a bike. One hand moves forward, the other back, and the couple created turns the handlebar, and with it the bike. Diagram In a simple d.c. electric motor and in a moving coil galvanometer a pair of parallel forces on a coil of wire exert a couple on the coil, resulting in the coil rotating. S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers Conditions for equilibrium 1. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Consider the below metre stick in equilibrium. As the stick is in equilibrium we know that the total ____________ must equal the ________________________. Find W, the weight of the stick. Show that the sum of the moments about any point is zero. 1. about 0 cm 2. about 50 cm S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers Questions Density and pressure The density of an object is its mass per unit volume. Formulae: __________________________________ Unit: __________________________________ Symbol: __________________ rho It is a ______________________ quantity. Pressure is defined as forces per unit area. Formulae: __________________________________ Unit: __________________________________ Symbol: __________________________________ It is a ______________________ quantity. S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers It can be proved that the pressure due to a liquid at a depth h in a liquid of density ρ where acceleration due to gravity g, the pressure P due to the liquid is given by: Demonstration of atmospheric pressure: Heat a can with air in it and then seal it. As it cools the walls are drawn in. Why? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ STS The Bends: As divers move down through water the pressure _____________. This _________________ is sufficient to ‘push’ more nitrogen into the blood stream where it is dissolved. AS the diver rises and the pressure _______________ this nitrogen will pass back out of the blood as small bubbles which can cause great damage as they pass through the brain. Boyle’s law states that at _________________ temperature the pressure on a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its volume i.e. This law is seen in effect in a bicycle pump. How? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Archmedes' principle states that a body immersed in a fluid will experience an upthrust equal to the weight of fluid that it has displaced. S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers The law of flotation states that when a body floats, it is displacing exactly its own weight if fluid. The objects float as the upthrust it experiences is equal to its weight. If the two forces were not equal the object would either ______________ or __________________. Diagram STS Archimedes’ Principle underlies the use of hydrometers. These are devices for measuring the density of liquids. In a dense liquid, the hydrometer can displace its own weight by displacing only a small quantity of liquid. In a less dense liquid, it must sink deeper in order to displace the same weight. S.C. PDST: The Professional Development Service for Teachers