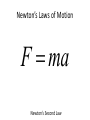* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introductory Physics
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
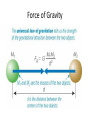
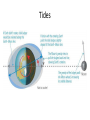
Introductory Physics How we describe motion • Speed – how fast something is moving • Velocity – speed and direction • Acceleration – change in velocity • Acceleration of Gravity – 9.8 m/s2 How we describe motion • Momentum – an object’s mass X velocity • Mass – amount of matter • Force – required to change on object’s momentum • Weight – force measured by a scale, mass X gravity’s accel. Newton’s Laws of Motion Newton’s First Law Newton’s Laws of Motion Newton’s Second Law Newton’s Laws of Motion F ma Newton’s Second Law Newton’s Laws of Motion Newton’s Third Law Angular Momentum • Similar to momentum, but moving in a circle • L=mXvXr • Angular momentum is conserved ENERGY Types of Energy • Kinetic Energy – involves motion • Radiative Energy – involves light • Potential Energy – might later be converted to other forms of energy Thermal Energy Potential Energy Gravitational Potential Conservation Laws • Conservation of momentum • Conservation of angular momentum • Conservation of energy Force of Gravity Newton’s Law vs. Kepler’s Law Newton’s Law vs. Kepler’s Law Newton’s Law Kepler’s Law M 1M 2 Fg G 2 d p ka 2 Newton’s Kepler’s Law 4 3 p a G M 1 M 2 2 2 3 Gravity, Energy and Orbits Orbital Energy Gravity, Energy and Orbits Gravitational Encounter Gravity, Energy and Orbits Escape Velocity Tides Spring Tides Neap Tides Tides