* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download to view the slides
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
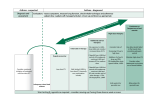
Break out session: Estimands in practice Mouna Akacha (Novartis) and Julia Saperia (MHRA) PSI Conference 2017 – London May 16th 2017 Aim Gain familiarity in deciding on estimands and apply structured framework in different clinical trial settings • Chronic pain • Asthma • Cancer-related wasting syndrome 2 Estimands A. Population Subjects targeted by the scientific question C. Intervention effect of interest How potential intercurrent events are reflected in the scientific question B. Variable Quantities required to address the scientific D. question Summary measure On which the treatment comparison will be based 3 A lot of this boils down to... How do we account for intercurrent events that themselves are informative about the effects of treatment? • E.g. study treatment discontinuation due to AE or LoE, intake of rescue or concomitant medication, inevaluable tumor assessment, switch to new antineoplastic therapy (ANP), death etc. Treatment discontinuation due to lack of efficacy Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 ? Patient 7 Randomisation 4 Rescue medication Death Patient 5 Patient 6 Treatment complete Study discontinuation Rescue medication TIMELINE Treatment discontinuation due to adverse events Study discontinuation ? Primary endpoint Some estimand approaches Treatment-Policy: Consider the variable regardless of whether the intercurrent event has occurred Composite: Define the intercurrent event as a component of a composite variable Hypothetical: Consider a given hypothetical outcome associated with the intercurrent event Principal Stratum: Focus on the stratum of patients in which an intercurrent event would not occur While-on-treatment: Consider the variable up to the time of the intercurrent event 5 Structured framework to bridge trial objectives with statistical inference Trial Objective Estimand (informing the trial design) 6 Main Estimator Sensitivity Estimator 1 ... Sensitivity Estimator 𝒌 Main Estimate Sensitivity Estimate 1 ... Sensitivity Estimate 𝒌 Case studies For these case studies • each table will focus on one case study and discuss the choice of estimands for licensing purposes (~ 50 minutes) • Justify your choice and if time allows discuss main and sensitivity estimators • choices of estimands and estimators will be shared and discussed in the last 30 minutes • Group’s responsibility to identify a person to feed back Note: For the case studies we assume a certain design is given – with the new framework the estimand choice should drive/inform design choice. 7 Case study 1 – Chronic pain Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study Compare a Drug X versus Placebo (on top of stable standard of care) in the treatment of chronic pain Measurement of clinical interest: Change from baseline in pain score at week 12 Week 12 Placebo Drug X • • • 8 May take prohibited medication or rescue medication in periods where pain is not well controlled – patients are followed up regardless May change stable SoC doses May discontinue study or treatment for various reasons, e.g. AEs and lack of efficacy Case study 2 – Asthma Randomised, double-blind, active-controlled phase III study Inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) + long-acting beta agonist (LABA) + long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) vs ICS + LABA • ICS + LABA + LAMA vs ICS + LABA • both are fixed dose combination products Measurement of clinical interest: Change from baseline in lung function at week 24 Week 24 ICS + LABA ICS + LABA + LAMA • • • 9 Unbalanced treatment discontinuations expected – more in ICS + LABA arm Alternative medication is given after stopping of randomised treatment Randomised treatment must stop and rescue given if severe exacerbation occurs Case study 3 – Cancer-related wasting syndrome Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study Compare Drug X against placebo for weight gain in late-stage cancer Measurement of clinical interest: Change from baseline in body weight at week 12 Week 12 Placebo Drug X • • 10 Some patients die before the end of 12 weeks Death may or may not be related to wasting syndrome What would be appropriate estimands? Note: Should you require more information on the specific settings to decide on the estimand then • Write down the information needed • Consider different scenarios related to this additional information • Decide on estimands in the different scenarios Moderators will help you 11 Moderators 12 Mouna Akacha Julie Anderson Anna Berglind Robert Cuffe Christine Fletcher Lisa LaVange Michael O’Kelly Alan Phillips James Roger Kaspar Rufibach Julia Saperia David Wright - Novartis - GSK - AstraZeneca - GSK - Amgen - FDA - Quintiles - ICON - LSHTM - Roche - MHRA - AstraZeneca Additional considerations What if the comparator was standard of care instead of placebo? Would you change your mind if your main focus was the patient’s or physician’s perspective? If you could, would you change anything in the design? What if we were interested in non-inferiority instead of superiority? 13