* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download External Environment
Competitive intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Resource-based view wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
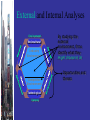
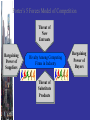
External and Internal Analyses Environment Sociocultural Industry Environment Competitor Environment Technological General By studying the external environment, firms identify what they might choose to do Opportunities and threats External and Internal Analyses General Environment Components Demographic Segment Population size Age structure Ethnic Mix Geographical Distribution Income distribution Immigration Sociocultural Segment Women in the workforce Workforce diversity Environmental Concerns Work life quality attitudes Concerns about the environment Shifts in 2 career preferences Shifts in preferences regarding product / service characteristics Political/Legal Segment Competition Laws Labour Laws Taxation laws Education philosophies & policy Government econ. involvement / ownership Philosophies De-/ Regulation philosophy General Environment Components Economic Segment Inflation & interest rates Personal savings rate Business savings rates Technological Product innovations Segment Process Innovations Applications of knowledge Global Segment Important political events Critical global markets Trade deficits or surpluses Budget deficits or surpluses Gross domestic product Focus of private & governmentsupported R&D expenditures New communication technologies Newly industrialized countries Different cultural and institutional attributes The Industry Environment The set of factors that directly influences a firm, it’s competitive actions & competitive responses: 1. The threat of new entrants 2. The power of suppliers 3. The power of buyers 4. The threat of product substitutes 5. The intensity of rivalry among competitors Competitor Analysis Predicting the dynamics of competitor actions, responses and intentions. Macro-environmental Forces External Environmental Analysis The external environmental analysis process should be conducted on a continuous basis. This process includes four activities: Scanning Monitoring Identifying early signals of environmental changes and trends Detect meaning by ongoing observations of environmental changes and trends Forecasting Assessing Developing projections of anticipated outcomes based on monitored changes and trends Determining the timing & importance of environmental changes and trends for firms' strategies & their management External Environmental Analysis The external environmental analysis process should be conducted on a continuous basis. This process includes four activities: Scanning Identifying early signals of environmental changes and trends Monitoring Detect meaning by ongoing observations of environmental changes and trend Forecasting Developing projections of anticipated outcomes based on monitored changes and trends Assessing Determining the timing & importance of environmental changes and trends for firms' strategies & their management Porter’s 5 Forces Model of Competition Threat of Threat of New New Entrants Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Rivalry Among Competing Firms in Industry Threat of Substitute Products Bargaining Power of Buyers Threat of New Entrants * Barriers Barriers Entry to to Entry * * * * Economies of Scale * Product Differentiation * Capital Requirements * Switching Costs Access to Distribution Channels Cost Disadvantages Independent of Scale Government Policy Expected Retaliation Bargaining Power of Suppliers Suppliers are likely to be powerful if: Suppliers exert power in the industry by: Supplier industry is dominated by a few firms. * Suppliers’ products have few substitutes. * * Threatening to raise * Buyer is not an important customer to prices or to reduce quality Powerful suppliers can squeeze industry profitability if firms are unable to recover cost increases * * supplier. * Suppliers’ product is an important input to buyers’ product. Suppliers’ products are differentiated. Suppliers’ products have high switching costs. Supplier poses credible threat of forward integration. * Bargaining Power of Buyers Buyer groups are likely to be powerful if: Buyers are concentrated or purchases are large relative to seller’s sales Purchase accounts for a significant fraction of supplier’s sales Products are undifferentiated Buyers face few switching costs Buyers’ industry earns low profits Buyer presents a credible threat of backward integration Product unimportant to quality Buyer has full information Buyers compete with supplying industry by: Bargaining down prices Forcing higher quality Playing firms off each other Threat of Substitute Products Keys to evaluating substitute products: * Products with similar function limit the prices firms can charge Products with improving price / performance tradeoffs relative to present industry products For Example: Electronic security systems in place of security guards Fax machines or e-mailed attachments in place of overnight mail delivery Rivalry Among Existing Competitors Intense rivalry often plays out in the following ways Jockeying for strategic position Using price competition Staging advertising battles Increasing consumer warranties or service Making new product introductions Occurs when a firm is pressured or sees an opportunity Price competition often leaves entire industry worse off Advertising battles may increase total industry demand, but may be costly to smaller competitors Rivalry Among Existing Competitors Cutthroat competition is more likely to occur when Numerous or equally balanced competitors Slow growth industry High fixed costs High storage costs Lack of differentiation or switching costs Capacity added in large increments Diverse competitors High strategic stakes High exit barriers Rivalry Among Existing Competitors High Exit Barriers are economic, strategic and emotional factors which cause companies to remain in an industry even when future profitability is questionable. Specialized assets Fixed cost of exit (e.g., labour agreements) Strategic interrelationships Emotional barriers Government and social restrictions Competitor Environment Competitor intelligence is the ethical gathering of needed information and data about competitors’ objectives, strategies, assumptions, and capabilities. • What drives the competitor as shown by its future objectives, • What the competitor is doing and can do as revealed by its current strategy, • What the competitor believes about itself and the industry, as shown by its assumptions, • What the the competitor may be able to do, as shown by its capabilities. Competitor Analysis Future Objectives: Future objectives • How do our goals compare with our competitors’ goals? • Where will the emphasis be placed in the future? • What is the attitude toward risk? Competitor Analysis Current Strategy: Future objectives Current strategy • How are we currently competing? • Does this strategy support changes in the competitive structure? Competitor Analysis Assumptions: Future objectives Current strategy Assumptions • Do we assume the future will be volatile? • Are we operating under a status quo? • What assumptions do our competitors hold about the industry and themselves? Competitor Analysis Future objectives Current strategy Assumptions Capabilities Capabilities: • What are our strengths and weaknesses? • How do we rate compared to our competitors? Competitor Analysis Future objectives Response Response: Current strategy • What will our competitors do in the future? Assumptions • Where do we hold an advantage over our competitors? Capabilities • How will this change our relationship with our competitors?