* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CORE Assignment unit 3 Probability
Indeterminism wikipedia , lookup
Probabilistic context-free grammar wikipedia , lookup
History of randomness wikipedia , lookup
Random variable wikipedia , lookup
Dempster–Shafer theory wikipedia , lookup
Infinite monkey theorem wikipedia , lookup
Probability box wikipedia , lookup
Boy or Girl paradox wikipedia , lookup
Birthday problem wikipedia , lookup
Inductive probability wikipedia , lookup
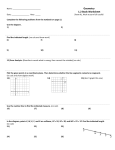
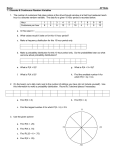
Name: Sha Tin College Mathematics Department Key Stage 4 CORE Level Course Unit 3 Assignment: Probability Total / 52 A: Probability and Relative Frequency #1(no calc) Jeremy, Michelle, Amanda, Chris and Elly are playing a game in which there are three prizes. No player can win more than one prize. What is the probability that Jeremy does not win a prize? Answer [2] #2(no calc)Seventy five tickets are put into a bag. The tickets are numbered from 1 to 75. All those ending in a 9 win a prize. Teresa takes out the first ticket. What is the probability that it is a prize winning ticket? Answer [2] #3(no calc) Sian has three cards, two of them black and one red. She places them side by side, in random order, on a table. One possible arrangement is Red, Black, Black. (a) (b) Write down the other possible arrangements. Answer (a) [1] Find the probability that the two black cards are next to each other. Give your answer as a fraction. Answer (b) [1] Sha Tin College Mathematics Department KS 4 CORE ASSIGNMENT Probability 1 #4 (no calc) A (a) A C U S Margaret chooses a card at random from the six cards shown in the diagram. What is the probability that the card is (i) (ii) (iii) (b) B an A, Answer (a)(i) [1] Answer (a)(ii) [1] Answer (a)(iii) [1] an A or a U, an E? From the six cards, the B is removed. Paul chooses a card at random from the five remaining cards. What is the probability that the card is an A? Answer (b) [1] #5 (no calc) Tony throws a biased dice 100 times. The table shows his results. Score Frequency 1 12 2 13 3 17 4 10 5 18 6 30 He throws the dice once more. (a) Find an estimate for the probability that he will get a 6. ..................................... (1) Sha Tin College Mathematics Department KS 4 CORE ASSIGNMENT Probability 2 #6 (no calc) Here is a fair 4-sided spinner. 4 2 6 8 The spinner has four sections numbered 2, 4, 6 and 8. The spinner is to be spun. It will land on one of the sections. On the probability scale below mark, with a letter, the probability that the spinner will land (iii) (i) on 2 (use the letter A), (ii) on an odd number (use the letter B), on a number greater than 3 (use the letter C). 0 1 2 1 (Total 3 marks) Total for Section A /14 B: Tree Diagrams and Two-way Tables #1.(no calc) Julie does a statistical experiment. She throws a dice 600 times. She scores six 200 times. (a) Is the dice fair? Explain your answer. ............................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................. (1) Sha Tin College Mathematics Department KS 4 CORE ASSIGNMENT Probability 3 Julie then throws a fair red dice once and a fair blue dice once. (b) Complete the probability tree diagram to show the outcomes. Label clearly the branches of the probability tree diagram. The probability tree diagram has been started in the space below. Red Dice 1 6 Blue Dice Six Not Six (3) (Total 4 marks) _________________________________________________________________________ #2 (no calcs) Julie and Pat are going to the cinema. The probability that Julie will arrive late is 0.2 The probability that Pat will arrive late is 0.6 The two events are independent. (a) Complete the diagram. Pat 0.6 Julie late late 0.2 not late late not late not late (2) Sha Tin College Mathematics Department KS 4 CORE ASSIGNMENT Probability 4 (b) Work out the probability that Julie and Pat will both arrive late. …………………………… (2) (Total 4 marks) #3(calc) 80 Year 12 students each study one Science. The table shows some information about these students. Biology Female Chemistry Physics 18 47 19 Male 21 Total (a) Total 33 80 Complete the table. (3) One of these students is picked at random. (b) Write down the probability that the student studies Physics. ………………. (1) (Total 4 marks) #4 (calc) 60 British students each visited one foreign country last week. The two-way table shows some information about these students. France Germany Female Male Total 9 34 18 60 15 Total (a) Spain 25 Complete the two-way table. (3) One of these students is picked at random. (b) Write down the probability that the student visited Germany last week. .......................... (1) (Total 4 marks) Total for Section B /16 Sha Tin College Mathematics Department KS 4 CORE ASSIGNMENT Probability 5 C: Finding Expected Value #1 ( calc) The probability that a biased dice will land on a four is 0.2 Pam is going to roll the dice 200 times. (a) Work out an estimate for the number of times the dice will land on a four. ......................... (2) Emma has a biased coin. The probability that the biased coin will land on a head is 0.7 Emma is going to throw the coin 250 times. (b) Work out an estimate for the number of times the coin will land on a head. ..................................... (2) _________________________________________________________________________ #2 (calc) The probability of winning a game of cards is 0.2. Pam is going to play the game 10 times. (a) Work out an estimate for the number of times she will win. ......................... (2) Pam wins 6 times. (b) Calculate how many games she played. ......................... (2) Total for Section C /8 Sha Tin College Mathematics Department KS 4 CORE ASSIGNMENT Probability 6 D: Solving Probability Problems using Venn Diagrams #1. (calc) If event A and event B are mutually exclusive and P(A) = 0.3 and P(B) = 0.5 what is the probability of A or B happening? ……………. (2) #2. (no calc) Draw a Venn Diagram to illustrate the idea of mutually exclusive covered in question 1. ……………. (2) _______________________________________________________________________ #3 (calc)If event A and event B are independent and P(A) = 0.3 and P(B) = 0.5 what is the probability of A and B happening? ……………. (2) #4 (calc) In a race the probability that John wins is 1/3, the probability that Paul wins is ¼ and the probability that Mark wins is1/5. Assuming that there are no dead heats; Find the probability that: a) John or Mark wins ……………. (2) b) neither John nor Paul wins. ……………. (2) Sha Tin College Mathematics Department KS 4 CORE ASSIGNMENT Probability 7 #5 (calc) The probability that a girl likes oranges is 0.8. The probability that she likes bananas is 0.3. The probability that she likes neither is 0.1. (a) Draw a Venn Diagram to illustrate this situation [3] (b) Calculate the probability that a girl likes both oranges and bananas. [1] Total for Section D /14 TICK HERE CAN DO STATEMENTS Investigating- being systematic, drawing pictures, looking for patterns, generalizing. RECAP Probability is a measure of chance ranging between 0 and 1 RECAP Calculate the Probability P(A) as a fraction, decimal or percentage. Understand the significance of its value. RECAP Understand and be able to calculate relative frequencies as an estimate of probability. RECAP List sample spaces and outcomes by using two-way tables and tree diagrams, with replacement. Simple cases only. Theory of Knowledge – applying mathematical skills to solving a real life problem. Probability simulation NEW Use tree diagrams to calculate probabilities with non-equallylikely events, with replacement. Simple cases only. NEW Use tree diagrams including successive selection without replacement. Simple cases only. Investigating- being systematic, looking for patterns, generalizing. NEW Find expected values from probabilities. NEW Finding probabilities with the use of Venn Diagrams NEW Understand the meaning of Mutually Exclusive. Combine mutually exclusive events. NEW Understand the meaning of Independent. Combine independent events. Sha Tin College Mathematics Department KS 4 CORE ASSIGNMENT Probability 8