* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Problems Of The Upper GI Tract
Survey
Document related concepts
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
Surgical management of fecal incontinence wikipedia , lookup
Colonoscopy wikipedia , lookup
Gastrointestinal tract wikipedia , lookup
Adjustable gastric band wikipedia , lookup
Esophageal cancer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
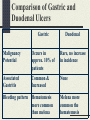
Problems of the Upper GI Tract Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Hiatal hernia Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) Upper GI Bleeding GERD Definition & Predisposing Factors Characterized by a reflux of gastric secretions into the esophagus causing esophagitis, dysphagia, & aspiration Predisposing conditions include: hiatal hernia, incompetent lower esophageal sphincter (LES), & decreased esophageal clearance and gastric emptying. Gerd Con’t signs/symptoms Pyrosis Regurgitation Dysphagia Bronchospasm/laryngospasm GERD Con’t Diagnosis & treatment Diagnosis Barium swallow Esophagoscopy esophageal motility studies Treatment: Preventative measures Pharmacologic management(antacids, motility agents, & H2 blockers) Surgical intervention prn Hiatal Hernia Definition & Predisposing Factors Herniation of a portion of the stomach into the esophagus (aka diaphragmatic & esophageal hernia). Predisposing factors include: intrabdominal pressure, increased age, trauma, congenital weakness & a forced recumbent position Classified into 2 types Sliding Rolling Hiatal Hernia con’t S/S, DX ,& RX Sign and symptoms Similar to those for GERD Frequently asymptomatic Diagnosis Similar to those for GERD Treatment Similar to those for GERD Surgical interventions: valvuloplasty or antireflux procedures PUD Definition, Incidence, & Classification Erosion of the GI mucosa r/t the digestive action of HCL & pepsin Approximately 10% of men & 4% of women in the U.S. will have duodenal ulcers in their lifetime. Classified as: Acute or chronic gastric or duodenal PUD Con’t Sign and Symptoms & Diagnosis Sign and Symptoms: Pain Diagnosis: Endoscopy with cultures Upper GI barium contrast studies Serum and stool studies PUD Con’t Treatment Rest and stress reduction Nutritional management Pharmacological management NG suction Surgical intervention Bilroth 1 & 11 Vagotomy & pyloroplasty Upper GI Bleeding Definition, Predisposing Factors, & Classification Massive upper GI hemorrhage defined as > 1500 ml blood loss or 25% intravascular blood volume loss. Predisposing factors include: drugs, esophageal varices/esophagitis, PUD/stress ulcer/ gastritis. & carcinoma. Classified as: Bleeding: venous, capillary, or arterial Origin: esophageal or stomach/duodenal Upper GI Bleeding Con’t Signs / Symptoms & Diagnosis Anemia & weakness r/t bleeding (obvious or occult) Diagnosis: Patient history Serum/ stool/ vomitus studies Endoscopy Angiography Barium contrast studies Upper GI Bleeding Con’t Treatments Supportive therapies Pharmacologic management Gastric lavage/Sengstaken-Blakemore tube Sclerotheraphy Cautery Surgical intervention Comparison of Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers Gastric Lesion Duodenal Superficial with smooth margins; round, oval or coneshaped Predominantly antrum, also in body & fundus of stomach Penetrating Gastric Secretion Normal to decreased Increased Incidence Greater in women Greater in men Peak age 50-60 yo Peak age 35-45 yo Location of lesion First 1-2 cm of duodenum Comparison of Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers Gastric Duodenal Malignancy Potential Occurs in approx. 10% of patients Rare, no increase in incidence Associated Gastritis Common & Increased None Bleeding pattern Hematemesis more common then melena Melena more common the hematemesis Problems of the Lower GI Tract Peritonitis Inflammatory Bowel Disease(IBD) Intestinal Obstruction Diverticulitis Peritonitis Definition Inflammation of the peritoneum causing varying degrees of pain depending on the extent of the inflammatory process. Peritonitis Signs & Symptoms Pain, front, back, sides, shoulders Electrolytes fall, shock ensues Rigidity or rebound of anterior abdominal wall Immobile abdomen and patient Tenderness with involuntary guarding Obstruction Nausea and vomiting Increasing pulse, decreasing blood pressure Temperature falls then rises;tachycardia Increasing abdominal girth Silent abdomen (no bowel sounds) Peritonitis Con’t Diagnosis and Treatment Diagnosis Patient history CBC with differential KUB (abdominal x-ray) Barium enema Colonoscopy Treatment Supportive therapies Pharmacological management NPO/NG tube Surgical intervention prn IBD Definition,Causes, Classification Characterized by chronic, recurrent inflammation of the intestinal tract Possible causes include: infectious agent,an autoimmune reaction,& heridity Classified as: Ulcerative colitis Crohn’s Disease IBD Con’t Diagnosis and Treatment Diagnosis Colonoscopy & sigmoidoscopy (with biopsy) Barium enema Serum and stool studies Treatment Pharmacological management Nutritional management NPO/NG tube Surgical intervention Intestinal Obstruction Definition & Classification Occurs when intestinal contents cannot pass through the GI tract Classified as: Partial or complete Mechanical or nonmechanical Intestinal Obstruction Con’t Diagnosis and Treatment Serum and stool studies KUB Barium enema Sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy Treatment placement of NG or intestinal Tubes Correction of fluid & electrolyte imbalance Surgical Intervention