* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sampling - samratsrivastava2016
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
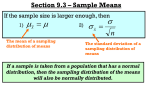
Sampling CHAPTER 5 Meaning Selection of some part of an aggregate or total on the basis of which a judgment about the aggregate or total is made Process of obtaining information about an entire population by examining only a part of it SAMPLING……. STUDY POPULATION SAMPLE TARGET POPULATION Essentials or characteristics of a good sample Representativeness Sample must be representative of the entire population Accuracy Must result in very small error Economy Viable in the context of funds available Size Factors affecting Sample size Nature of Universe Whether universe is homogenous or heterogeneous Dispersion factor Size of Population Nature of study For intensive and continuous studies, small size is appropriate Type of Sampling With random sample, small size also may be allowed Standard of Accuracy and acceptable confidence level Availability of finance Sampling Methods Probability Sampling Non Probability Sampling Probability Sampling Each unit should have a known chance of being selected in the population Simple Random Sampling Systematic Sampling Stratified Sampling Cluster Sampling Simple Random Sampling Applicable when population is small, homogeneous & readily available. Each element has an equal probability of selection. A table of random numbers or computer generated random numbers can be used. Method impractical with large samples Systematic Sampling An alternative to random sampling Selection of first unit is on random basis Remaining units selected at fixed intervals Steps Number of units in the population-N Sample size –n Interval size –k =N/n Select the first unit randomly Select every kth unit Stratified Sampling Involves dividing the population into homogenous sub groups and then taking simple random sample in each subgroup Stratification improves sample’s representativeness Cluster Sampling Divide the population into a number of non- overlapping areas (clusters) Randomly select a number of these clusters Measure all units within selected clusters Two types Area Sampling- Clusters happen to be geographic subdivisions Multi stage Sampling-Clusters formed at in different stages, applicable to inquiries extending to large geographical areas Non Probability Sampling Methods Method does not adopt any basis for estimating the probability that each item in the population has to be included in the sample Methods Convenience Sampling Purposive or Judgment Sampling Quota Sampling Snowball Sampling Convenience Sampling Sometimes known as grab or opportunity sampling or accidental or haphazard sampling Sample drawn from that part of the population which is close to hand Most useful for pilot testing Purposive or Judgment Sampling Deliberate selection of sample units that conform to some pre determined criteria Selection of those samples that are considered most appropriate ones for the study Based on the judgment of the researcher Quota Sampling Selecting people non randomly based on some fixed quota Two types Proportional Non proportional Not aimed at precision but need results quickly Snowball Sampling Identify those who meet the criteria of study Ask them to recommend others who meet the criteria Method suitable when population is difficult to find