* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood Types - MrsSconyersAnatomy
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
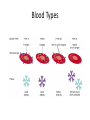
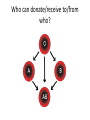
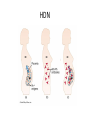
Blood Types Ch. 19-2 Blood Types • Blood cells have surface markers called antigens • ABO Blood Group – RBC with A antigens – A blood type – RBC with B antigens – B blood type – RBC with A and B antigens – AB blood type – RBC with no antigens – O blood type Blood Types • Blood plasma contains proteins called antibodies • Antibodies will react with antigens if mixed – Type A blood – A antigens, anti-B antibodies – Type B blood – B antigens, anti-A antibodies – Type AB blood – A and B antigens, no antibodies – Type O blood – no antigens, anti-A and anti-B antibodies Blood Types Transfusions • Transfusion – transfer of whole blood or blood components (RBC or plasma) • Agglutination – clumping of RBCs, hemolysis occurs, kidney damage and death can result – This only causes problems between recipient antibodies and donor antigens – Donor antibodies become diluted in blood plasma • Example – – – – (recipient) A person receives blood from (donor) B person Recipients blood contains anti-B antibodies Donor’s blood contains B antigens Antigen/antibody complex forms Who can donate/receive to/from who? Rh Blood Group • Antigen was discovered in the rhesus monkey • Rh+ people have the Rh antigen, Rh- people do not have the Rh antigen • People do not naturally have anti-Rh antibodies • If Rh- person receives blood from Rh+ person, immune system will make anti-Rh antibodies • If they receive Rh+ blood again, the anti-Rh antibodies will cause agglutination Who can donate/receive to/from who? • • • • • + should not be given to – + can receive + or – - can give to + or – Universal donor – OUniversal recipient – AB+ Hemolytic Disease of Newborn (HDN) • Fetal blood can cross placenta into maternal blood stream • If baby is Rh+ and mother is Rh-, mother’s immune system starts making anti-Rh antibodies • During the next pregnancy the antibodies can cross into the fetal blood • If the second fetus is Rh+, agglutination can occur HDN Review of Inheritance • Blood type Punnett squares • Rh Punnett squares – Rh+ is dominant to Rh– Rh+ could have Rh+/Rh+ – Rh + could have Rh+/Rh– Rh- must be Rh-/Rh-