* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (MSWindows, LINUX, UNIX) (China)
Windows Phone 8.1 wikipedia , lookup
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
MTS system architecture wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Windows NT startup process wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
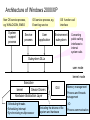
Overview of PC Operating System LI Xiang Telecommunication Division, NMC, China E-mail: [email protected] 1 An operating system is the software that provides the interface between the hardware of a computer system and the applications programs that are used on it. 2 1. Introduction to Windows Windows is a series of operating systems developed by Microsoft. Object oriented and easy-to-use Graphical User Interface (GUI) Multitasking Operating systems Multiprocessing allowing multiple processors to be utilized. Multithreading allowing multiple software processes to be run at the same time. allowing different parts of a software program to run concurrently. Abundant in development tools and applications Visual Basic, Visual C, Visual FoxPro, Delphi, Power Builder, ……. Microsoft Office, Microsoft Visio, Internet Explorer,…… 3 MS Windows kernal • Windows 9X kernal • Windows 3.X/95/98/ME • In 2001, Microsoft announced ceasing the development of Windows 9X kernal. • Windows NT kernal • Windows NT/2000/XP 4 Architecture of Windows 2000/XP Non OS service process, eg. WINLOGON, SMSS System support process OS service process, eg. Event log service Service process User application OS function call interface Environment subsystem Converting public calling interfaces to internal system calls Subsystem DLLs user mode kernel mode Executive kernel Device Drivers GUI Hardware Abstraction Layer Scheduling threads • Scheduling interrupt • Synchronizing multiprocessor -Memory management -Process and threads management - I/O • Including the drivers of file system and hardware -Process communication Major components of Windows Windows Desktop Control pannel Icons, Start Button, Taskbar Configuration and management hardware Configuration and management system resources Install and uninstall application software File manager Files and folders program files: executable data files: not executable and associated with a specific program or file format file naming a file name can contain up to 255 characters including letters, numbers, spaces and some other printable characters. a file name can’t contain the following characters: /\:*?"<>| Tasks manager Displaying the status of processes current running on system Stopping a process Network Supporting NetBEUI, TCP/IP, IPX, …… Providing the network application programs and tools, such as ftp, telnet, ping, tracert, netstat,…… Allowing sharing disks, files and printers among MS Windows machines. 6 2. Introduction to Unix Developed at Bell Laboratories in 1969. Written with the high-level programming language C. Initially designed for medium-sized minicomputers, and then moved to mainframe computers and personal computers. For different hardware platforms, there are many different Unix versions. AIX, Digital Unix, Hp Unix, …… Sco Unix, which is a PC-based Unix operating system 7 Features of Unix Mature and stable operating system Graphical User Interface operating system Multitasking capability Multiprocessing Multithreading Multiuser capability System portability allowing multiple users to utilize the computer and run programs at the same time. Capable of moving from one brand of computer to another with a minimum of code changes . The operating system could be upgraded without having all the user's data inputted again. Containing many tools and applications 8 Unix functionally organized at three levels offering additional functionality to the operating system Tools and applications shell kernel - Surrounding the kernel and acting as a user interface to the Unix operating system - Command language interpreter - Interprets the command users enter - Selects and runs the command or program - Provides the results to the screen or file as directed by the command -C shell, Bourne shell, Korn shell The main part of operating system, and responsible for controlling system resources. -Loaded into memory when the system boots -Process control and scheduling -Memory management -Device I/O -System error handling -User programs requesting services from the kernel through system calls -Hardware devices getting kernel response through interrupts User interface Providing two methods for user to interact with the operating system GUI, for users of workstations or intelligent terminals with bit-mapped displays. Command line interface, for users of a character cell terminal or terminal emulator. 10 File system A hierarchical file system a root filesystem: /bin, /lib, /etc, /dev,…… a /usr filesystem: programs and unchanging data a /var filesystem: changing data (such as log files) a /home filesystem: user’s files Types of files Ordinary disk files Special files Directory flies Naming files and directories Each physical device on a Unix system is treated as a special file. Located in the /dev directory. File and directory names can include letters, numbers, periods(.), underscores(_), and some other printable characters. Avoid characters with special programming or system meanings, such as /, *?[]<>$’”&!. Generally, a name of file and directory can contain up to 255 characters. Accessing directories and files Accessing directories: cd , ls, pwd Finding files: find Viewing files: more, cat, tail, head Editing files: vi, ed 11 Controlling Processes (1) A process Is a program that is currently executing Can be created and destroyed Has resources allocated to it Has an environment associated with it that: Process and process group IDs Open files Working directory File creation mask Real and effective user and group IDs Resource limits: maximum file size, maximum amount of memory Signal action settings A set of named variables Can create other processes Can communicate with other processes 12 Controlling Processes (2) Creating a process Running jobs in the foreground: command Running jobs in the background: command & Obtaining process status jobs ps Displays status of jobs in the current session Job number, job status, PID Shows current status of processes PID, state, accumulated execution time, command, …… Controlling and managing jobs Placing a job in the foreground: fg Restarting a job in the background: bg Stopping a process: Ctrl/C, kill Setting process priority: nice Scheduling jobs to run at appropriate times: at, crontab 13 Networking Services UUCP TCP/IP Allowing transparent file access over TCP/IP networks among computers, including Unix, Linux and MS Windows machines. IPX/SPX rlogin, rcp, rsh, telnet, ftp Ping, netstat, trouceroute Network File System (NFS) Unix to Unix copy program A batch-processing/spooling system Typically used between systems with dial-up telephone lines or direct serial lines Netware clients can log in Unix servers via Novell network. LAN Manager Client allowing the sharing of files with MS Windows machines (via Network Neighbourhood). allowing the sharing of printers across machines. 14 Online documentation Unix commands are documented on line in the man pages. The man command provides online access to the system's reference pages. 15 3. Introduction to Linux A free Unix-type operating system originally created by Linus Torvalds with the assistance of developers around the world. The source code for Linux is freely available to everyone. GUI operating system, including many of the tools that Windows users are familiar with such as, A file manager A Window manager A help system A configuration ……. Requiring less system resources. A Linux based system can operate smoothly on a 386 or 486. Application software support Office applications: Corel WordPerfect Office 2000 for Linux Deluxe Graphics tool: Gimp Browsers: Netscape Communicator 4.75, Opera browser 16 Examples PCVSAT, DVB, DAB CMA’s domestic communication system MS Windows NICC: AIX RICC, PICC: AIX, Digital Unix CIMS: Sco Unix, will be replaced by Linux in future. CMA’s GTS system VMS, will be replaced by UNIX in next year 17 FTP FTP TCP (get) (put) scokets Data management PCVSAT Mux and storage - PC - IBM H50 - Windows NT - AIX - Sybase NICC PCVSAT receiver Data Database management - PC - PC - PC - Windows 98 - Sco Unix - Sco Unix - Sybase CIMS Thank you 19