* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Install the Operating System
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Windows Vista wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Windows Phone 8.1 wikipedia , lookup
Windows NT startup process wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 5: Operating Systems IT Essentials 5.0 Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 1 Chapter 5 Objectives 5.1 Explain the characteristics and basic functions of modern operating systems 5.1 Describe and compare types of operating systems to include purpose, limitations, and compatibilities 5.1 Determine operating system based on customer needs 5.2 Install an operating system 5.3 Navigate a GUI (Windows) 5.4 Explain the advantages of Virtualization and install Virtual PC Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 2 Chapter 5 Objectives (continued) 5.5 Identify and apply common preventive maintenance techniques for operating systems 5.6 Troubleshoot operating systems Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 3 The Purpose of an Operating System The operating system (OS) controls almost all functions on a computer. In this chapter, you will learn about the components, functions, and terminology related to the Windows 7, Windows Vista , and Windows XP operating systems. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 4 Characteristics of an Operating System Multi-user – Two or more users have individual accounts that allow them to work with programs and peripheral devices at the same time. Multitasking – The computer is capable of operating multiple applications at the same time. Multiprocessing – The operating system can support two or more CPUs. Multithreading – A program can be broken into smaller parts that are loaded as needed by the operating system. Multithreading allows individual programs to be multitasked. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 5 Basic Function of an Operating System All computers rely on an operating system (OS) to provide the interface for interaction between users, applications, and hardware. The operating system boots the computer and manages the file system. The operating system has four main roles: • Control hardware access • Manage files and folders • Provide user interface • Manage applications Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 6 Processor Architecture 32-bit Windows Operating System and x86 Processor Architecture • Capable of addressing 4 GB of RAM • x86 uses a Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC) • x86 processors use fewer registers than x64 processors 64-bit Windows Operating System and x64 Processor Architecture • Capable of addressing 128+ GB of RAM • Enhanced performance for memory management • Additional security features • x64 architecture is backward compatible with x86 • Process much more complex instructions at a much higher rate Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 7 32-bit and 64-bit Compatibility in Windows OS Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 8 Types of Operating Systems Desktop Operating System Presentation_ID Network Operating System • Supports a single user • Supports multiple users • Runs single-user applications • Runs multi-user applications • Shares files and folders • Robust and redundant • Shares peripherals • Provides increased security • Used on a small network • Used on a network © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 9 Types of Operating Systems Desktop operating systems: • Microsoft Windows: Windows 7 • Macintosh: Mac OS X • Linux • UNIX A desktop OS has the following characteristics: • Supports a single user • Runs single-user applications • Shares files and folders on a small network with limited security Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 10 Network Operating Systems (NOS) Common NOS include: • Microsoft Windows Server • Linux • UNIX • Mac OS X Server NOS has the following characteristics: • Supports multiple users • Runs multi-user applications • Robust and redundant • Provides increased security compared to desktop operating systems Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 11 Customer Requirements for an OS To select the proper operating system for a customer first determine: •Budget constraints •Compatibility with current hardware •Compatibility with new hardware •How the computers will be used •Compatibility with existing applications •Types of new applications to be used Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 12 Identify Minimum Hardware Requirements Customer may need to upgrade or purchase additional hardware to support the required applications and OS. A cost analysis will indicate if purchasing new equipment is a better idea than upgrading. Possible hardware upgrades: •RAM capacity •Hard drive size •CPU •Video card memory and speed •Motherboard Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 13 Hardware Compatibility Most operating systems have an HCL. HCLs can be found on the manufacturer's website. HCL includes list of hardware that is known to work with the operating system. Use Microsoft Compatibility Center for Windows 7 and Vista. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 14 Operating System Upgrades Operating systems must be upgraded periodically. • To remain compatible with the latest hardware and software. • Because support for older OS is eventually withdrawn. Ensure that the new OS is compatible with the computer. • Use Microsoft Upgrade Advisor to scan the system for incompatibility issues before upgrading. Upgrade Advisor is free and downloadable from the Microsoft Windows website. Backup all data prior to beginning the upgrade. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 15 Data Migration One of the following tools can be used to migrate data and settings: User State Migration Tool migrates all user files and settings to the new OS. Windows Easy Transfer migrates personal files and settings when switching from an old computer to new. Note: Windows Easy Transfer replaced the Windows XP File and Settings Transfer Wizard. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 16 Installing the Operating System Reasons to perform a clean installation of an OS: •When a computer is passed from one employee to another. •When the operating system is corrupted. •When the primary hard drive is replaced in a computer . Before performing a clean installation: •Back up all data first. •Explain to the customer that existing data will be erased. •Confirm that all needed data has been successfully transferred. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 17 Hard Drive Setup Procedures Operating system setup methods: •Install an OS over a network from a server. •Install from OS files stored on CDs or DVDs. Partitioning and Formatting: •Hard drive must be logically divided (partitioned). •File system must be created on the hard drive. •During the installation phase, most operating systems will automatically partition and format the hard drive. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 18 Hard Drive Formatting The first portion of the installation process deals with formatting and partitioning the hard drive. The second portion prepares the disk to accept the file system. The file system provides the directory structure that organizes the user's operating system, application, configuration, and data files. Examples of file systems: •The New Technology File System (NTFS) - Supports partition sizes up to 16 exabytes •The FAT32 file system - Supports partition sizes up to 2 TB. Used by Windows XP and earlier OS versions. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 19 Install the Operating System When a computer boots up with the Windows installation CD, the Windows 7 installation process starts with three options: • Install now - Sets up and installs the Windows 7 OS. • What to know before installing Windows - Opens Help. • Repair your computer - Opens the System Recovery Options. Under Install now three options are available: • Upgrade - Upgrades Windows but keeps your current files, settings, and programs. You can use this option to repair an installation. • Custom (advanced) - Installs a clean copy of Windows in your choice of location and allows you to change disks and partitions. It is also known as a clean installation. • Quit - Exits Setup. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 20 Account Creation Windows 7 has three types of user accounts: Administrator, Standard, and Guest. The Administrator Account must be created when Windows 7 is installed. To create or remove a user account in Windows 7 use the following path : Start > Control Panel > User Accounts > Add or remove user accounts Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 21 Complete the Installation When Windows 7 installation completes: •Computer will reboot •Prompts to create user account •Register Windows 7 and verify that you are using a legal copy of the OS •Verification enables you to download patches and service packs Use Microsoft Update Manager to scan for new software. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 22 Custom Installation Options – Disk Cloning With Microsoft System Preparation Follow these steps for disk cloning: 1. Create a master installation on one computer. 2. Run Sysprep. 3. Create a disk image of the configured computer using thirdparty disk-cloning software. 4. Copy the disk image onto a server. When the destination computer is booted: Presentation_ID • A shortened version of the Windows setup program runs. • Setup installs drivers, creates user accounts, and configures network settings. © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 23 System Recovery Options Repair Disc- For Windows 7. Use the system repair disc to boot the computer System Image Recovery – For Windows 7. It allows users to back up the contents of their hard drive, including personal files and settings. Factory Recovery Partition – Some computers with Windows 7 preinstalled from the factory contain a hidden recovery partition with an image of the bootable partition. Automated System Recovery (Windows XP Professional only) – The ASR is a backup of the system state, services, and OS components. Used with Windows installation disc to recover computer. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 24 Startup Modes Pressing the F8 key during the boot process opens the Windows Advanced Startup Options menu, which allows you to select how to boot Windows. Safe Mode – Starts Windows but only loads drivers for basic components, such as the keyboard and display. Safe Mode with Networking Support – Starts Windows identically to Safe Mode and also loads the drivers for network components. Safe Mode with Command Prompt – Starts Windows and loads the command prompt instead of the GUI interface. Last Known Good Configuration – Enables a user to load the configurations settings of Windows that was used the last time that Windows successfully started. It does this by accessing a copy of the registry that is created for this purpose. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 25 Multiboot Procedures Multiple OS can be installed on one computer To create a dual-boot system in Microsoft Windows: • Must have more than one hard drive or a hard drive with more than one partition. • Install the oldest OS on the primary partition or the hard drive marked with an active partition. • Install the second OS on the second partition or hard drive. • The boot files are automatically installed in the active partition. During the dual-boot process: • The BOOTMGR file indicates that more than one OS is present. • You are prompted to choose the OS that you want to load. • NOTE: In Windows XP, the BOOT.INI file fills the role of the BOOTMGR file. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 26 Disk Management Utility This utility can be to used to complete the following tasks: • View drive status • Extend partitions • Split partitions • Assign drive letters • Add drives • Add arrays To access the Disk Management utility in Windows 7 and Windows Vista, use the following path: Select Start > right-click Computer > Manage > select Disk Management Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 27 Directory Structures The root level of the Windows directory structure, the partition, is usually labeled drive C. • Contains a set of standardized directories, called folders, for the operating system, applications, configuration information, and data files. • Directories may contain subdirectories. Subdirectories are commonly called subfolders. Drive Mapping - letters are used to name physical or logical drives. Mounting a Volume - mapping a drive to an empty folder on a volume. Mounted drives are assigned drive paths instead of letters. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 28 File Extensions and Attributes Windows file system naming conventions: •Maximum of 255 characters may be used. •Characters such as a period (.) or a slash (\ /) are not allowed. •An extension of three or four letters is added to the filename to identify the file type. •Filenames are not case sensitive. Windows filename extension examples: •.docx- Microsoft Word •.txt - ASCII text only •.jpg - graphics format •.pptx - Microsoft PowerPoint •.zip - compression format Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 29 Windows Desktop, Tools, and Applications To customize the Start Menu or the Taskbar, right-click it and choose Properties. The Task Manager allows you to view all applications that are running and to close any applications that have stopped responding: •CTRL-ALT-DEL and select Start Task Manager. •right-click the taskbar and select Start Task Manager. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 30 Computer and Windows Explorer Computer allows access to the various installed drives (My Computer in Windows XP) Windows Explorer - used to navigate the file system includes: • Search box - Access previous searches. Filter search results. • New folder button - Create new folders with one click. • Arrange by - Organize items easily according to different criteria. • Preview pane button - Turn the preview pane on or off. Applications can be launched in several ways: • Click the application on the Start menu or Taskbar. • Double-click the application shortcut icon on the desktop. • Double-click the application executable on the desktop or in Windows Explorer. • Launch the application from the Run window or command line. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 31 Windows 7 Libraries Allows for easy organization of content from storage devices on local computer and network. Are virtual folders that present content from different locations within the same view. Include four default Libraries - Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos. To add a file to a library, right-click it, select Include in library, and then choose which library to add the item. To create a new library, open a folder and select Include in Library > Create new library Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 32 Control Panel Utilities System and Security - To configure system and security settings Network and Internet - To configure network connection types Hardware and Sound - To configure devices connected to the computer and settings for sound Programs - To remove, change, and repair applications User Accounts and Family Safety - To create and remove user accounts and set up parental controls Appearance and Personalization - To control the look and feel of the Windows GUI Clock, Language, and Region - To specify location and language Ease of Access - To configure Windows for vision, hearing, and mobility needs Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 33 User Accounts User Accounts Utility: •Create a user account. •Manage password, change picture, change account name and type, manage another account, and change User Account Control (UAC) settings. •Start > Control Panel> select User Accounts User Account Control (UAC): •Monitors programs on a computer and warns users when an action might present a threat to the system. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 34 Internet Options To access Internet Options select Start > Control Panel > Internet Options Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 35 The System Utility View basic system information, access tools and configure advanced settings including: • Computer Name -View or modify the name and workgroup settings for a computer, as well as change the domain or workgroup. • Hardware - Access the Device Manager or adjust the device installation settings. • Advanced -Configure settings for performance, user profiles, startup, and recovery. • System Protection - Access System restore and configure protection settings. • Remote -Adjust settings for Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop. Start > Control Panel > System Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 36 Device Manager View settings for devices in the computer and: • Update a driver - Change the currently installed driver. • Roll back a driver - Change the currently installed driver to the previously installed driver. • Uninstall a driver • Disable a device • Start > Control Panel > System > Device Manager Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 37 Event Viewer Logs a history of events regarding applications, security, and the system. These log files are a valuable troubleshooting tool. Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Event Viewer Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 38 Services and Performance Monitor Services: •Start, stop, or disable services. •Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services. Presentation_ID Performance Monitor: •Record performance data and configure alerts. •Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Performance Monitor 39 © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential Disk Defragmenter and Disk ErrorChecking Tool Disk Defragmenter makes files on the hard drive contiguous and speeds up the reading of files. To access the Disk Defragmenter in Windows 7, select Start > All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Disk Defragmenter. CHKDSK checks the integrity of files and folders by scanning the hard disk surface for physical errors. Access CHKDSK from within the Disk Defragmenter or enter CHKDSK in command line to detect and repair disk errors. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 40 Remote Desktop Remote Desktop •View and control a computer from a remote location. Remote Assistance •Also allows user to view what the remote technician is doing to the computer. To access in Windows 7 or Windows Vista, select Start > All Programs > Accessories > Remote Desktop Connection Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 41 Control Panel Utilities Unique to Specific Windows Versions Windows 7 Windows XP •HomeGroup •Add/Remove Programs •Action Center •Printers and Faxes •Windows Defender •Automatic Updates •RemoteApp and Desktop Connections •Network Connections •Network Setup wizard •Troubleshooting Windows Vista •Tablet PC settings •Pen and Input Devices •Offline Files •Problem Reports and Solutions •Printers Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 42 Command-Line Tools Start > Type Cmd in the search box > Press Enter Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 43 Run Line Utility Enter commands to configure settings and system modifications. To access in Windows 7 select Start > Search box > Type run > Enter. Common Commands • CMD –Used to execute command line programs. • DXDIAG - Displays details for all DirectX components and drivers. • EXPLORER – Opens Windows Explorer. • MMC - Opens the Microsoft Management console (MMC). • MSCONFIG - Opens the System Configuration Utility. • MSINFO32 - Displays complete system summary of the computer. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 44 Virtualization Host machine uses its system resources to host a virtual machine. Hosting a virtual machine allows users to access the functionality and resources provided by an OS that is not on the local PC. Provides access to applications, file-sharing services, and other productivity tools. Users can further increases the functionality of their system by running multiple virtual machines. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 45 Virtualization The software that creates and manages a virtual machine on a host machine is called the hypervisor, or Virtual Machine Manager (VMM). • Allocates the physical system resources, such as CPU, RAM, and hard drive, to each virtual machine as needed. Windows Virtual PC is the virtualization platform for Windows 7 • Allows you to partition system resources for a Window OS among virtual machines . Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 46 Virtual Machine PC Requirements Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 47 Preventive Maintenance Planning Components of a preventive maintenance plan: Updates to the operating system and applications Updates to anti-virus and other protective software Hard drive error checking Hard drive backup Hard drive defragmentation Device drive updates Firmware updates Startup programs Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 48 Schedule Tasks The CLI at command launches tasks at a specified time using the command line interface. The Windows Task Scheduler launches tasks at a specified time using a graphical interface. To access the Windows Task Scheduler in Windows 7 and Windows Vista, select Start > All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Task Scheduler. Both of these tools allow users to set commands to run at a certain time just once, or to repeat at selected days or times. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 49 Restore Point If a computer crashes, the OS can roll back to a restore point using the System Restore Utility. •The restore utility only operates on OS and application files. •Anti-virus software should be run to remove malware before creating a restore point. When to create a restore point: •Before updating or replacing the OS. •When installing or updating hardware. •When an application or driver is installed. Start > All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > System Restore Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 50 Backup the Hard Drive Use the Microsoft Backup Tool to perform backups. Establish a backup strategy that will allow for the recovery of data. Decide how often the data must be backed up and the type of backup to perform. It is only necessary to make copies of the files that have changed since the last backup. To access the backup utility in Windows 7, select Start > Control Panel > Backup and Restore. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 51 Types of Backups Description Clear marker Normal Selected files and folders Yes Copy Selected files and folders No Differential Selected files and folders that changed since the last backup No Incremental Selected files and folders that changed since the last backup Yes Daily Selected files and folders that changed during the day No Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 52 Troubleshooting Process Step 1 Identify the problem Step 2 Establish a Theory of Probable Cause Step 3 Test the Theory to Determine Cause Step 4 Establish a Plan of Action to Resolve the Problem and Implement the Solution Step 5 Verify Full System Functionality and Implement Preventive Measures Step 6 Document Findings, Actions, and Outcomes Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 53 Chapter 5 Summary (Continued) Establish a backup strategy that allows for the recovery of data. Normal, copy, differential, incremental, and daily backups are all available in Windows operating systems. Virtualization has become a popular method of providing staff with critical resources, such as applications, filesharing services, and other productivity tools. Preventive maintenance techniques help to ensure optimal operation of the operating system. Some of the tools available for troubleshooting an OS problem include administrative tools, system tools, and CLI commands. Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 54 Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 55








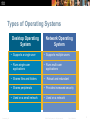

















































![Computer Networks [Opens in New Window]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001432217_1-c782ef807e718d5ed80f4e9484b1006a-150x150.png)