* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C_SCOPE - Arp ISD HOME
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Imamate (Twelver doctrine) wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islam
©2010, TESCC
©2010, TESCC
Quotes from the Koran
• 42.3] Thus does Allah, the Mighty, the
Wise, reveal to you, and (thus He
revealed) to those before you.
©2010, TESCC
Quotes from the Koran
• [42.4] His is what is in the heavens and
what is in the earth, and He is the High,
the Great.
©2010, TESCC
Quotes from the Koran
• [42.5] The heavens may almost rend
asunder from above them and the angels
sing the praise of their Lord and ask
forgiveness for those on earth; now surely
Allah is the Forgiving, the Merciful.
©2010, TESCC
• Islam teaches that one can only find peace
in one's life by submitting to Almighty God
(Allah) in heart, soul and deed.
• The same Arabic root word gives us
"Salaam alaykum," ("Peace be with you"),
the universal Muslim greeting.
©2010, TESCC
Who is a Muslim?
• A person who believes in and consciously
follows Islam is called a Muslim, also from
the same root word. So, the religion is
called "Islam," and a person who believes
in and follows it is a "Muslim."
• Muslims worship Allah and recognize
Muhammad as the last prophet.
©2010, TESCC
How Many and Where?:
• Islam is a major world religion, with over 1
billion followers worldwide (1/5 of the world
population). It is considered one of the
Abrahamic, monotheistic faiths, along with
Judaism and Christianity.
©2010, TESCC
How Many and Where?
• Although usually associated with the
Arabs of the Middle East, less than 10% of
Muslims are in fact Arab. Muslims are
found all over the world, of every nation,
color and race.
©2010, TESCC
Who is Allah?:
• Allah is the proper name for Almighty God, and
is often translated merely as "God." Allah has
other names that are used to describe His
characteristics: the Creator, the Sustainer, the
Merciful, the Compassionate, etc.
• Muslims believe that since Allah alone is the
Creator, it is He alone that deserves our devout
love and worship. Monotheistic deity, also
recognized as the God of Abraham. (Yahweh)
©2010, TESCC
How strict is the religion?
• Islam holds to a strict monotheism. Any
worship and prayers directed at saints,
prophets, other human beings or nature is
considered idolatry.
©2010, TESCC
• As part of the Islam
religion, all true
Muslims must
perform 5 duties,
called the Five
Pillars of Faith.
©2010, TESCC
©2010, TESCC
Shahada
(affirmation)
• The duty to recite the creed:
"There is nothing worthy of worship save
Allah, and Muhammad is the Messenger
of God."
©2010, TESCC
• Salat
• (prayer)
The duty to worship the One God
in prayer five times each day
• Zakat
• (almsgiving)
The duty to give away alms and to help the
needy
©2010, TESCC
• Siyam
– (fasting)
The duty to keep the
Fast of Ramadan
• Hajj
– (pilgrimage)
The duty to make the
pilgrimage to Mecca
at least once in a
lifetime (Hijrah)
©2010, TESCC
Muhammad
– Born in 570 (?) and is considered the
founder of Islam. Caravan manager
from Mecca, rich trading city and host
to many religious shrines (Ka’bah);
married to a rich widow
– Was becoming disillusioned with the
corruption in the city and the growing
gap between the urban dwellers and
the Bedouins (nomadic herders)
©2010, TESCC
–While meditating in the hills, the
Angel Gabriel visited him and
revealed to him that he was the
next and final prophet.
–Recited the revelations (later written
down as the Qur’an)
©2010, TESCC
–He began to preach but
attracted few followers; many
enemies feared he would
upset the political and social
order.
–So in 622, Muhammad and his
followers fled to Medina. (the
Hegira)
©2010, TESCC
Islamic Beliefs
©2010, TESCC
– No separation between Church
and State.
– Belief that salvation and the
afterlife will be obtained by
submitting to the will of Allah.
©2010, TESCC
–Qur’an (Koran): ethics and laws
of the Islamic community
• Written in Arabic and cannot
officially be translated to another
language. To study the Qur’an you
must learn Arabic.
• Book of the writings of the
prophet Muhammad
©2010, TESCC
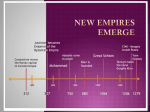
Growth of Islam
–
–
–
©2010, TESCC
Medina supported Muhammad and he
attracted the support of the Bedouins.
In 630, Muhammad returned to Mecca
(the Holy City of the Islamic Faith) with a
force of 10,000 soldiers and quickly took
the city.
As Islam began to spread through the
Arabian Peninsula, Muhammad died in
632.
Why did Islam spread?
• Easy to learn and practice
• No priesthood
• Non-Muslims in conqueror territory
are allowed religious freedom (for an
additional tax)
• Spread through trade route
• Jihad (Holy Struggle): “Holy War”
against infidels and it is the expansion
of the Islamic state and control.
©2010, TESCC