* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Review
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
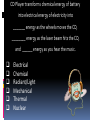
ENERGY REVIEW Jan. 7, 2014 – Welcome back!! Questions to answer: 1. What is potential and kinetic energy? 2. How is energy “made”? 3. Where does our electrical energy come from? Potential Energy Stored energy Potential Energy (position/Elastic) Drawing a Bow Stretching a Rubber Band Potential Energy (position/Gravity) Yo-Yo in the hand Water at the top of a waterfall Potential Energy Chemical Examples: (Chemistry) Oil Gas Potential Energy (Chemistry) Wood Coal Battery Kinetic Energy Energy of movement Kinetic Energy Wood Burning Rock Falling Running Kinetic Energy Yo Yo in Motion Shooting Rubber Band Water Falling Shooting Arrow How is energy “made”? Law of Conservation of energy (or why energy cannot be “made”)! The law states: Energy cannot be created nor destroyed. What does this mean? It means that energy can only change its form from one type to another. The energy of the world is a constant because the total amount of the energy does not change. Examples of Energy Transformations Due to the Law of Conservation of Energy, energy cannot be created nor destroyed. Meaning, energy just changes forms! Let’s go through the examples on the right. So, energy isn’t made, it just changes forms. What are those forms of energy again? Forms of Energy are: Chemical Electrical Radiant mechanical electrical Mechanical Thermal Nuclear nuclear Chemical Energy: Energy STORED in matter because of its CHEMICAL bonds. It is released during a chemical reaction. Electrical Energy: Energy in the form of electricity. Energy from flowing electrons in a current. Radiant or light Energy • Type of energy from the sun. Energy carried by ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION. • Radiant=LIGHT (but it Isn’t always visible) • Examples: – – – – Visible Light/Sunlight (What you see) X-Rays (invisible) Microwaves (invisible) UV Light (invisible) Mechanical Energy Energy of matter caused by its POSITION or MOTION. Thermal Energy transfers from hotter objects to colder objects. This energy comes from the motion of atoms and molecules. The faster the particles in an object move, the more thermal energy is produced. Nuclear Energy Energy that is released when the nuclei of atoms are split (fission)or combined (fusion). Example: Nuclear Power Plant To put it all together… Where does our electrical energy come from? Our energy resources come from two main types of resources, nonrenewable and renewable. Sources of Energy Non - Renewable – an energy source that is used much faster than it can be replaced. Mainly fossil fuels Renewable – an energy source that can be replaced by natural processes in a “short period of time”. Short period of time in geological terms, sometimes can be replaced within a human lifetime, but not always Non-Renewable: Means finite or limited (it will run out) Types: Coal Oil/Petroleum Natural Gas Nuclear power Renewable resources Uses sources of energy that can be replaced Types: Hydropower Biomass Wind Geothermal Solar Energy Transformation Practice Hair Dryer Electrical Mechanical Thermal Flashlight Chemical Electrical Radiant Describe the energy transformations needed for you to watch your favorite TV show at home. radiant energy chemical energy (photosynthesis) plants/animals die and become fossil fuel (coal) Coal is converted to electrical energy Electrical energy is converted to radiant (light) & mechanical energy (sound) by TVs. Outlets in homes provide electrical energy Power lines transport electrical energy to homes Let’s take this one step further: What are the energy transformations in an (coal-based) electrical power plant? The energy transformations in an electrical power plant: Coal is burned Water is heatedSteam turns the blades of a turbine Turbine spins coil in generator Generator produces electricity Energy Changes form worksheet A hairdryer converts electrical energy into __________ energy which then transforms into _____________ energy. Electrical Chemical Radiant/Light Mechanical Thermal Nuclear A computer monitor converts electricity into _____________ energy. Electrical Chemical Radiant/Light Mechanical Thermal Nuclear A toy car transforms chemical energy of battery into electrical energy of electricity then into ________ energy when the wheels move. Electrical Chemical Radiant/Light Mechanical Thermal CD Player transforms chemical energy of battery into electrical energy of electricity into _______ energy as the wheels moves the CD, ________ energy as the laser beam hits the CD, and ______ energy as you hear the music. Electrical Chemical Radiant/Light Mechanical Thermal Nuclear An electric power generator converts __________ energy of a turning turbine into _____________energy. Electrical Chemical Radiant/Light Mechanical Thermal Nuclear When your worksheet is complete, check with a neighbor that you have completed all of the steps. First set of boxes: 1. Filled in the top box with form of energy 2. Drawn a picture Second set of boxes (after the arrow) 1. Filled in the top box with form of energy it has been converted into 2. Drawn a picture