* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Study Guide for Chapter 1
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
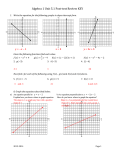
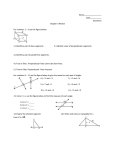
Geometry Study Guide for Chapter 3 1. Study the last 2 quizzes on 3.1 to 3.4 and do the problems without looking at the answers. 2. Know key vocabulary: Parallel lines (pg. 126), Parallel Planes (126), Transversal (126), Corresponding, Alternate Interior, Alternate Exterior, and Consecutive Interior angles (pg. 128), Slope Intercept form (145), Point-Slope form (145), Slope (pg.139). See problems 1-7 on page 167. 3. There will be several questions like 8-15 on page 167. 4. Know theorems: 3.1 to 3.7 and postulate 3.1 (Corresponding Angles Postulate). a. Know how to do problems like 16 to 22 page 168. b. You will need to remember complementary, supplementary, vertical angle and linear pair angle relationships from Chapter 1. c. Practice with problems 35-40 on page 170. 5. Know the slope formula, m = y2 - y1 , and how to find the slope when you are x2 - x1 given 2 points. 6. Know how to determine whether 2 lines are parallel, perpendicular or neither given 2 points for each line. See problems 23-26 page 169. 7. Be able to write an equation in either slope-intercept or point-slope if you are given: The slope and the y-intercept The slope and a point Two points The graph of a line with two points labeled 8. Be able to write an equation of a line that passes through a point and is parallel or perpendicular to another line, whose equation or points are given. See problems 27-28 on page 169. Remember that 2 parallel lines have the same slope. Also, Remember that when 2 lines are perpendicular to each other their slopes are 2 negative reciprocals. For example, if the slope of one line is , then the slope of 3 2 the other is - . 3 9. Know how to use the distance formula to find the shortest distance between 2 given equations of lines that are parallel. See problems 35-40 page 170. Remember that the distance between 2 parallel lines is the length of any perpendicular segment joining the two lines. 10. Take the exam that is online for practice at: http://www.glencoe.com/sec/math/geometry/geo/geo_04/index.php/ca/2004 11. Go to www.classzone.com for practice on problems online. Click on math, CA and “GO”. Click on your textbook “2007”. Click on “eWorkBook”.