* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Terms
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
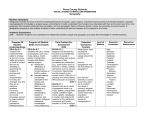
Social Studies II Curriculum Map PLCS Connections A/H Connections Writing/Literacy Connections Date Content Skills Activities/Assessments Key Terms Aug. 7-9, 2013 Class overview/syllabus; AE 2.19Apply geographical knowledge; SSHS—4.1.1(using geographic tools, DOK 3); 4.2.2 (physical/human characteristics— advantages/disadvantages, DOK 2); 4.3.1(movement/ settlement—i.e. push/pull factors, DOK 3); 4.3.2(impact of technology; increased economic interdependence, DOK 2) 4.4.2(impact of modifications—i.e. global impact, DOK 2)—chapters 1, 2, and 3 in World Geography Today and chapter 1 in World History: Perspectives on the Past Define/explain key geographic terms; explain/ analyze reasons for distribution of physical/ human characteristics create advantages/disadvantages for human activities; describe movement/settlement patterns and analyze causes/ impacts; explain how technology has impacted people, including increasing economic interdependence and development of economic centers; explain how human modifications of Earth/use of natural resources/natural disasters have had global effects; 5 “themes of geography”; meaning of “place.” Class syllabus/yearly overview; Multiple Intelligences surveys from History Alive!; student classwork/home-work(assigned readings, study guides, handouts, research, etc.); group /individual work/ presentations (posters/ PowerPoints/oral reports); lecture/ discussion; audiovisuals (videotapes/PowerPoints, etc.); use of technology (Internet, etc.); chapter test/quizzes; discussion/ completion of open-ended response questions Geography, 5 themes (location, place, interaction, movement, region), patterns, human/ physical characteristics, weather, climate, geographic tools (map, globe, database, etc.), centralization, dispersion, regions, urban/rural, migration, stereotypes, “push/pull” factors, technology, economic interdependence, modifications, natural resources, natural disasters, global impact/ effect. Aug. 12-23, 2013 AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge; AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events; AE 2.14Democratic principles; AE 2.15Describe & analyze governments; SS-HS—4.1.1 (DOK 3); 5.1.1 (interpretive nature of history, DOK 3); 5.1.2(cause-and- effect, multiple causations, DOK 3) 5.3.1(Renaissance and Reformation, DOK 2)—prologue and chapter 1 in Modern World History Define/explain key terms; use of various historical tools (primary/secondary sources, data, artifacts, etc.) to analyze perceptions/ perspectives of people/ historical events; analyze history as a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships; explain how humans began to rediscover Classical Age ideas and question their place in the universe; geographic perspective. Student classwork/ homework; lecture/ discussion; audiovisuals (i.e. Gladiator; The Agony and the Ecstasy); synthesis/application activity; chapter tests/ quizzes; open-ended questions; personal timeline activity/writings; Renaissance Art analysis; primary source analysis, Renaissance DBQ; History, perspective, interpretation, timelines, historical documents, artifacts, primary sources, secondary sources, cause-andeffect, multiple causation, bubonic plague, Classical Age, civilizations, empires, GrecoRoman philosophies, Renaissance, patrons, vernacular, humanism, secularism, Utopia, Johann Gutenberg/ printing press, indulgence, Michelangelo, Machiavelli, Reformation, Martin Luther, Protestant, Anglican, predestination, John Calvin, clergy, theocracy, Henry VIII, Elizabeth I, Huguenots. Aug 26-30, 2013 AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge; AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events; AE 2.14Democratic principles; AE 2.15Describe & analyze governments; AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors; AE 2.17- multicultural cooperation; AE 2.18- Economic principles; SS-HS—1.1.1(Types of governments, DOK 3); 2.1.1 (Culture, DOK 2); 2.3.1(Cultural conflict/competition, DOK 2); 2.3.2(Cultural compromise/ cooperation, DOK 2); 3.2.1 (Economic systems, DOK 2); 3.2.3 (Free enterprise system, DOK 2); 3.4.3 (Economic interdependence, DOK 2); 4.1.1; 5.1.1; 5.1.2; 5.3.2(Age of Exploration; absolute monarchies of Europe, DOK 2)—chapters 3, 4, and 5 in Modern World History Define key terms; explain how belief systems/ knowledge/technology/ behavior patterns define cultures and help explain modern historical perspectives; explain why conflict/competition may develop as cultures emerge; explain/give examples of compromise/cooperation that influence social interactions; explain/give examples of how new ideas/technologies led Europeans to an Age of Exploration bringing great wealth to the absolute monarchies and causing significant political/ economic/social changes to other regions of the world; compare/contrast various forms of government(i.e. monarchy, democracy, republic), sources of their power and effectiveness in establishing order/providing security/accomplishing common goals; compare/ contrast economic systems (traditional, command, market, mixed) on abilities to achieve broad socials goals (freedom, efficiency, etc.); explain how individuals in free enterprise economies attempt to maximize their profits; explain/give examples of how interdepen-dence of personal/national/ international economic activities often result in international issues/concerns; geographic perspective. Student classwork/ homework; lecture/ discussion; audiovisuals (i.e. Age of Exploration: Just the Facts; The Last of the Mohicans; Roots; 1492; The New World); chapter tests/quizzes; open-ended response questions; primary source activities; feudalism simulation; “Sunken Ship” simulation from History Alive!; student research projects with posters/bio-boards/ PowerPoint presentations, artifact analysis, Period art analysis, primary source analysis Culture, society, feudalism, Age of Exploration, caravel, astrolabe, missionary, Christopher Columbus, colony, conquistadors, mestizo, Pilgrims, Puritans, French and Indian War, Atlantic slave trade, plantation, triangular trade, middle passage, Columbian Exchange, Commercial Revolution, joint-stock company, mercantilism, favorable balance of trade, monarchies, absolute monarch, absolutism, divine right, Louis XIV, skepticism, Oliver Cromwell, Restoration, religious tolerance, Glorious Revolution, constitutional monarchy. Sept. 3-Nov. 1, 2013 AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge; AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events; AE 2.14Democratic principles; AE 2.15Describe & analyze governments; AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors; AE 2.17- multicultural cooperation; AE 2.18- Economic principles; SS-HS—2.1.1; 2.3.1; 2.3.2; 3.2.1; 3.2.3; 4.1.1; 5.1.1; 5.1.2; 5.3.3(Age of Revolution, DOK 3)— chapters 6, 7, 9, and 10 in Modern World History Define key terms; primary sources; cause-and-effect; cultural conflict/competition; economic systems; free enterprise system; analyze how the Age of Revolution brought changes in science, thought, government, and industry that shaped the modern world; geographic perspective. Student classwork/ homework; lecture/ discussion; French Revolution simulation from History Alive!; audiovisuals(i.e. Master and Commander: The Far Side of the World; 1776); chapter tests/ quizzes; open-ended response questions; Period art analysis; primary source analysis; Industrial Revolution Essay; careers & changes due to technolgoy Age of Revolution, Scientific Revolution, geocentric theory, Nicolaus Copernicus/ heliocentric theory, Galileo Galilei, scientific method, Sir Isaac Newton/law of universal gravitation, Enlightenment, John Locke, natural rights, philosophe, separation of powers, enlightened despot, Declaration of Independence, Thomas Jefferson, checks and balances, federal system, Bill of Rights, French Revolution, Declaration of the Rights of Man, guillotine, Napoleon Bonaparte, bourgeoisie, agricultural revolution, agrarianism, Industrial Revolution, industrialization, factory, entrepreneur, urban areas, urbanization, corporation, laissez faire, Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations, capitalism, stock, utilitarianism, socialism, Karl Marx, communism, union, collective bargaining, strike, suffrage, anti-Semitism, manifest destiny, the Civil War, Charles Darwin/theory of evolution, psychology Nov. 4-Dec. 6, 2013 AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge; AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events; AE 2.14Democratic principles; AE 2.15Describe & analyze governments; AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors; AE 2.17- multicultural cooperation; AE 2.18- Economic principles; 1.1.1; 2.3.1; 3.2.1; 4.1.1; 5.3.4(Conditions in Europe lead to World War I, post- WWI conditions lead to economic booms and busts, the rise of totalitarian governments in Europe, DOK 3)—chapters 8, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, and 16 in Modern World History Define key terms; geographic perspective; types of governments/ sources of power; cultural conflict/competition; types of economies; analyze how nationalism, militarism, and imperialism led to World War I, post-WWI world-wide economic depression, rise of totalitarian governments in Europe; World War II and its aftermath. Student classwork/ homework; lecture/ discussion; audiovisuals (i.e. Sergeant York; The Grapes of Wrath; Seabiscuit; Cinderella Man; One Survivor Remembers); chapter tests/quizzes; student writing on Holocaust; poverty activity from History Alive!; openended response questions; Period art analysis; primary source analysis Conservatives, liberals, radicals, czar, nationalism, militarism, imperialism, racism, assimilation, geopolitics, annexation, colonialism, economic imperialism, protectorate, sphere of influence, alliances, totalitarian, dictator, World War I, Bolshevik Revolution, Central Powers, Allies, trench warfare, total war, rationing, propaganda, armistice, Woodrow Wilson, “Fourteen Points”, self-determination, League of Nations, civil disobed-ience, Albert Einstein, theory of relativity, Sigmund Freud, irrational, existentialism, surrealism, Great Depression, Franklin D. Roosevelt, New Deal, Fascism, Benito Mussolini, Nazism, Adolf Hitler, Aryans, Holocaust, appeasement, isolationism, “Final Solution”, genocide, concentration camps, blitzkrieg, Isoroku Yamamoto, Dwight D. Eisenhower, D-Day, kamikaze, Douglas Mac-Arthur, World War II, Axis powers, Winston Churchill, Josef Stalin, soviet, Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, command economy, United Nations, Nuremberg trials, war crimes, demilitarization. Dec. 9-18, 2013 AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge; AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events; AE 2.14Democratic principles; AE 2.15Describe & analyze governments; AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors; AE 2.17- multicultural cooperation; AE 2.18- Economic principles; SS-HS—1.1.1; 2.3.1; 4.1.1; 5.1.2; 5.3.5 (Cold War, DOK 3)—chapters 17, 18, and 19 in Modern World History Define key terms; types of governments/sources of power; cultural conflict/ competition; geographic perspective; cause-and- effect/multiple causations; explain the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union to superpower status after WWII, their subsequent “cold war” conflicts, formation of new nations in Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and the Middle East; the global impact of these events. Student classwork/ homework; lecture/ discussion; audiovisuals (i.e. Dear America: Letters Home from Vietnam); chapter tests/ quizzes; open-ended response questions; Period Art analysis; primary source analysis Cold War, “iron curtain”, containment, NATO, Warsaw Pact, brinkmanship, Mao Zedong, Jiang Jieshi(Chiang Kai-shek), Ho Chi Minh, guerrilla war, Islam, political unrest, “domino theory”, Vietcong, Vietnamiza-tion, Third World, Fidel Castro, Ayatollah Ruholla Khomeini, Nikita Khrushchev, John F. Kennedy, Lyndon Johnson, détente, Richard Nixon, SALT, Jimmy Carter, Anwar Sadat, Menachem Begin, Camp David Accords, Ronald Reagan, SDI/”Star Wars”, Palestinians, PLO, Yassir Arafat, extremists, standard of living, recession, martial law, dissident, apartheid, Nelson Mandela, Mikhail Gorbachev, glasnost, perestroika, reunification, ethnic cleansing. May 6-14, 2013 AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge; AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events; AE 2.14Democratic principles; AE 2.15Describe & analyze governments; AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors; AE 2.17- multicultural cooperation; AE 2.18- Economic principles; SS-HS—1.1.1; 3.2.1; 3.2.3; 3.4.3; 4.1.1; 4.3.2; 5.1.2; 5.3.6(Changes in the world in the second half of the 20th Century, DOK 2)—chapter 20 in Modern World History Define key terms; types of governments; cause-and-effect; cultural conflict/ competition; economic systems; free enterprise system; economic interde-pendence; explain how the second half of the 20th Century included rapid social/political/economic changes creating new challenges globally, give examples of how countries addressed these challenges; geographic perspective. Student classwork/ homework; lecture/ discussion; audiovisuals; chapter test/quiz; open-ended response questions; Period art analysis; primary source analysis Population growth, diminishing resources, environmental/human rights issues, genetic engineering, cloning, ozone layer, acid rain, technological/scientific advances, mass media, Internet, green revolut-ion, lasers, developed/ developing nation, political alliances, European Union, global-ization, global economy, multinational corpora-tion, free trade, Gulf War, biological weapons, chemical weapons, weapons of mass destruction/WMDs, nuclear proliferation, refugees, terrorism, War on Terror, fundamentalism, materialism, Universal Declaration of Human Rights.