* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
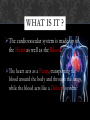
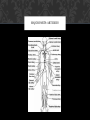
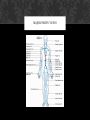
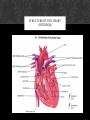
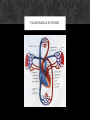
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Presentation by Ruby Nicholls & Dillon Cady? WHAT IS IT ? The cardiovascular system is made up of the Heart as well as the Blood. The heart acts as a Pump, transporting the blood around the body and through the lungs, while the blood acts like a Delivery system. FUNCTION Transportation Protection Regulation WHAT IS BEING TRANSPORTED? 1. Nutrients: O2, CO2, Electrolytes, proteins, hormones, carbs, and lipids. a. Electrolytes include K, Mg, Na, N, Cl, and H2CO3 (carbonic acid) 2. Waste from cells like CO2, nitrogenous waste a. Nitrogenous waste is the outcome of nitrogen molecules bonding with other molecules, producing ammonia PROTECTOR White blood cells, antibodies, and platelets flow in the blood stream protecting against foreign bodies and stop wounds from bleeding out. REGULATING Regulates body temperature, fluid PH, and the water content of other cells MAJOR PARTS Arteries Veins Arterioles Venules Capillaries MAJOR PARTS: ARTERIES Carries oxygenated and deoxygenated blood away from the heart and towards the lungs and the body. Largest artery on the heart is the Aorta Made up of dense connective tissue MAJOR PARTS: ARTERIES MAJOR PARTS: ARTERIOLES smaller arteries that branch off of larger arteries and provide capillaries with nutrients MAJOR PARTS: VEINS Carries oxygenated and deoxygenated blood towards the heart. Made of dense connective tissue but thinner than the walls of an artery MAJOR PARTS: VEINS MAJOR PARTS: VENULES Small veins that take blood from capillaries and drain into larger veins that lead to the heart MAJOR PARTS: CAPILLARIES Tiny, extremely thin-walled vessels that act as a bridge between arterioles and venules. They allow oxygen and nutrients to pass from the blood into tissues and allow waste products to pass from the tissues and into the blood MAJOR PARTS: CAPILLARIES STRUCTURE OF THE HEART (INTERIOR) STRUCTURE OF THE HEART (EXTERIOR) PATHWAY THROUGH THE HEART 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Vena cava Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pulmonary valve (semilunar valve) Pulmonary arteries Lungs Pulmonary veins Left atrium Bicuspid valve left ventricle 12. Aortic valve (semilunar valve) 13. Aorta 14. Body SYSTOLIC & DIASTOLIC The Systolic phase occurs when the heart contracts increasing the pressure causing the blood to move out the heart The Diastolic phase occurs when the heart relaxes decreasing pressure causing the heart to fill up with blood SYSTOLIC & DIASTOLIC Normal blood pressure is less than 120/80 mm Hg Blood pressure is recorded as a ratio systolic over diastolic SYSTOLIC & DIASTOLIC PULMONARY & SYSTEMIC Pulmonary circulation: the circuit through the lungs where blood is oxygenated Systemic circulation: the circulation where the entire body receives oxygenated blood. PULMONARY & SYSTEMIC HEARTBEATS 5 waves (PQRST) P wave: when the atria's depolarize filling the ventricles with blood QRS wave: this is when the ventricles depolarize it causes the AV valves to shut creating the “lub” sound. The S-T segment represents ventricular systole, increased pressure opens the pulmonary and aortic valves, rushing blood out the arteries. The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, or when the ventricles relax, this action causes the pulmonary and aortic valves to shut creating the “dub” sound. Atrial repolarization cannot be seen on an ECG because it is masked by the QRS complex HEARTBEATS Electrocardiogram BLOOD Plasma is a complex mixture of water, amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins, hormones, electrolytes, and cellular waste. Plasma takes over about 55% of the bloods volume. Red blood cells carry oxygen with the help of hemoglobin. RBCs also carry away waste. Leukocytes or white blood cells protect the blood stream from foreign invaders like bacteria, germs and viruses. Platelets ,or thrombocytes, help clot blood during bleeding, when they detect bleeding they release fibrinogen that turns into fibrin which is a long and threadlike material that tangles RBCs and stick to the surface of the cut to stop the bleeding. RED BLOOD CELLS Each blood type is classified by the types of antigens on the Red blood cell and the antibodies that are present Type AB blood has both A and B antigens on its surface Type O blood has no antigens on the surface of the red blood cells. People who are type O can donate blood to anyone, but can only receive type O blood. RBC RED BLOOD CELLS: RH FACTOR Any of several substances on the surface of red blood cells that induce a strong antigenic response in individuals lacking the substance. Those having inherited such antigens being designated Rh + (Rh positive) and those lacking them, a much smaller group, being designated Rh− (Rh negative) http://homegrownherbalist.net/products/the-cardiovascular-system-part-1-anatomy-physiology http://3.bp.blogspot.com/LYsBKkZQLC4/TjkS3u840NI/AAAAAAAAASU/xhtm5mv8x0s/s1600/blood_cells_RBCs.jp g http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/58/Fruit_bowl.jpg https://www.pinterest.com/ http://www.thefreedictionary.com/Rh+factor http://www.ehsbloodtype.com/blood-types/ http://glencoe.mheducation.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::800::600::/sites/dl/free/021 8378151/512870/cardiac_cycle.swf::The Cardiac Cycle Boundless. “Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation.” Boundless Anatomy and Physiology. Boundless, 27 Jun. 2014. Retrieved 01 Apr. 2015 from https://www.boundless.com/physiology/textbooks/boundless-anatomy-and-physiologytextbook/the-cardiovascular-system-18/circulation-and-heart-valves-173/systemic-andpulmonary-circulation-872-1153/ http://www.pbs.org/wnet/redgold/basics/whatisblood.html http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/heart_vascular_institute/clinical_services/centers_excellence/ womens_cardiovascular_health_center/patient_information/health_topics/platelets.html http://www.cliffsnotes.com/sciences/anatomy-and-physiology/the-cardiovascularsystem/functions-of-the-cardiovascular-system http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/dox/nitrogenouswaste.html http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/dox/nitrogenouswaste.html http://people.eku.edu/ritchisong/342notes9.html http://biologyonline.us/Online%20A&P/AP%201/Northland/AP1lab/Lab%20Online /Lab%2012/24.htm http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/heart_and_blood_vessel_disorders/biology_of_t he_heart_and_blood_vessels/blood_vessels.html http://bloods-pressure-monitors.blogspot.com/2014/10/systolic-and-diastolicpressure.html http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/HighBloodPressure/AboutHighBlood Pressure/Understanding-Blood-Pressure-Readings_UCM_301764_Article.jsp http://internal-optimist.blogspot.com/ http://www.netwellness.org/healthtopics/blood/bloodtypes.cfm