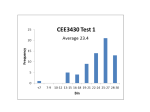
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Awareness of Stored Energy - Part I
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Grid energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
• Hazard Control • Safety Engineering - Technology • Identification of Hazards • Evaluation of Hazards • Control of Hazards • Safety Management – Administrative • Safety Program Elements • Establishment of Policies • Development of Procedures Alive & Well • Hazard Control Priority • Eliminate Hazard • Not Always Possible • Reduce Hazard • Modify Design • Redundancy – Requiring Multiple Point Failure • Safety Devices • Guards, Interlocks, Fences • Yet may be circumvented by operators • Warning Devices • Do Not Eliminate Hazard, Nor Do They Provide Protection • Requires Human Perception and a Willingness to Participate • Procedures • Require Learning, Understanding, Practice • Design of Procedures Critical and must Reflect Human Characteristics, Capabilities, and Limitations • Vary Greatly Between Individuals • Hazard Identification • Energy Analysis • Injury cannot occur without the presence of some form or Exchange of Energy • Thus: Hazard Identification – Energy Identification • i.e. An unanticipated, undesirable release or exchange of energy in a system may cause an accident and subsequent operator injury and/or system damage • Energy Management • • • • • Type of energy Amount of energy Release of energy Rate at which energy is released To a level tolerable by humans Lockout Programs must address Stored Energy • • • Awareness of how Energy is Transferred and Potentially Stored is essential An Assessment of the Systems involved is required Simply locking out a particular machine is not enough • • • • All stored energy must be Relieved Verify that there is No Potential for Re-Accumulation Assessment of related equipment A clear policy and written procedures and instructions are essential and address: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Scope Purpose Authorization Rules Techniques 7 – Step Lockout Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Prepare to shut down equipment Shut down equipment Isolate equipment from ENERGY SOURCES (???) Apply lockout devices Verify isolation Control STORED ENERGY Prepare for Startup (After work is done) • SLAM RISKS (Things Change !) • Stop – and consider the work involved • Look – for and identify the hazards • Analyze – what needs to be done • Manage – safety by developing & implementing controls • Remember – to look for changes • Identify – all potential risks • Share –what you find, include others impacted by job & risk • Know – what others on your jobsite are doing • Safety – is everyone’s job! • Hazard Identification - A Primary Concern 1) Personnel must be aware of Hazardous Energy in its many different forms 2) Systems, whether Energized or Not, can produce Hazardous Energy 3) Unexpected and unrestricted Release of Hazardous Energy can occur if: a)All energy sources are not Identified b)Provisions are not made for Safe Work Practices with energy present c) Stored energy associated with Deactivated Energy Source has not been Dissipated • Reduced to levels that are tolerable by humans • Case A • Explosives (Chemical Energy) • Individuals realize the Potential • Government Regulations (CFR) • Manufacture • Storage • Transportation • Use • Electric Blasting • Nonelectric Blasting • Extraneous Electricity • Equipment / Tools • General Requirements • Safe Operating Procedures (SOP’S) • Written document setting out the procedures that must be followed • Yet - - - Case B - - - Case C - - - etc. • Energy • Types of Energy • Potential Energy – Stationary (Stored?) • Kinetic Energy – Moving (Contains?) • Forms of Energy • • • • • • • • Mechanical Electrical Chemical Nuclear Thermal Radiant Acoustic Other • Examples of Potential Energy • Gravitational • Supporting structures • Suspended loads • Mechanical • Cable in tension • Spring • Pressurized Fluids • Hydraulic • Pneumatic • Steam • Electrical • Capacitors • Electromagnetic • Chemical • Fuels • Batteries • Nuclear • Magnetic field • Other • Examples of Kinetic Energy • Gravitational • Falling object • Radiant • Mechanical • • • • Flying object Impact of a moving against a stationary object Impact of two objects moving toward each other By virtue of its Motion • Inertia – A measure of a bodies resistance to change in motion • A Stable object resistance to being moved • A Moving object resistance to being stopped • “Stored” Energy • With regard to physics Stored only represents Potential • Yet all six of the major energy classifications can be “Stored” in some form of this general energy classification except Radiant or electromagnetic which purely transitional • • • • Mechanical can be stored as potential or kinetic – flywheel Electrical can be stored as either inductive or electrostatic field Chemical and Nuclear are pure forms of stored energy Thermal can be stored as either • Sensible heat – simply increase in temperature • Latent heat – involves a phase change - - - solid to liquid Assessment of Stored Energy • • • • Identify energy sources & potential means for storage of energy De-energize equipment by isolating or blocking energy sources Lock-out the equipment’s energy isolating device(s) Isolate or Relieve all stored energy and verify that energy has been dissipated • Verify that there is no potential for re-accumulation • Critique the situation • Gravitational Energy • By virtue of its Position • Supporting structures • An accident waiting to happen • Gravitational Energy • Loss of structural integrity as a result of Corrosion • Unauthorized Modification of Structure • Impact to a Member results in Weakening of Structure Oops – Bad Day • Gravitational • Fall of roof or back • Scaling, Bolting • Look for deterioration in ground support • Use of RF remote controls • Redundancy in controls “Proximity” • Fall of Roof or Back Fatalities 2006 • • • • 01/10/06, 44yr, 15yr exp –Rock fell from roof 02/16/06, 33yr, 7yr exp –Struck by draw rock 03/29/06, 57yr, 23yr exp –Rock fell from roof 04/20/06, 28yr, 2yr exp –Rock fell from roof • Gravitational Energy • Cables In Tension • Never stand below suspended load • Use of tag lines • Understanding Loads • Imposed on equipment • Applied to the cable • Capacity of equipment • Design • Testing – Plate/Johnny’s Prevention of Rigger Mortis • Slip / Fall of Individual Fatalities • 05/22/06, 42yr, 15yr exp –Fell 17ft from forks of forklift • 06/28/06, 49yr, 20yr exp –Fell through roof hatch cover • 08/17/06, 37yr, 15yr exp –Fell 28ft to concrete floor • Mechanical / Gravitational Energy • Conveyors • Belt • Flighted • Bucket Elevators • Belt • Chain link • Cable Assemblies • Aerial Tramways • Slings & Bridles • Cable & Chokers Systems • Power Transmission • Electric Brake system • Backstops or Holdbacks • Mechanical / Gravitational Energy • Power Transmission • • • • Electric drives Drive Belts Reducers Backstops or Holdback • Not always beneficial • Mechanical / Gravitational Energy • Potential Energy Size reduction equipment • Involve large heavy components • Crushing • Cleared Ore from unit before servicing • Grinding • Potential Energy resulting from unbalanced charge • Classification • Position of counterweight • Springs, etc • Mechanical Energy • Cables In Tension • Danger Zones • Potential failure of cable - Loss of foot • Inertia of Conveyor & Coal • Powered Haulage Fatalities 2006 • 04/04/06, 23yr, 1m exp –Entangled in belt & tail pulley • 05/03/06, 19yr, 4w exp –Entangled in belt & return idler • 05/23/06, 44yr, 11yr exp–Crushed between loader/conveyor • Machinery Fatalities 2006 • 01/12/06, 39yr, 12yr exp -pinned by rear frame of loader • 02/13/06, 25yr, 2 1/2yr exp -Struck by suspended load • Gravitational Energy • Mobile Equipment • Pre-Operational checks • Inspect Dumping locations prior to dumping first load • Gravitational Energy • Mobile Equipment • Grade Level / Inclined surface • Stability of surface • Recent weather • Seat Belts !!! • Mobile Equipment Powered Haulage Fatalities 2006 • • • • • • 01\27\06, 60yr, 10yr exp –Dozer traveled over 50ft wall 04/11/06, 22yr, 9m exp –Struck by skid steer backing up 04/22/06, 53yr, 33yr exp –Run over by front-end loader 06\12\06, 39yr, 14m exp –Boom fell & pinned against frame 07/15/06, 61yr, 40yr exp–Backed truck into water filled pit 08/29/06, 61yr, 31yr exp –Struck by front-end loader • Fall / Sliding Material Fatalities 2006 • 04\21\06, 35yr, 11m exp –Pinned by loose off highwall • 05\26\06, 58yr, 12yr exp –Bank collapsed & slid into water