* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 2: The Sun and the Heliophysics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
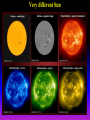
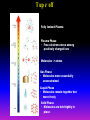
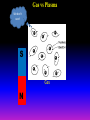
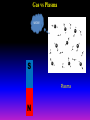
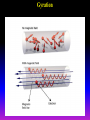
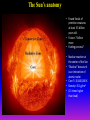
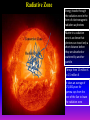
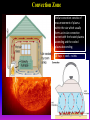
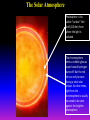
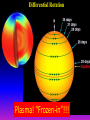
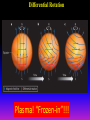
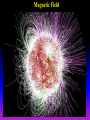
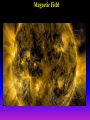
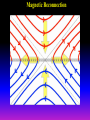
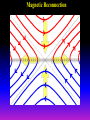
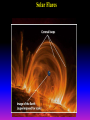
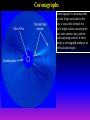
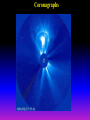
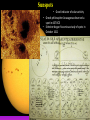
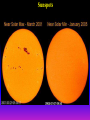
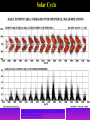
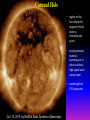
Lecture 2: The Sun and the Heliophysics Sun – Earth system Magnetospheric Physics Heliophysics Ionospheric Physics Heliosphere • Plasma • Dust • Cosmic rays Heliosphere is the bubble-like region of space dominated by the Sun Pressure of the interstellar medium = Solar wind pressure Heliosphere on August 25, 2012, Voyager 1 exited the Heliosphere, when it measured a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times 1 AU= 100 million km https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L4hf8HyP0LI Heliosphere Spacecraft Spacecraft GGS WIND measures solar wind and energetic particles from the Sun. SOHO studies the sun from core to outer corona RHESSI explores the particle physics behind solar flares. ACE observes energetic solar, interplanetary, interstellar, and galactic particles. Onehour warnings of approaching geomagnetic storms. Hinode is the Japanese word for sunrise. It is a joint mission between JAXA, NASA and the ESA to study the sun's magnetic cycles. NASA’s twin STEREO spacecraft provide stereoscopic views of the sun to better understand coronal mass ejections. SDO records the Sun's dynamic solar activity to understand how it affects life on Earth. Very different Sun Very different Sun Surface of the Sun Surface? Not really… Sharp transition. T up e- off Fully Ionized Plasma Plasma Phase • Free electrons move among positively charged ions Molecules -> atoms Gas Phase • Molecules move essentially unconstrained Liquid Phase • Molecules remain together but move freely Solid Phase • Molecules are held tightly in place Gas vs Plasma We don’t care! S Gas N Gas vs Plasma WOW! S Plasma N Gyration Gyromotion • • • • Differential motion produces current Currents produce the magnetic field Plasma and Magnetic field are ‘frozen-in” together The plasma cannot move unless the magnetic field moves The Sun’s anatomy • Found fossils of primitive creatures at least 3.5 billion years old. • Future: 7 billion more • Fueling process? • Nuclear reaction at the center of the Sun • “Nuclear” because it is an interaction of atomic nuclei • Core T=15,600,000 K • Density=151 g/cm3 • (13 times higher than lead) Fusion Min T=14,000,000 K Neutrino Positron Deuterium Mass(alpha particle) is 0.7% lighter than 41H So what? Alpha particle Mass(alpha particle) is 0.7% lighter than 41H Every second 700,000,000,000 kg of H fuses into He H Used Left 37, 37% 63, 63% 0.7%=5,000,000,000 kg E=(5,000,000,000 kg)*c2 C=3*108 m/s E=4.5*1026 Joules In 2015 world consumed 5.67 × 1020 Joules Neutrinos 70 billion solar neutrinos pass through each square centimeter of the Earth’s surface facing the Sun If we can detect neutrinos then indeed the Sun is powered by the H fusion! In 2002 Ray Davis and Masatoshi Koshiba won part of the Nobel Prize in Physics Neutrino detection The water Cerenkov neutrino detector of the SuperKamiokande experiment in Japan comprises a tank filled with 50,000 tons of water and lined with more than 11,000 photomultiplier tubes. The interaction of a muon neutrino inside the SuperKamiokande detector Radiative Zone Energy travels through the radiation zone in the form of electromagnetic radiation as photons Matter in a radiation zone is so dense that photons can travel only a short distance before they are absorbed or scattered by another particle T drops from 15 million K to 1.5 million K it takes an average of 171,000 years for gamma rays from the core of the Sun to leave the radiation zone Convection Zone Stellar convection consists of mass movement of plasma within the star which usually forms a circular convection current with the heated plasma ascending and the cooled plasma descending. 10 days -> cools -> sinks The Solar Atmosphere Photosphere = the visible “surface” thin shell (100 km) from where the light is radiated The chromosphere emits a reddish glow as super-heated hydrogen burns off. But the red rim can only be seen during a total solar eclipse. At other times, light from the chromosphere is usually too weak to be seen against the brighter photosphere. Very nice coincidence Chromosphere Luc Viatour Solar Corona WHAAAAAAAAAT???? Wave Heating Theory • Magneto-acoustic waves • Alfven waves • turning into shock waves and dissipate their energy as heat. Differential Rotation Plasma! “Frozen-in”!!! Differential Rotation Plasma! “Frozen-in”!!! Magnetic Field Magnetic Field Magnetic Reconnection Magnetic Reconnection Magnetic Field https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1jQ0M7K0E3s&ebc=ANyPxKqiBKDz6jocME2LSj0miw81cQQUb_zN_tIQDLF4unByX25uOwgKz3RVSe2kWLhCFo__HUMjafQs17wN GqJjpc1gsn75Q&nohtml5=False Solar Flares Coronagraphs A coronagraph is a telescope that can see things very close to the Sun. It uses a disk to block the Sun's bright surface, revealing the faint solar corona, stars, planets and sungrazing comets. In other words, a coronagraph produces an artificial solar eclipse. Coronagraphs Coronagraphs https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZnDDIYm55y4 Van Gogh Sun https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index. php?title=File%3AVan_Gogh_Sun.ogv STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) 60-80 thousand C 1 million C 1.5 million C 2.5 million C Sunspots • Good indicator of solar activity • Greek philosopher Anaxagoras observed a spot in 467 BCE • Scheiner began his serious study of spots in October 1611 Sunspots Sunspots Solar Cycle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P2hN5M4 g5bY&feature=youtu.be Coronal Hole • region on the Sun where the magnetic field is open to interplanetary space • sending coronal material speeding out in what is called a high-speed solar wind stream • wavelengths of 193 Angstroms Oct. 10, 2015, by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory