* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5 Checklist - Kilmarnock Academy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
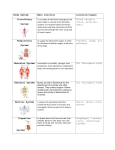
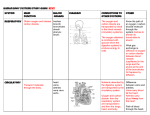
New Science Course Part 5: Biology Section. What you should know. Living and Non-Living Things Some things are living and some are non-living. Only living things show all of the following characteristics:Gas exchange Reproduction Movement They need energy They respond They produce waste Growth Basic Needs of Living Things. Living things have basic needs for survival. Animals need the following to stay alive. Food Oxygen Water Warmth Shelter Plants need the following to stay alive. Light Water Carbon dioxide and oxygen. Warmth Nutrients from the soil. Using a Microscope. A microscope is made up of many parts. You should be able to name the following parts of a microscope. Eyepiece lens, objective lens, stage, lamp, focusing controls, base. You should know that the image is what you see. The microscope makes things look bigger. The image of an object is upside down and flipped over, left to right. You work out the total magnification by multiplying the magnifications of the two lenses together. Cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of living things. Plant and animal cells have three things in common. They have a nucleus which is the control centre of the cell. They have a membrane which lets substances in and out of the cell. They have cytoplasm which is where all the cell chemistry takes place. Plant cells always have a cell wall. Animal cells do not. This is a way of telling them apart. Plant cells also sometimes contain small, green chloroplasts and a bag of water called a vacuole. There are many different types of cell in plants and animals. Using a microscope. You should be able to make a slide of some cells. You should know what a slide is and what a cover slip is. You should know what a cavity slide is. You should know that cells are tiny and transparent. You can make them easier to see by staining them with a coloured substance such as iodine solution or methylene blue. Onion is stained yellow by iodine solution. Cheek cells are stained blue by methylene blue. Some living things are unicellular. Body Organs and Body Systems. Cells are built up into tissues e.g. muscle cells are built into muscle tissue. Different tissues are built up into organs e.g. your stomach is an organ made up of muscle tissue and skin tissue. Organs are built up into systems e.g your digestive system includes organs called the stomach, pancreas and intestines. You should be able to name some body systems e.g. digestive system, skeletal system, nervous system, reproductive system. You should be able to name some parts of body systems. You should know the functions of some of the body systems. Digestion and the Digestive System. You should know that only small particles of food can pass through your gut wall into your blood. These particles need to be able to dissolve (soluble). Digestion is the process which dissolves food. You should know the tests for starch and glucose. Starch goes blue-black with iodine solution which is brown at the start. Glucose turns Clinistix from pink to purple. Glucose turns brick-red when heated with Benedict’s solution which is blue at the start. This is a dangerous experiment. Food is digested (broken down) in the gut by chemicals called enzymes. Some enzymes break down chemicals in the body and other enzymes build up chemicals in the body. Saliva contains an enzyme which breaks down starch into sugar. The digestive system is made up of the following organs:Mouth, oesophagus (or gullet), stomach, liver, pancreas, appendix, small intestine and large intestine, rectum and anus. You should be able to identify these organs. Nervous System. The nervous system is made up of three parts :- the brain, the spinal cord and the nerves. You should be able to identify these organs. Your brain controls many things :Movement, thinking, memory, personality, senses and so on…. Your brain sends messages down the spinal cord and along your nerves to communicate with the body. The body sends messages back along the nerves and spinal cord to communicate with the brain. Messages travel to and from the brain very quickly. The length of time this takes is called your reaction time. Circulatory System. Your circulatory system is made up of the heart and blood vessels. There are two main types of blood vessel. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins carry blood towards the heart. The heart is a pump which sends blood round the body. The blood carries oxygen and food to the cells of the body. The blood carries away waste products such as carbon dioxide away from the cells. Your heart rate is how many times your heart beats in one minute. Your heart rate will increase during exercise. Skeletal System. Your bones make up your skeletal system. Bones have several functions :They support the body. Muscles pull on the bones to cause movement. Bones protect major organs. Bone marrow is the factory for making new blood cells. X-rays go through soft tissues and show up bones. You should be able to identify some major bones e.g. the skull, the spine which is made up of vertebrae, the pelvis, the femur or thighbone, the radius, the ulna, the tibia, the fibula, the shoulder blade. You need a mineral called calcium to build bones and teeth. You need a vitamin called vitamin D for a healthy skeleton. Rickets is a disease caused by an unhealthy diet and the bones become bent. Respiratory System. Your respiratory system is your breathing system. It is made up of your lungs and windpipe along with your ribcage and diaphragm. Your vital capacity is the volume of the biggest breath you can take. Breathed out (exhaled) air contains more carbon dioxide than fresh (inhaled air). Exhaled air turns lime water milky. This is a test for carbon dioxide. Your ribcage and diaphragm make your chest smaller and squeeze air out of your lungs. They then make the chest bigger and air if forced back into your lungs. You should be able to identify the lungs, windpipe, rib cage and diaphragm. Monitoring Health. Doctors can use instruments to monitor the health of the body. Scanners and X-ray machines can look inside the body. High tech instruments are usually electronic. Low tech instruments are not. You can work out your BMI to tell whether you have a healthy body weight.