* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Structures and functions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
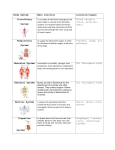
Course CIP Code: Agriculture Biology Standard # 5 Objective # 2 Instructor: Mr. Nathan Bushman Lesson Title: Structures and Functions Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: 1. describe the function of the skeletal system 2. identify the major types of bones 3. describe the function of the muscular system 4. differentiate between, skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle 5. explain the functions, and structures of the digestive system 6. differentiate between, monogastric and ruminant digestive systems 7. describe the function and structure of the circulatory system 8. summarize the functions and structures of the respiratory system 9. explain the functions and structures of the nervous system 10. identify the importance of the endocrine system 11. identify the parts excretory system 12. label the parts of the female reproductive system 13. label the parts of the male reproductive system 14. list and explain reproductive technologies Interest Approach: Students will be asked to get a piece of paper out and create any animal of there choice. The one stipulation is that the animals need to be able to stand upright on the table. The students will soon find that the animal won’t be able to stand without a structure system. The instructor will then hand out tooth picks and tape. The students will use them to give their animal structure. This activity will be tied into the lesson plan by discussing the importance of skeletal systems in the body. Curriculum and Instruction Plan: Power Point, lecture and class discussion Objective 1: Describe the function of the skeletal system 1. Animals as an organism a. Animals are composed of a variety of interdependent systems b. No one system can function entirely on its own c. In order to keep animals healthy, producers make sure that all systems function properly. 2. Skeletal System a. Function - provides frame and support for all other systems and organs b. Cartilage -- firm, flexible tissues that is not as hard as bone c. Bones a. Function -- attach muscles, means of movement, protect internal organs, storage of minerals, blood formation 3. Layers of Bone a. Periosteum -- outer layer; cushions the hard portion of the bone; repair of broken bones b. Compact Bone -- beneath periosteum, layer of hard mineral matter; gives bones strength c. Spongy Bone -- Inside hard outer layer; fills ends of bones; lines hollow portions d. Red marrow -- inside cavities of spongy bone; formation of blood cells e. Yellow marrow -- Located inside hollow portion; fat storage cells; energy storage Objective #2: identify the major types of bones 4. Types of Bone a. Long Bones -- longest; provide support and movement; levers; example -- legs, ribs, pelvic bones b. Short Bones -- smaller than long; joints; comfort and mobility example -- feet and hands c. Irregular Bones -- have an irregular shape; support and protect example -- vertebrae d. Flat Bones -- thin and flat; protect organs example – skull 5. Joints a. where different bones meet b. Ligaments connects bones together; tough tissue c. Movement none; hinge; ball and socket; gliding; Objective #3: Describe the function of the muscular system 6. Muscular System a. Function -- to move the animal about, to provide movement for the proper functioning of the organs. b. Meat production -- muscles are processed into meat; 30-40% of the animal’s body is muscle. Objective # 4: Differentiate between, skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle 7. Skeletal Muscle a. Movement -- movement for the bones of the skeleton and other voluntary movement; composed of long, striated bundles that contract and relax b. Tendons -- connect muscles to bones c. Red Muscle -- contain many mitochondria; lots of bood; contract for long periods of time d. White Muscle -- Fewer mitochondria; contract faster; fatigue faster. 8 .Smooth Muscle a. Movement -- Controls movements of the internal involuntary; non-striated sheets. b. Examples-- Digestive tract, urinary tract organs; 9. Cardiac Muscle a. Movement -- muscles that control the heart; striated and arranged in bands; involuntary; amazing b. Stamina -- # of times a heart beats in a lifetime? Class Activity – Students add skeletal system to their poster. 1. Students need to place skeletal system on animal allowing it to flip up so that the internal organs may be added later. 2. Students also need to label: a. Three long bones b. Three Short bones c. Three Irregular bones d. Three Flat bones Objective # 5: Explain the functions, and structures of the digestive system 10. Digestive System a. Function-- Supplies energy by converting ingested food into usable forms b. Conversion-- breaking food down into components that can be absorbed. c. Absorption-- bringing nutrients into the blood and ultimately into the cells Objective # 6: Differentiate between, monogastric and ruminant digestive systems d. Monogastric System -- Simple stomach examples of animals: pig, dog, cat, birds,bear, humans e. Process a. Mouth b. Esophagus c. Peristalsis -- contractions of muscles that move food from the mouth to stomach d. Stomach -- breaks down food by muscle contractions and gastric juice f. Small intestine a. Duodenum -- breaks down food using enzymes b. Jejunum -- absorbs food into bloodstream c. ileum -- more absorption takes place her d. villi-- fingerlike projections that absorb food g. Large Intestine a. Cecum -- contains microorganisms in some animals, useless in others b. Colon -- removal of water and minerals, breakdown by microorganisms c. Rectum -- passes waste material through to the anus h. Accessory Organs i. Liver -- filters blood, stores nutrients, and produces bile ii. Pancreas -- produces enzymes (insulin, etc) that break down food iii. Gall Bladder -- stores bile for use as needed. i. j. Examples of Animals --horses and rabbits Differences from simple monogastric -- enlarged cecum containing many microorganisms so that cellulose can be broken down and used. k. Ruminant Digestive System Examples of Animals -- cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk a. Rumen -- storage vat; food is soaked, mixed and fermented ( lots of microorganisms). b. Reticulum -- indigestible hard objects are removed, sorts feed for regurgitation (“cud”) c. Omasum -- grind roughage and remove some water d. Abomasum -- “true stomach”; break down like nonruminant stomach Writing Activity The students will be giving a journal entry assignment on the digestive systems of a ruminant animal. They will need to imagine that they are a blade of grass. They will write their travels through the digestive system after the cow eats them, being sure to have explicit details of each stop along the way. (Example, esophagus, rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasums, etc…) Class Activity – Students add digestive system to their poster (ruminant). 1. Students need to place digestive system on animal allowing it to flip up so that other internal organs may be added later. 2. Students also need to label: a. Rumen b. Reticulum c. Omasum d. Abomasum Lecture, class discussion and Power Point Objective # 7: Describe the function and structure of the circulatory system 11. Circulatory System a. Function -- transports food, nutrients, water, oxygen and wastes throughout the body; regulates temperature; removes disease. b. Heart -- center of the circulatory system; large muscle that pumps continuously c. Four Chambers d. Atria -- receives blood into heart; right from venacava, left from lungs e. Ventricles -- pumps blood out into arteries; right to lungs; left to aorta a. Blood Vessels a. Arteries -- vessels that take blood from the heart b. Veins -- vessels that return blood to the heart c. Capillaries -- connect arteries and veins; deliver nutrients to the cells and take away wastes d. Blood -- 1/2 is plasma (clear), 1/2 is cells b. Blood Components a. Red Blood cells -- give blood color; carry oxygen b. White Blood cells -- destroy disease; pus c. Platelets -- fragments of cells; aid in clotting Class Activity – Students add circulatory system to their poster. 3. Students need to place circulatory system on their animal allowing it to flip up so that other internal organs may be added later. 4. Students need to label: a. Four Chambers of the heat b. Veins c. Arteries d. And arrows showing how the blood flows through the heart Objective # 8: Summarize the functions and structures of the respiratory system 12. Respiratory System Function a. Takes oxygen from the air and places it in the bloodstream for distribution to the cells of the animal’s body. b. Removes carbon dioxide Structures a. Nostrils -- large amounts of air, open into nasal cavity b. Mouth -- brings in air c. Pharynx -- nasal cavity leads here; common passageway for food, water, and air; controlled by epiglottis d. Larynx -- voice box (Adam’s apple); prevents material from entering lungs. e. Trachea -- large tube; made of rigid cartilaginous rings; branch into bronchi f. Bronchi -- branch out further g. Alveoli -- surrounded by blood vessels; carbon dioxide is removed from blood, and oxygen is absorbed h. Diaphragm -- large muscle under the lungs; when contracted, rib cage expands and air comes in; when the diaphragm relaxes, air is forced out Respiratory System Types a. Lungs b. Gills Class Activity – Students add respiratory system to their poster. 5. Students need to place resperatory system on their animal allowing it to flip up so that other internal organs may be added later. 6. Students need to label: a. Parts covered in class Objective # 9: Explain the functions and structures of the nervous system 13. Nervous System Function a. The central system that controls all movements and processes of the body b. Impulse Movement -- sends information through a system of nerves electric impulses Structures a. Motor Neurons - nerves that conduct impulses from the brain to the body b. Sensory Neurons - send impulses from the body to the brain c. Spinal Cord - all nerves are connected directly or indirectly d. Brain 14. Lobes of the Brain a. Cerebrum - largest part; wrinkled and folded; controls thought processes and memory b. Cerebellum - coordination center; at the back of the brain c. Medulla oblongata - controls involuntary activities of the body a. (heartbeat, breathing, body temp, digestion) Feelings-happy, sad, mad Class Activity – Students add nervous system to their poster (brain). 7. Students need to place nervous system on their animal allowing it to flip up so that other internal organs may be added later. 8. Students need to label: a. Three main parts of the brain i. Cerebellum ii. Cerebrum iii. Medulla Oblongata Objective # 10: Identify the importance of the endocrine system 15. Endocrine System a. Function - glands that secrete hormones (chemical control) b. Hormones - chemicals that are sent to specific areas of the body; have a specific response c. Glands - produce hormones Pituitary Gland a. base of brain b. controls other glands c. growth and reproduction Hypothalamus a. lower front of brain b. controls body temp., hunger, sleep and digestion Adrenal glands a. on top of kidneys b. adrenaline -- fight or flight Thyroid gland a. on front of trachea b. thyroxin c. controls metabolism Pancreas a. secretes insulin and glucagon b. regulates sugar in the body Testes/Ovaries a. produce sex hormones Objective #11: Identify the parts excretory system 16. Excretory System Function a. Remove waste products from the body Structures a. Kidneys - filter blood and remove water, salts, and ammonia b. Bladder - store wastes from the kidneys before release c. Lungs - removes CO2 and H2O d. Skin - removes H2O and salts 17. Reproductive Systems Major Organs of the Reproductive System a. Ovaries - FEMALE reproductive gland in which EGGS are formed and hormones are produced. b. Testes -- MALE reproductive gland that produces SPERM and TESTOSTERONE. Sex Cells a. Contain HALF the normal number of chromosomes b. Female Reproductive Cell - EGG (OVULE) c. Male Reproductive Cell – SPERM d. Semen - the fluid that carries sperm Reproductive Terms a. Zygote -- a cell formed by the union of EGG and SPERM at fertilization. b. EMBRYO -- organism in early stages of development. c. PREGNANCY -- carrying a fetus d. Fertilization -- the union of the EGG and SPERM nuclei e. CONCEPTION - occurrence of fertilization f. Ovulation - release of an OVULE from the female. g. Gestation - the time from FERTILIZATION or conception of a female until she gives BIRTH Objective #12: Label the parts of the female reproductive system 18. Female Reproductive Organs Structure 19. Female Reproductive Organs Function a. Vulva -opening of reproductive tract b. Vagina - channel for birth and copulation c. Cervix - divides vagina and uterus d. Uterus - provides nourishment for fetus e. Horns of Uterus - where fetus grows f. Fallopian Tube - where fertilization occurs g. Ovaries - produces eggs and hormones Objective #13: label the parts of the male reproductive system 20. Male Reproductive Organs Structure 21. Male Reproductive Organs Function a. Testes - produce sperm and testosterone b. Epididymis - collects and stores sperm c. Vas deferens - transports sperm d. Ampulla - temporary storage e. Penis - places sperm in female f. Urethra - transports urine g. Cowper's Gland - produces semen h. Prostrate Gland - produces semen i. Seminal Vesicle - produces semen j. Retractor Penis Muscle k. Scrotum - protects testes, maintains temp l. Sheath - opening of reproductive tract m. Spermatic cord - supports testes Lab activities and Power Point Objective # 14: List and explain reproductive technologies 22. Reproductive Technologies a. Any method of REPRODUCTION that is different from NATURAL methods 23. Artificial Insemination a. Placing SPERM into the female reproductive tract by means other than natural mating. 24. EMBRYO transfers b. The transfer of FERTILIZED egg(s) from a DONOR female to one or more RECIPIENT females 25. Cloning a. The production of an exact GENETIC COPY of an organism Review and Evaluation: Objectives will be reviewed before examinations. Exams will be developed based on objectives as taught in class. Materials, Equipment and Supplies Required Classroom Attendance Role White Board Dry Erase Markers Computer Projector PowerPoint Presentation Overhead Projector Markers for Overheads White Screen References: Campbell, D. Reece, J. Mitchell, H. (1999) Biology, 5th Ed Appendices: Power Point presentations