* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the discriminant?
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Numerical continuation wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Number theory wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic reciprocity wikipedia , lookup
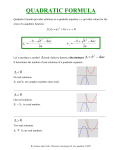
12/12/2016 (67) Discriminant review | Solving quadratics using the quadratic formula | Quadratic equations and functions | Algebra I | Khan Academy Discriminant review The discriminant is the part of the quadratic formula underneath the square root symbol: b^2-4ac. If the discriminant tells us whether there are two solutions, one solution, or no solutions. Share Tweet Email Quick review of the quadratic formula The quadratic formula says that 2 −b ± √ b − 4ac x= 2a for any quadratic equation like: 2 ax + bx + c = 0 What is the discriminant? The discriminant is the part of the quadratic formula under the square root. 2 −b ± √ b − 4ac x= 2a The discriminant can be positive, zero, or negative, and this determines how many solutions there are to the given quadratic equation. A positive discriminant indicates that the quadratic has two distinct real number solutions. https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/quadratics/solving-quadratics-using-the-quadratic-formula/a/discriminant-review 1/4 12/12/2016 (67) Discriminant review | Solving quadratics using the quadratic formula | Quadratic equations and functions | Algebra I | Khan Academy A discriminant of zero indicates that the quadratic has a repeated real number solution. A negative discriminant indicates that neither of the solutions are real numbers. Want to understand these rules at a deeper level? Check out this video. Example We're given a quadratic equation and asked how many solutions it has: 2 6x + 10x − 1 = 0 From the equation, we see: a=6 b = 10 c = −1 Plugging these values into the discriminant, we get: 2 b − 4ac 2 =10 − 4(6)(−1) =100 + 24 =124 This is a positive number, so the quadratic has two solutions. This makes sense if we think about the corresponding graph. y https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/quadratics/solving-quadratics-using-the-quadratic-formula/a/discriminant-review 2/4 12/12/2016 (67) Discriminant review | Solving quadratics using the quadratic formula | Quadratic equations and functions | Algebra I | Khan Academy y 4 2 −4 2 4 x −4 Graph of y=6x^2+10x-1 Notice how it crosses the x-axis at two points. In other words, there are two solutions that have a y -value of 0, so there must be two solutions to our 2 original equation:6x + 10x − 1 = 0. Practice PROBLEM 1 2 f (x) = 3x + 24x + 48 What is the value of the discriminant of f ? How many distinct real number zeros does f have? Check Explain Want more practice? Check out this exercise. https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/quadratics/solving-quadratics-using-the-quadratic-formula/a/discriminant-review 3/4 12/12/2016 (67) Discriminant review | Solving quadratics using the quadratic formula | Quadratic equations and functions | Algebra I | Khan Academy https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/quadratics/solving-quadratics-using-the-quadratic-formula/a/discriminant-review 4/4