* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Systems - Dickinson ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
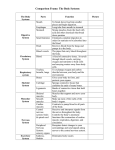
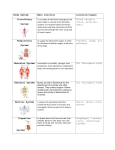
Function: Carries oxygen and nutrients to body cells; carries waste products away from cells; helps produce cells to fight infection. The circulatory system consists of a liquid called blood, a pump called the heart and a series of vessels called arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins carry blood to the heart. The blood in arteries is bright red because it is rich in oxygen. The blood in veins is dark red because it is low in oxygen. Capillaries are small vessels that join the arteries and veins. Function: Coordinates and controls body actions. Facts: There are two main divisions to the nervous system: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Peripheral Nervous System is made of the nerves and the sense organs. Messages carried throughout the body by nerves. The neuron is the basic structural unit of the nervous system. Function: Produces movement, protects internal organs, produces body heat, maintain posture Facts: Over 600 muscles make up the system known as the muscular system. There are three main kinds of muscle: cardiac, skeletal, smooth. Some muscles are called voluntary, that means that you choose to use them. Some muscles are called involuntary because they work without you thinking about them. Cardiac muscle is involuntary and only found in the heart. Skeletal muscles are voluntary and move bones. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons. Smooth muscles are involuntary and move the internal organs. Function: Creates framework of body, protects internal organs, produces blood cells, acts as levers for muscles. Facts: There are around 206 bones in the adult human body. The skeletal system also gives us our shape. Without a skeleton, we would be shapeless blobs like a jellyfish. Our bones, which are connected by ligaments, provide a frame for the rest of the organs, giving us our unique body shape. The skeletal system also helps us move. Muscles, which are attached to bones by tendons, cause the bones to move, which makes our bodies move. Bones also help your body store minerals such as calcium. If there is too much calcium in the blood, some of it becomes bone. If there is not enough calcium, then the bones give some to the blood. Function: Breathes in oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide Facts: When you inhale, air enters the body through the mouth or the nose. From there it passes through the trachea, which forces air into the lungs and food into the esophagus. The air travels down the trachea into two branching tubes called bronchi and then on into the lungs. In the lungs oxygen from the air enters the bronchi. At the same time, the waste gas carbon dioxide leaves the blood and then leaves the body when you exhale. Some water vapor also leaves the body when you exhale, which is why mirrors get foggy when you breathe on them. The diaphragm is the muscle that controls the lungs. Function: Carries some tissue fluid and wastes to blood, assists with fighting infection. Facts: The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system and is comprised of a network of vessels that circulate body fluids. Lymph is the fluid that is circulated through the lymphatic system. Function: Digests food physically and chemically, transports food, absorbs nutrients, eliminates wastes. Facts: The digestive system is composed of two separate categories of organs: digestive organs and accessory digestive organs. The gastrointestinal (GI) tract organs include the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, and large intestines. The GI tract forms a continuous tube that extends about 30 feet from mouth to anus. Food is propelled through the digestive tract via peristalsis. Function: Produces and secretes hormones to regulate body processes. Facts: The endocrine system exerts is control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones. Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems. Function: Provides for reproduction; provides new life. Facts: Although the anatomical parts differ in males and females, the reproductive system of both have the same types of organs: gonads (sex glands); ducts (tubes) to carry the sex cells and secretions; and accessory organs.