* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 06 Serving Global Markets
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Competition (companies) wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
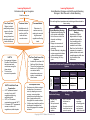
Chapter 06 Serving Global Markets Exploring alternative distribution strategies Generating additional revenue and spreading risks Global marketers are well positioned to compete Learning Objective 01 Importance of Global Marketing New insights into consumer behaviour • • • The size, per capita income of a nation, stage of economic development provides prospects for international expansion The infrastructure of a country (transportation, banking, communications etc.) also pays an important role Changes in exchange rate, domestic economic indexes such as inflation, growth also have varying impact on trade International Economic Environment • • • A nation’s culture, language, education, religious attitudes and social values does have an important impact on international marketing efforts Language plays a very important role in many fronts Cultural differences will have a significant impact in developing communication messages, customer service, communicating with local staff, distributors and other local support groups in carrying out a successful operation International Social – Cultural Environment • • • • Economies of scales of operations Enhanced reputation building global brands Technology has opened up many opportunities for companies to open up their operations across the world The internet transcends political, economic and cultural barriers reaching out to the globe Provides an opportunity for developing nations to be competitive with developed nations Technology do pose many challenges beyond innovation and communications that marketers are expected to handle International Technological Environment • • • • Global marketers must stay abreast of laws and trade regulations of countries they engage with Companies will need to carry out political risk assessments of countries they deal with The legal environment entails international laws, Canadian law and legal requirements of host nations International business agreements set terms for various aspects of commercial relations with other countries. ISO certification is an example of a similar arrangement International Political-Legal Environment Learning Objective 02 International Marketing Environment Trade barriers affect global marketing. They fall into two main categories Tariffs – Taxes levied against imported goods • Revenue Tariffs – taxes designed to raise funds for the importing government • Protective Tariffs – Taxes designed to raise the retail price of an imported product to match or exceed that of a similar domestic tariff Trade Barriers Other Trade Barriers • Import Quotas – trade restrictions that limit the number of units of certain goods that can enter a country for resale • Embargo – a complete ban on the import of a product • Subsidies – government financial support of a private industry • Exchange control –regulate importing goods by controlling access to foreign currencies Copyright © 2013 Nelson Education Ltd. Learning Objective 03 Multinational Economic Integration Learning Objective 05 Global Marketing Strategies and Multi-Domestic Marketing Strategies – Multi Domestic to Global Marketing Could be set up as • • • • • Customs Union Common Market Establishment of a free trade area plus a uniform tariff for trade with nonmember unions Extension of a customs union by seeking to reconcile all government regulations affecting trade The Free Trade Area of the Americas • Includes 34 countries of all North and South America • This will be the largest free trade zone. It offers low to non-existent tariffs, streamlines customs no quotas, no subsidies or other barriers NAFTA An agreement between Canada, US and Mexico that removes trade restrictions among the three nations. This is only an economic cooperation GATT & the World Trade Organization GATT sponsored several rounds of major tariff negotiations reducing worldwide tariffs WTO, a 153 member organization succeeds GATT It overseas GATT agreements, serves as a forum for negotiations, settle disputes • • The European Union Customs union that is moving in the direction of an economic union by adopting a common currency, removing trade restrictions and permitting free flow of goods and workers throughout the member nations It offers many benefits as well as challenges to marketers that hope to engage with its member countries Global Marketing Strategy Standardized marketing mix with minimal modifications that a firm uses in all of its domestic and foreign markets • Brings out economies of scales to production and marketing • Works effectively in targeting certain segments that share cultures and languages • • Effective strategy for luxury goods Multi-Domestic Marketing Strategy • Application of market segmentation to foreign markets by tailoring the firm’s marketing mix to match specific target markets in each nation • Most firms find that this is necessary to compete in global markets since each market/segments differ due to cultural and other differences International Product and Promotions Strategies – Five Strategy Options Same Product Promotion Strategy Free Trade Area Region in which participating nations agree to the free trade of goods among themselves abolishing tariffs and trade restrictions Multinational Corporations A firm with significant operations and marketing activities outside its home country Same Promotion Straight Extension Different Promotion Promotions Adaptation International Distribution Strategy • • Decide entry method Set up channels and physical distribution options Copyright © 2013 Nelson Education Ltd. Product Strategy Product New Product Adaptation Product Product Adaptation Invention Dual Adaptation Counter Trade International Pricing Strategy • PEST will place limitations on pricing • Pricing decisions will also depend on how prices are quoted • Form of exporting whereby goods and services are bartered rather than sold EXPORTING AND IMPORTING CONTRACTUAL AGREEMENTS INTERNATIONAL DIRECT INVESTMENTS Low DEGREE OF RISK Moderate High High DEGREE OF CONTROL Moderate Low Learning Objective 04 Strategies for Entering International Markets Franchising Foreign Licensing Subcontracting • Importing – a firm that brings in goods produced abroad to sell domestically or to be used as components in its products • Exporting – involves a continuous effort in marketing a firm’s merchandise to consumers in other countries. This would be a first step in the internationalization process. Can reach customers with the use of export trading companies, export management companies or off set agreements A contractual arrangement in which a wholesaler or retailer agrees to meet the operating requirements of a manufacturer or other franchiser. It reduces the risk since it is often a proven concept. Standardized operations reduce costs. It maintains a fair balance between local preferences and standard practices Refers to agreements that grant foreign marketers the right to distribute firm’s merchandise or to use its trademark, patent or process in a specified geographic area. It provides benefits such as access to local partner’s marketing resources etc. Allows market entry when there are embargos on imports Refers to contractual agreements that assign the production of goods or services to local or smaller firms. Manufacturers often subcontract a local company to produce their goods. It protects against import duties and will be able to compete with local offerings Acquisitions • Joint Ventures Overseas Divisions • • • • Direct investments in foreign firms, production and marketing facilities are another form of market entry This method of entry is a high risk option but would offer many competitive advantages Direct investment could take several forms o A company can acquire an existing firm o It can enter into a joint venture agreement with another firm o It can set up an independent division in a foreign country Each of these methods will pose its advantages and disadvantages The company should select the method considering the level of control required, risk it is willing to take and barriers that it would encounter as they engage in international marketing efforts Copyright © 2013 Nelson Education Ltd.