* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 28 Pregnancy and Human Development
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
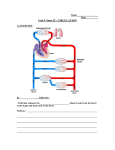
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 28 Pregnancy and Human Development 11/18/2013 MDufilho 1 Preeclampsia-Eclampsia Syndrome • Symptoms – Hypertension and proteinuria caused by vascular spasms – decreased blood flow in fetus • Classifications – Mild – systolic increase of >30 mmHg or diastolic of >15 mmHg. – Severe = Eclampsia – convulsive state • Treatment – bed rest, high protein diet, reduced sodium (?), Calcium and Mag supplements, drugs for hypertension and sedatives – if severe give Mag sulfate • Believed due to immunological abnormalities • Correlated with number of fetal cells that enter maternal circulation 11/18/2013 MDufilho 2 Lactation • Production of milk by the mammary glands • Toward the end of pregnancy – Placental estrogens, progesterone, and lactogen stimulate the hypothalamus to release prolactin-releasing factors (PRFs) – Anterior pituitary releases prolactin 11/18/2013 MDufilho 3 Lactation • Colostrum – Yellowish secretion rich in vitamin A, protein, minerals, and IgA antibodies – Released the first 2–3 days – Followed by true milk production • Suckling initiates a positive feedback mechanism • Oxytocin causes the letdown reflex 11/18/2013 MDufilho 4 Figure 28.19 Milk production and the positive feedback mechanism of the milk let-down reflex. Hypothalamus releases prolactin releasing factors (PRF) to portal circulation. Start Positive feedback Stimulation of mechanoreceptors in nipples by suckling infant sends afferent impulses to the hypothalamus. Hypothalamus sends efferent impulses to the posterior pituitary where oxytocin is stored. Anterior pituitary secretes prolactin to blood. Oxytocin is released from the posterior pituitary and stimulates myoepithelial cells of breasts to contract. Prolactin targets mammary glands of breasts. Milk production Let-down reflex. Milk is ejected through ducts of nipples. 11/18/2013 MDufilho 5 Advantages of Breast Milk • Fats and iron are easily absorbed; amino acids more easily metabolized, compared with cow’s milk • Beneficial chemicals: IgA, complement, lysozyme, interferon, and lactoperoxidase • Interleukins and prostaglandins prevent overzealous inflammatory responses • Natural laxative effect helps eliminate bile-rich meconium, helping to prevent physiological jaundice • Encourages bacterial colonization of the large intestine 11/18/2013 MDufilho 6 Development of Fetal Circulation • First blood cells arise in the yolk sac • By the end of the third week – Embryo has a system of paired vessels – Vessels forming the heart have fused 11/18/2013 MDufilho 7 Development of Fetal Circulation • Unique vascular modifications – Umbilical arteries and umbilical vein – Three vascular shunts (all are occluded at birth) • Ductus venosus: bypasses liver (umbilical vein ductus venosus IVC) • Foramen ovale: opening in interatrial septum; bypasses pulmonary circulation • Ductus arteriosus: bypasses pulmonary circulation (pulmonary trunk ductus arteriosus aorta) 11/18/2013 MDufilho 8 Figure 28.14a Circulation in fetus and newborn. Fetus Aortic arch Superior vena cava Ductus arteriosus Ligamentum arteriosum Pulmonary artery Pulmonary veins Heart Lung Foramen ovale Fossa ovalis Liver Ductus venosus Ligamentum venosum Hepatic portal vein Umbilical vein Ligamentum teres Inferior vena cava Umbilicus Abdominal aorta Common iliac artery Umbilical arteries Medial umbilical ligaments Urinary bladder Umbilical cord Placenta 11/18/2013 MDufilho High oxygenation Moderate oxygenation Low oxygenation Very low oxygenation 9 Figure 28.14b Circulation in fetus and newborn. Aortic arch Superior vena cava Ductus arteriosus Newborn Ligamentum arteriosum Pulmonary artery Pulmonary veins Heart Lung Foramen ovale Fossa ovalis Liver Ductus venosus Ligamentum venosum Hepatic portal vein Umbilical vein Ligamentum teres Inferior vena cava Umbilicus Abdominal aorta Common iliac artery Umbilical arteries Medial umbilical ligaments Urinary bladder 11/18/2013 MDufilho High oxygenation Moderate oxygenation Low oxygenation Very low oxygenation 10 Congenital Heart Defects • Patent ductus arteriosis – duct does not close which leads to increase pulmonary BP • Atrial septal defect – foramen ovale does not close which leads to poor oxygenation of blood • Coarctation of aorta – aorta is constricted which leads to increase workload on heart • Tetralogy of Fallot – multiple defects 11/18/2013 MDufilho 11 Figure 18.25 Three examples of congenital heart defects. Narrowed aorta Occurs in about 1 in every 500 births Ventricular septal defect. The superior part of the inter-ventricular septum fails to form, allowing blood to mix between the two ventricles. More blood is shunted from left to right because the left ventricle is stronger. 11/18/2013 MDufilho Occurs in about 1 in every 1500 births Coarctation of the aorta. A part of the aorta is narrowed, increasing the workload of the left ventricle. Occurs in about 1 in every 2000 births Tetralogy of Fallot. Multiple defects (tetra = four): (1) Pulmonary trunk too narrow and pulmonary valve stenosed, resulting in (2) hypertrophied right ventricle; (3) ventricular septal defect; (4) aorta opens from both ventricles. 12 Neural Tube Defects • Anencephaly – lack of cerebrum and parts of brain stem Spina bifida – incomplete formation of lamina and spinous processes – prevented by taking folic acid And…….. • Idiopathic Respiratory Distress Syndrome 11/18/2013 13 MDufilho Estrogen Oxytocin (+) from placenta from fetus and mother’s posterior pituitary Induces oxytocin receptors on uterus Stimulates uterus to contract Stimulates placenta to make (+) Prostaglandins Stimulate more vigorous contractions of uterus 11/18/2013 MDufilho 14 Figure 28.17 Umbilical cord Placenta Uterus Cervix Vagina (a) Dilation (early) 11/18/2013 MDufilho 15 Figure 28.18a Pubic symphysis Sacrum (b) Dilation (late) 11/18/2013 MDufilho 16 Figure 28.18b Perineum (c) Expulsion 11/18/2013 MDufilho 17 Figure 28.18c Uterus Placenta (detaching) Umbilical cord (d) Placental 11/18/2013 MDufilho 18 Figure 28.18d Complications with Placenta • Placenta previa – placenta partially covers opening to cervix • Placenta abruptio – placenta separates from uterine wall prematurely 11/18/2013 19 MDufilho Menopause • Ovulation and menses cease entirely • Without sufficient estrogen, reproductive organs and breasts atrophy – Irritability and depression result – Skin blood vessels undergo intense vasodilation (hot flashes occur) – Gradual thinning of the skin and bone loss • Males have no equivalent to menopause 11/18/2013 20 MDufilho “Juno, honey, it’s because doctors are sadists and like to watch lesser people scream!” In 2007, Juno and Knocked Up, two movies about unexpected pregnancies, raked in over $300 million at the box office combined. Who knew that unplanned parenthood could be so much fun? 11/18/2013 MDufilho 21