* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Community Acquired MRSA - KU School of Medicine
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
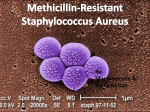
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
CommunityAssociated MRSA Maha Assi, MD, MPH MRSA Hits the Media October 16, 2007 Lead story on MRSA “superbug killing many in US” MRSA Kills High School Student 17 year old Ashton Bonds died of disseminated MRSA infection Prompts closing of school for cleaning MRSA kills Football Player 20 year old college football player who developed a skin infection. He was seen and treated with antibiotics. MRSA was not suspected. He died within days of disseminated CA-MRSA CA-MRSA An Epidemic A great deal of media attention Public concern MRSA and the Media How Common is CA-MRSA colonization ? General population analysis of data from the NHNES Colonized with Staph aureus 31.6% 84 million Colonized with MRSA 0.84% 2 million Annals of Internal Medicine. 2006 March 7;144(5):318-25 How common is disease due to CA-MRSA? In 2005 in US 94,360 cases of invasive MRSA infection with 18,650 deaths. Of those, 14% were community-acquired infections. Traditional MRSA Risk Factors Newborns, elderly, hospital workers, HD, IVDU, Diabetics, patients with chronic dermatitis Hospitalized patients, antibiotic receipt, chronic illness of any kind Community-Associated MRSA without Identifiable Risk Factors Herold 1988- reported 25 fold increase in MRSA colonization in children at a Chicago Hospital Adcock 1998-2 day care centers with from 3-24% colonization- 40% in children with no contact with health care system Deaths of 4 children in MN/ND 1999 Herold et al JAMA 1998:279:593-8 Adcock et al JID 1998:178:577-80 MMWR 1999;48:707-10 Community outbreaks Native and aboriginal communities Sports teams Child care centers Military personnel Men who have sex with men Prison inmates and guards Risk factors Skin trauma (e.g. lacerations, abrasions, tattoos, injection drug use), cosmetic body shaving, incarceration, sharing equipment that is not cleaned or laundered between users, and close contact with others who have MRSA colonization or infection. Animals can also carry MRSA and function as a source of transmission. What about me? Importantly, many patients with CA-MRSA have no risk factors. Is that all? CA-MRSA may cause disease without previous nasal colonization, and/or favor other sites of colonization over the nares (such as the skin, throat, or gastrointestinal tract). The Molecular Biology of MRSA Resistance to Penicillin=B-lactamases Resistance to Methicillin=Penicillin binding protein 2a (PBP 2a) Alterations in PBP 2a carried on SCCmec Nosocomial MRSA=SCCmec II and III CA-MRSA=SCCmec IV The USA300 strain Necrotizing pneumonia caused by CA-MRSA Outcomes in Patients Treated for CA-MRSA 33% nonresponse at day 30 Failure related to lack of I & D (p=.005) Failure not associated with wrong antibiotic choice Trend for close contacts to develop a similar infection by day 30 Clin Infec Dis. 2007;44:483-92 Eradication of MRSA Colonization The role of decolonization in the control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) spread is uncertain. Decolonization does not appear to be consistently effective for eliminating MRSA carriage. The optimal regimen and duration of therapy for eradicating MRSA colonization is uncertain. Topical regimen Chlorhexidine washes Mupirocin or Bactroban ointment applied to nares with a cotton-tipped applicator two to three times daily Prevention of CA-MRSA Handwashing Isolation Decolonization Vaccination?? Vaccine for Staph aureus Capsular polysaccharides serotypes 5 and 8 Conjugated with protein from Pseudomonas exotoxin Randomized trial in hemodialysis patients Partial immunity, decreased Staph aureus bacteremias at 40 weeks By 54 weeks no difference ?booster doses Passive immunization