* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SNC2D1 Date: Name: MAIN FUNCTION OF THE CIRCULATORY
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
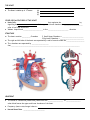
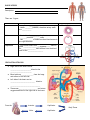
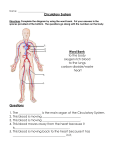
SNC2D1 Date: __________________ Name: _______________________ MAIN FUNCTION OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. 2. 3. 4. ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ WHAT DOES THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TRANSPORT? 1. 2. 3. 4. ________________________: ________________________: ________________________: ________________________: absorbed from the intestines during digestion released from the Endocrine system in conjunction with the Nervous system inhaled by the lungs during respiration Ex: CO2 eliminated via veins and the lungs Ex: other waste via kidneys and urine There are 3 main parts: Blood – Blood Vessels – Heart – PARTS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD: There are 4 components: Component Description and Function RED BLOOD CELLS (RBCs) - Contains protein _____________________ that allows RBCs to bind to ___________ and transports it - Fights, destroys and defends the body from ____________________ caused by _____________, ____________ and other _______________________________ - Help in __________________, to __________ wounds and stop bleeding - Blood clots when a _____________ is damaged - _____________________ liquid which carries blood cells, wastes, nutrients and hormones WHITE BLOOD CELLS (WBCs) PLATELETS PLASMA % of Blood THE HEART The Heart is Made up of 3 Tissues: (A) (B) (C) OTHER SPECIAL FEATURES OF THE HEART Node Cells – that regulates the by signalling the of the upper and lower chambers to ______________________ after it has filled with blood Valves – keeps blood _______________________ in the ________________________ direction STRUCTURE The heart contains __________ Chambers 2 Small Upper Chambers = _________________________ 2 Big Lower Chambers = ____________________________ The right and left side of the heart are separated by a wall of muscle called the _____________________ The chambers are separated by ____________________ that_________________________________________________________________________________ HEARTBEAT The sound of a heartbeat [Dubb-Lubb] comes from the __________________ of _________________ when blood leaves the upper and lower chambers of the heart Frequency (heart rate) change is due to: Normal Heart Rate – _________________________ BLOOD VESSELS Description: There are 3 types: Blood Vessel Arteries Description - Carry blood ___________ from the heart - Under ________ pressure, therefore artery walls are ___________ Veins - Carries blood ___________ the heart - _______ pressure, _______ walls - Has ___________ to make sure that blood moves in the right direction - Tiny blood vessels with _______________ walls to allow ___________________ to occur Ex. ________________ must diffuse from the blood cells to the __________________ Capillaries Diagram CIRCULATION OF BLOOD Right side of the heart carries ________________________ blood to the _________________________ Blood picks up ______________ from the lungs and moves to the left side Left side of the heart carries _____________________________ blood to ___________________________________ Tissues use _____________________ and return oxygenated blood to the right side of the heart From the Arteries Capillaries Body Tissue Veins Capillaries DISORDERS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM CIRCULATORY DISORDER HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE TARGET CAUSES Increased ____________ Some have blood pressure all the time HEART ATTACK Plaques shut off ________________ and prevent ___________ from getting to the heart STROKE __________ or ___________________ in the ______________ leading to the brain DETECTION AND DIAGNOSING Angiogram: ECG: Homework Read 3.4, Complete #1-9. SYMPTOMS PREVENTION/ TREATMENT Exercise regularly Eat healthy No smoking Regular medical check-ups No alcohol or drink in moderation SURGERY MAY BE NEEDED IN EXTREME CASES