* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angular Measurement
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Planetarium wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
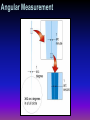
Astronomy Background from Chapter 1: •Scientific Method •Measurement How Do We Know All This? Scientific Method Allows theories to evolve through a combination of observations, theoretical reasoning, and prediction—which in turn suggests new observations. How Do We Know All This? Testable experimental verification Tested continual testing allows theories to be changed Simple Occam’s razor Elegant why make a new theory when you can amend an old one? Chain of Scientific Method Observation Prediction Theory Scientific Method Gravity is a theory? Yes, however, this theory has guided scientists’ calculations with technology from the days of Sir Isaac Newton to Space Travel calculations Observations The natural thing to do with observations, for humans, is to give them an order. Long ago, people have recognized patterns in the sky and applied mythology . . . Constellation constellation A human grouping of stars in the night sky into a recognizable pattern Constellations Constellations Constellations Near Orion The region of the sky near Orion, together with some neighboring constellations. Some prominent stars are labeled in lowercase letters. The 88 constellations span the entire sky, so that every astronomical object lies in precisely one of them Constellations Benefits to mapping the night sky? Constellations Benefits to mapping the night sky? Directional/Navigational Culture/Myths Seasons Astrology (i.e. Miss Cleo) Constellations Now remember that space is 3-D 1,000 light-years celestial sphere Surrounding earth we see a “canopy of stars resembling an astronomical painting on a heavenly ceiling.” Measurement light year The distance that light, moving at a constant speed of 300,000 km/s, travels in one year. One light year is about 10 trillion kilometers Angular Measurement -- 1 •A full circle contains 360 degrees (360°). •Thus, the half-circle that stretches from horizon to horizon, passing directly overhead and spanning the portion of the sky visible to one person at any one time, contains 180°. Angular Measurement -- 2 •Each 1° increment can be further subdivided into fractions of a degree, called arc minutes. •There are 60 arc minutes (written 60´) in one degree. •Both the Sun and the Moon project an angular size of 30 arc minutes on the sky. Your little finger, held at arm’s length, does about the same, covering about a 40' slice of the 180° horizon-to-horizon arc. Angular Measurement -- 3 •An arc minute can be divided into 60 arc seconds (60´´). •Put another way, an arc minute is 1/60 of a degree, and an arc second is 1/60 x 1/60 = 1/3600 of a degree. • An arc second is an extremely small unit of angular measure—it is the angular size of a centimeter-sized object (a dime, say) at a distance of about two kilometers (a little over a mile). Angular Measurement Angular Measurement -- 4 The angular size of an astronomical object depends on: 1.its actual size 2. its distance from us Angular Measurement -- 5 • For example, the Moon, at its present distance from Earth, has an angular diameter of 0.5°, or 30´. • If the Moon were twice as far away, it would appear half as big—15´ across—even though its actual size would be the same. • Thus, angular size by itself is not enough to determine the actual diameter of an object—the distance must also be known. Solar Days •24-hour solar day, is our basic social time unit. The daily progress of the Sun and the other stars across the sky is known as diurnal motion. •As we have just seen, it is a consequence of Earth’s rotation. •But the stars’ positions in the sky do not repeat themselves exactly from one night to the next. •Each night, the whole celestial sphere appears to be shifted a little relative to the horizon, compared with the night before Sidereal Days •Because of this shift, a day measured by the stars—called a sidereal day after the Latin word sidus, meaning "star"—differs in length from a solar day. •Evidently, there is more to the apparent motion of the heavens than simple rotation. Sidereal Days •sidereal day The time needed for a star on the celestial sphere to make one complete rotation in the sky. Night Sky •Typical Night Sky (a) A typical summer sky above the United States. Some prominent stars (labeled in lowercase letters) and constellations (labeled in all capital letters) are shown. (b) A typical winter sky above the United States. Night Sky •The 12 constellations through which the Sun passes as it moves along the ecliptic—that is, the constellations we would see looking in the direction of the Sun, if they weren’t overwhelmed by the Sun’s light—had special significance for astrologers of old. These constellations are collectively known as the zodiac. Night Sky •The Zodiac The view of the night sky changes as Earth moves in its orbit about the Sun. As drawn here, the night side of Earth faces a different set of constellations at different times of the year. The twelve constellations named here comprise the astrological zodiac.