* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How we DON*T Hear
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
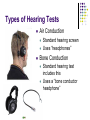
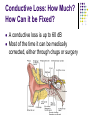
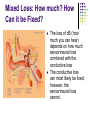
How we DON’T Hear Types of Hearing Loss, How they Happen, and What can be Done about Them How Does a Person Hear? http://www.earinfo.com/howread1.html What are the “Levels of Deafness”? Types of Hearing Tests Air Conduction Standard hearing screen Uses “headphones” Bone Conduction Standard hearing test includes this Uses a “bone conductor headphone” Conductive Hearing Loss Occurs in the external or middle ear Can be caused by a number of reasons: Closed external auditory meatus Blocked EAM from wax, debris, tumors Damaged tympanic membrane Damaged ossicles Otitis Media (Ear Infection) Other problems Conductive Loss: How Much? How Can it be Fixed? A conductive loss is up to 60 dB Most of the time it can be medically corrected, either through drugs or surgery Sensorineural Loss Occurs in the Inner Ear (cochlea, auditory nerve, or the brain) Can be caused by a number of reasons: Age Illness (high fever, lack of oxygen) Medicines Loud Noises Tumors Sensorineural Loss: How Much? How Can it be Fixed? A sensorineural loss can be complete (beyond 120 db) It can NEVER be fixed A hearing aid can amplify what is being heard, but cannot correct the hearing A cochlear implant can be surgically implanted to restore a “hearing-like” sensation, but does not sound like normal hearing 90% of hearing loss is in this category Mixed Loss A combination of a conductive loss and a sensorineural loss Can be caused by a number of reasons: Medicinally damaged cochlea + otitis media Tumor on 8th cranial nerve + closed external auditory meatus Noised-induced hearing loss + wax build-up Basically, any conductive less + nerve damage Mixed Loss: How much? How Can it be Fixed? The loss of dB (how much you can hear) depends on how much sensorineural loss combined with the conductive loss The conductive loss can most likely be fixed; however, the sensorineural loss cannot.