* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Chemistry 5 Problems (2014)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
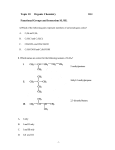
Chemistry 11 (HL) Unit 7 / IB Topics 10.4 and 20.4 Organic Chemistry 5 Reactions of Molecules with Oxygen - Problem Set 1. 2. Alcohols may be used as fuels. a) Write the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of ethanol. b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of ethanol when oxygen is limiting. c) Predict, with a reason, how the energy released in reaction (b) would compare to that in reaction (a). d) With reference to Table 12 in the Data Booklet, compare the standard enthalpy of combustion of ethane with ethanol. Suggest a reason for the difference. Write a chemical equation for these reactions, and name the organic product produced. (Simply use [O] for the oxidizing agent for now.) a) butan-1-ol reacts with acidified potassium dichromate under reflux b) propan-2-ol reacts with acidified potassium dichromate c) 2-methylbutan-2-ol reacts with acidified potassium dichromate under reflux d) 2-methylpropan-1-ol reacts with acidified potassium dichromate under distillation Chemistry 11 (HL) 3. Unit 7 / IB Topics 10.4 and 20.4 Compounds X and Y and Z are isomers with the formula C5H12O. Each compound is mixed with acidified potassium dichromate and heated. After 30 minutes, the reaction mixture containing Y remains orange while the mixtures containing X and Z turn green. When X and Z react completely with acidified potassium dichromate under reflux conditions in separate setups, the compounds K and L are produced, respectively. Compound L is found to have a higher boiling point than K. a) Deduce the name and structural formula of X, Y and Z. b) Deduce the name and structural formula of K and L. c) Heating one of X, Y and Z with acidified potassium dichromate in a distillation apparatus will produce a different compound M. Which substance will produce M under these conditions and what is the name and structural formula of M? d) Compound W is also a structural isomer of X, Y and Z but it belongs to a different homologous series. Deduce the structure of W. e) Compare, giving a reason, the solubility in water of compounds W and Z. Chemistry 11 (HL) 4. Unit 7 / IB Topics 10.4 and 20.4 a) Using structural diagrams, show the reaction between propan-1-ol and ethanoic acid. Identify the conditions required for the reaction. Name the organic product formed. b) Predict the reactants required for the formation of ethylbutanoate. Using structural formulas, show the formation of ethylbutanoate. 5. An organic compound A is 54.5% carbon by mass, 9.1% hydrogen by mass and the remainder is oxygen. a) Determine the empirical formula of A. b) The molar mass of A was found to be 87.8 g mol . Determine the molecular formula of A. c) Draw and name all possible isomers of A. -1 Chemistry 11 (HL) 6. Unit 7 / IB Topics 10.4 and 20.4 What is an oxidizing agent? Name and give the formula of the oxidizing agent most commonly used in the oxidation of alcohols. Describe the colour change for this oxidizing agent when it reacts with alcohols. 7. a) Why are distillation conditions necessary for the production of an aldehyde by the oxidation of an alcohol? b) Why are reflux conditions necessary for the production of a carboxylic acid by the oxidation of an alcohol?












![+ [O] - MrFisherChemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008194573_1-9c1e57b3af8f6a74ecb3216d2ce704f3-150x150.png)