* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (local - allergic, cardiovascular, inflammatory, general
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Williams syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Marfan syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
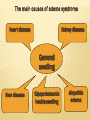
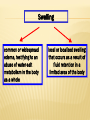
EDEMATOUS SYNDROME. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF EDEMA OF VARIOUS ETIOLOGIES (LOCAL ALLERGIC, CARDIOVASCULAR, INFLAMMATORY, GENERAL - CIRCULATORY INSUFFICIENCY, RENAL, ENDOCRINE, HUNGRY). TACTICS GPS. INDICATIONS FOR REFERRAL TO A SPECIALIST OR HOSPITAL ADMISSIONS IN THE PROFILE DEPARTMENT. PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT OF CLINICAL SUPERVISION, CONTROL AND REHABILITATION IN THE SVP OR SP. PRINCIPLES OF PROPHYLAXIS. PRINCIPLES OF TEACHING TOPICS. THE PURPOSE OF THE LESSON: TO TEACH GPS ON TIMELY DIAGNOSIS AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS, CHOICE OF OPTIMAL TREATMENT STRATEGY EDEMA DUE TO VARIOUS REASONS, AS WELL AS THE PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS IN A PRIMARY HEALTH CARE PROVIDED BY THE REQUIREMENTS OF "QUALIFICATION CHARACTERISTICS OF GENERAL PRACTITIONERS' PEDAGOGICAL OBJECTIVES: • CONSIDER THE DIAGNOSIS OF EDEMATOUS SYNDROME. • DEMONSTRATE PATIENTS WITH EDEMA SYNDROME • DISCUSS THE RESULTS OF CLINICAL, LABORATORY AND INSTRUMENTAL STUDIES WITH EDEMA. • CONDUCT A DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF EDEMA SYNDROME. • DISCUSS THE PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT (NON-DRUG AND DRUG). • DISCUSS THE PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT, SUPERVISION AND MONITORING OF PATIENTS IN A HOVERCRAFT OR A JOINT VENTURE. • DISCUSS THE PRINCIPLES OF PRIMARY, SECONDARY AND TERTIARY PREVENTION IN THESE DISEASES. LEARNING OUTCOMES: THE GENERAL PRACTITIONER (GP) SHOULD KNOW: GPS SHOULD KNOW: 1. THE MECHANISM OF EDEMA SYNDROME. 2. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF DISEASES INVOLVING OTCHENYM SYNDROME 3. DIAGNOSIS EDEMA SYNDROME 4. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF DISEASES WITH EDEMA SYNDROME 5. OF DRUGS USED IN THE TREATMENT OF EDEMA SYNDROME, THEIR PHARMACODYNAMICS AND DOSE. 6. TACTICS GPS. 7. THE PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT (DRUG AND NON-DRUG) IN THESE DISEASES. 8. PRINCIPLES OF CLINICAL SUPERVISION AND MONITORING OF PATIENTS IN A HOVERCRAFT OR A JOINT VENTURE. 9. THE PRINCIPLES OF PRIMARY, SECONDARY AND TERTIARY PREVENTION IN THESE DISEASES. TEACHING METHODS 1. LECTURE, CASE STUDIES, TESTS, DEMONSTRATION, ENTERTAINMENT EXPERIENCE, DISCUSSION, CONVERSATION, BRAINSTORMING EDUCATIONAL GAME. INDIVIDUAL WORK, GROUP WORK, TEAMWORK, CLASSROOM, EXTRACURRICULAR. 2. TUTORIALS, HANDOUTS, A COLLECTION OF CASE STUDIES AND TESTS, SET EKG.TELEVIZOR, VIDEO EQUIPMENT, MULTIMEDIA. 3. QUIZ, TESTING 4. PRESENTATION OF RESULTS OF A LEARNING TASK 5. FILLING MEDICAL HISTORY, PERFORM PRACTICAL SKILL TESTS -INTERPRITATSIYA Venous edema: 1. Acute deep vein thrombosis, 2. Chronic venous insufficiency, 3. venous obstruction Lymph edema: 1. Idiopathic: a) birth b) early. 2. Inflammatory. 3. Obstructive. local swelling Fatty swelling. Other types of edema The main causes of edema syndrome heart disease kidney disease General swelling liver disease Gipoproteinemic heskie swelling diopathic edema The defeat of the myocardium (myocarditis, dilated cardiomyopathy, myocardial, ischemic heart disease). The overload of the heart muscle (aortic or mitral regurgitation, ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus). Causes of cardiac edema. The overload of the heart muscle pressure (hypertension, aortic stenosis, narrowing of the mouth of the pulmonary artery). Systemic and pulmonary hypertension. Overloading infarction combined (combination of the above reasons, complex congenital and acquired heart defects). Causes of cardiac edema The state with the highest cardiac output (hyperthyroidism, severe anemia, massive obesity, cirrhosis of the liver). Violation of diastolic ventricular filling: hypertrophic and restrictive cardiomyopathy, hypertensive heart disease (in the absence of dilatation of the left ventricle), isolated mitral stenosis, constrictive pericarditis and pericardial). Swelling common or widespread edema, testifying to an abuse of water-salt metabolism in the body as a whole local or localized swelling that occurs as a result of fluid retention in a limited area of the body