* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation–evolution controversy wikipedia , lookup
Mormon views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
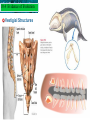
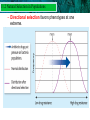
10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution • Spontaneous Generation – living things could come from nonliving things • Biogenesis – all living things come from other living things 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution • Francesco Redi – questioned the belief that flies were generated spontaneously from rotting meat • Observation – Tiny wormlike maggots turned into sturdy oval cases, from which flies eventually emerge • Experimental Group – jars with nets over them that contained meat inside – Netting allowed air to enter but not flies • Control Group – uncovered jars with meat inside • Result – maggots swarmed over the meat in the open jars while the experimental remained maggot free 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution Control Experimental A: Independent Variable - cork Experimental B: Independent Variable - net 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution Spallanzani • Hypothesis – microorganisms form not from air but from other microorganisms • Experiment – boiled broth in a flask to kill all microorganisms in it • Experimental Group – boiled then sealed flask • Control Group – boiled then left open • Result – sealed flask remained clear and free of microorganisms; open flasks became cloudy *Disagreed – heated the flasks too long, killing the “vital force” in the air inside the flask 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution Louis Pasteur – Made a goose-neck flask that prevented solid particles from entering but allowed air – remained clear for up to a year – he broke the neck off & the broth became cloudy 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution Fossil – trace of a long dead organism • Found in sedimentary rock – deposited by wind & water • Develop from hard body parts • Overtime hard minerals replace the tissue leaving rocklike structures • Mold – imprint in the rock in the shape of the organism • Cast – mold has been filled with hard minerals making a rocklike model 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution Distribution of Fossils • Law of Superposition – successive layers of rock or soil were deposited on top of one another by wind or water • Lowest stratum (rock layer) is the oldest • Relative age – using law of superposition to figure out the age of one fossil compared to another 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution. • Evolution is biological change over time • A species is a group of organisms that can reproduce and have fertile offspring. 10.2 Observations 10.1Darwin’s Early Ideas About Evolution • There were many important naturalists in the 18th century. Naturalist – collect specimens and keep careful records of observations Lamarck: Similar species descended from a common ancestor – Acquired Trait – trait not determined by genes but by experience or behavior – Believed acquired traits could be passed down 10.2 Observations 10.1Darwin’s Early Ideas About Evolution Charles Darwin • H.M.S. Beagle • 5-year mapping and collecting expedition to South America and South Pacific 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution 10.2 Observations 10.1Darwin’s Early Ideas About Evolution • Variation is a difference in a physical trait. – Galápagos tortoises that live in areas with tall plants have long necks and legs. – Galápagos finches that live in areas with hard-shelled nuts have strong beaks. 10.2 Observations 10.1Darwin’s Early Ideas About Evolution • An adaptation is a feature that allow an organism to better survive in its environment. – Adaptations can lead to genetic change in a population. – The change in genetic makeup of the population is evolution 10.2 Observations 10.1Darwin’s Early Ideas About Evolution Darwin’s Theories • Descent with Modification – newer forms appearing in the fossil record are actually the modified descendants of older species • Natural Selection – Organisms with favorable traits survive, reproduce, and pass the variations to the next generation 10.1 EarlyofIdeas About Evolution 10.3 Theory Natural Selection 10.4 Evidence of Evolution • Artificial selection is the process by which humans select traits through breeding. neck feathers crop tail feathers 10.1 EarlyofIdeas About Evolution 10.3 Theory Natural Selection 10.4 Evidence of Evolution • The study of geography provides evidence of evolution. – island species most closely resemble nearest mainland species – populations can show variation from one island to another Biogeography - Study of the distribution of organisms around the world. 10.1 EarlyofIdeas About Evolution 10.3 Theory Natural Selection 10.4 Evidence of Evolution • Embryology provides evidence of evolution. – identical larvae, different adult body forms – Similarites in Biochemistry: DNA, RNA, ATP. Etc – Embryos of Vertebrates and gill slits? Larva Adult crab Adult barnacle 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution 10.1 EarlyofIdeas About Evolution 10.3 Theory Natural Selection 10.4 Evidence of Evolution • Anatomy provides evidence of evolution. – Homologous structures are similar in structure but different in function. Human hand Mole foot Bat wing 10.1 EarlyofIdeas About Evolution 10.3 Theory Natural Selection 10.4 Evidence of Evolution • The study of anatomy provides evidence of evolution. – Analogous structures –similar function but different Human hand structure Mole foot Fly wing Bat wing 10.1 EarlyofIdeas About Evolution 10.3 Theory Natural Selection 10.4 Evidence of Evolution Vestigial structures are remnants of organs or structures that had a function in an early ancestor. • Ostrich wings are examples of vestigial structures. 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution 10.4 Evidence of Evolution Vestigial Structures 10.1 EarlySelection Ideas About Evolution 11.2 Natural in Populations Natural selection can change the distribution of a trait in one of three ways. • Normal Distribution – Frequency is highest near the mean value (average) and decreases toward each extreme end of the range. 10.1 EarlySelection Evolution 10.3 Natural Theory ofIdeas NaturalAbout 11.2 inSelection Populations – Stabilizing selection favors the intermediate (average) phenotype rather than either extremes. 10.1 EarlySelection Evolution 10.3 Natural Theory ofIdeas NaturalAbout 11.2 inSelection Populations – Directional selection favors phenotypes at one extreme. 10.1 EarlySelection Evolution 10.3 Natural Theory ofIdeas NaturalAbout 11.2 inSelection Populations – Disruptive selection favors both extreme phenotypes. 10.1 Earlyofin Ideas About Evolution 10.3 Patterns Theory Natural Selection 11.6 Evolution • Convergent evolution – Evolution toward similar characteristics in unrelated species. • Different species must adapt to similar environments. • Ex: Aquatic organisms 10.1 Earlyofin Ideas About Evolution 10.3 Patterns Theory Natural Selection 11.6 Evolution • Divergent evolution – 2 or more related populations become more dissimilar. – Response to differing habitats kit fox red fox ancestor How do convergent and divergent evolution illustrate the directional nature of natural selection? 10.1 Earlyofin Ideas About Evolution 10.3 Patterns Theory Natural Selection 11.6 Evolution Coevolution – change of 2 or more species in close association with each – occur in beneficial and competitive relationships. 10.1 Earlyofin Ideas About Evolution 10.3 Patterns Theory Natural Selection 11.6 Evolution Species can become extinct. • Extinction is the elimination of a species from Earth. 10.1 Earlyofin Ideas About Evolution 10.3 Patterns Theory Natural Selection 11.6 Evolution • Mass extinctions are rare but much more intense. – destroy many species at global level – thought to be caused by catastrophic events – at least five mass extinctions in last 600 million years 10.1 Early in Ideas About Evolution 10.4 Patterns Evidence ofEvolution Evolution 11.6 • Adaptive radiation – The diversification of one ancestral species into many species. – descendent species usually adapted to wide range of environments 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution Punctuated Equilibrium • A repeating pattern in the history of life • reflected in the fossil record • shows bursts of evolutionary activity that are followed by long periods of stability.