* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Question - ChemConnections
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
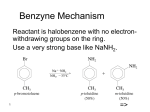
Question Chemical Behavior of Aromatic Compounds • Which compound has the lowest pKa? • Acidity • A) B) • C) D) The Benzene Ring as a Substituent Free-Radical Halogenation of Alkylbenzenes C C C• C• allylic radical benzylic radical Benzylic carbon is analogous to allylic carbon. Resonance in Benzyl Radical H • C Resonance in Benzyl Radical H H H H H H H H C H H • H H H Unpaired electron is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. Unpaired electron is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. Resonance in Benzyl Radical H C H H • Resonance in Benzyl Radical H H H H H H H C • H H H H Unpaired electron is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. Unpaired electron is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. Density in Benzyl Radical N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) is a convenient reagent for benzylic bromination Br CH2CH3 O NBr + O Unpaired electron is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. CCl4 benzoyl peroxide, heat CHCH3 O NH + O Question • Which reagent would you use for the reaction below? Oxidation of Alkylbenzenes • • • • A) B) C) D) Br2, CCl4 Br2, FeCl3 HBr, peroxides NBS, peroxides, heat (87%) Example Site of Oxidation is Benzylic Carbon O CH3 CH3 or CH2R or Na2 Cr2 O7 H2 SO4 COH Na2 Cr2 O7 H2 SO4 O H2 O heat COH H2 O heat NO2 NO2 p-Nitrotoluene CHR2 p-Nitrobenzoic acid (82-86%) Example Question O CH(CH3)2 COH Na2 Cr2 O7 H2 SO4 H2 O heat CH3 • Select the best reagent(s) to accomplish the transformation shown. • COH O (45%) • • • • A) B) C) D) PCC, CH2 Cl2 K 2 Cr2 O7, H2 SO4, heat LiAlH4 then H2 O NBS then CH3ONa Benzylic SN 1 Reactions Relative solvolysis rates in aqueous acetone: CH3 SN 1 Reactions of Benzylic Halides C CH3 620 CH3 Cl CH3 C Cl CH3 1 Tertiary benzylic carbocation is formed more rapidly than tertiary carbocation; therefore, more stable. Benzylic SN 1 Reactions Compare Relative rates of formation: CH3 CH3 C+ CH3 CH3 C+ C C C+ C+ CH3 more stable less stable allylic carbocation benzylic carbocation Benzylic carbon is analogous to allylic carbon. Resonance in Benzyl Cation H + C Resonance in Benzyl Cation H H H H H H H H H C H + H H H Positive charge is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. Positive charge is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. Resonance in Benzyl Cation Resonance in Benzyl Cation H C H H + H H H H H H H C + H H H H Positive charge is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. Positive charge is delocalized between benzylic carbon and the ring carbons that are ortho and para to it. Solvolysis Question CH3 C Cl • Which compound would undergo solvolysis at a faster rate? CH3 CH3CH2 OH • A) B) • C) D) CH3 C OCH2CH3 CH3 (87%) Primary Benzylic Halides O2 N CH2Cl Mechanism is SN2 SN 2 Reactions of Benzylic Halides O Like allylic halide, substitution is faster than a normal primary halide. NaO NaOCCH3 acetic acid O O2 N CH2OCCH3 (78-82%) Question • Which product will be siolated when 4chlorobenzyl chloride is treated with K2CO3 in H2O? • A) • • C) B) Preparation of Alkenylbenzenes •dehydrogenation •dehydration D) •dehydrohalogenation Acid-Catalyzed Dehydration of Benzylic Alcohols Dehydrogenation •Industrial preparation of styrene Cl Cl •Almost 12 billion lbs. produced annually in U.S. KHSO4 CHCH3 CH2CH3 630°C ZnO CH CH heat OH CH2 CH2 (80-82%) Cl + H2 CHCH3 + Dehydrohalogenation H3 C CH2CHCH3 Question • Which product(s) will be isolated from the reaction shown here? Br NaO NaOCH2 CH3 ethanol, 50°C • A) • B) H3 C CH CHCH3 (99%) • C) Equal amounts of A and B. • D) Neither A nor B. Hydrogenation CH3 Addition Reactions of Alkenylbenzenes C CHCH3 CHCH2 CH3 H2 •hydrogenation •halogenation •addition of hydrogen halides CH3 Pt Br Br (92%) Addition of Hydrogen Halides Halogenation Cl CH HCl Br2 CH2 CH CH2 Br Br (75-84%) + (82%) via benzylic carbocation Free-Radical Addition of HBr CH CH2 HBr CH2CH2 Br peroxides CH • Polymerization of Styrene CH2Br via benzylic radical Polymerization of Styrene H2 C CHC CHC6H5 H2 C CH2 CH C6 H5 CH2 Mechanism •• RO •• • CH C6 H5 polystyrene CH2 CH C6 H5 CHC CHC6H5 Mechanism •• RO •• H2 C CHC CHC6H5 • H2 C H2 C H2 C Mechanism CHC CHC6H5 H2 C CHC CHC6H5 CHC CHC6H5 CHC CHC6H5 H2 C CHC CHC6H5 CHC CHC6H5 • H2 C CHC CHC6H5 • H2 C Mechanism •• RO •• H2 C Mechanism H2 C CHC CHC6H5 • CHC CHC6H5 •• RO •• H2 C H2 C H2 C CHC CHC6H5 • CHC CHC6H5 •• RO •• H2 C Mechanism •• RO •• CHC CHC6H5 CHC CHC6H5