* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Level 2
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Tangent lines to circles wikipedia , lookup
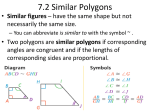
Name: Teacher: Columbia High School Math Department Geometry Summer Packet Level 2 Overview: This geometry summer packet is to acquaint you with the thinking, reasoning, and basics of your geometry program in the fall. Please carefully work through your packet, working with a peer or seeking help from a high school teacher who will be available for assistance. You are expected to have the packet completed within the first week of school and will be given an assessment on the material. Both will count toward a first marking period grade. Materials: compass, protractor, straight edge, tracing paper, calculator Symbols for marking diagrams: means congruent(the same size) | : Perpendicular: intersect to form right angles ⁄⁄ means parallel (do not intersect) Geometric Figures 1. Describe the shape below thoroughly. Describe the whole figure and the parts. B . C A 40 940 0 460 2. Look at the three shapes below. How are they alike? j Al 47 23 67 90 90 40 900 500 How are they different? What do you notice about the angles? 3. Look at the 2 sets of diagrams below. Write a definition for a polygon. Polygons Not Polygons 43 4. Create a diagram for each term below: point endpoint line congruent segments collinear midpoint line segment 5. Measure each angle using the protractor above: a. m ∠AQC = _______ b. m ∠AQB = ______ c. m ∠XQA = ______ d. m ∠ AQY = _____ e. m ∠ZQY = ______ f. m ∠ZQX = ______ Reading a Diagram May assume: Lines are straight and intersect in 1 point. May NOT assume: Items that look congruent are congruent. Lines that look parallel or perpendicular are parallel or perpendicular. (Need markings) 6. Angles - Write a definition for each bold faced word. Be sure to look at differences between what are and what are not. 7. Triangles - Write a definition for each bold faced word. Be sure to look at differences between what are and what are not. Right Triangles - 8. Look back at your definition for polygons (#3). Write a definition for the special polygons. Be sure to look at differences between what are and what are not. Polygon Names Sides Name 3 triangle 4 quadrilateral 5 pentagon 6 hexagon 7 heptagon 8 octagon 9 nonagon 10 decagon 12 dodecagon 9. Write a definition for the special quadrilaterals. Be sure to look at differences between what are and what are not. a zoid 10. Circles - . Write a definition for the bold faced words.. Be sure to look at differences between what are and what are not. Questions 1. Can a chord also be a diameter? ____ Explain. 2. Can a chord also be a tangent? _____Explain. 3. Can 2 circles be tangent to the same line at the same point? ______ Draw a diagram to illustrate. 11. Solids - 3 dimensional objects The 6 types of geometric solids: Nets - a 2 dimensional pattern that you can cut and fold to make a geometric figure. 12. Solids 13. Draw a diagram to determine if each statement below is true or false. _____a. For any 2 points there is exactly one line that can be drawn through them. _____b. If 2 lines are perpendicular to the same line in the same plane then the 2 lines are parallel. _____ c. If 2 lines in the same plane do not intersect, then they are parallel.