* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
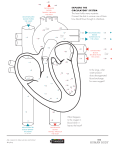
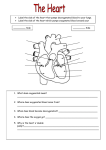
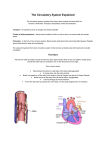
B3 Revision Trade questions: Transport in animals + Plants How many chambers are in a heart? Which heart chamber has the thickest muscle? 4 Left ventricle Which heart chamber pumps blood to the lungs? Which heart chamber receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary vein? Left atrium Right ventricle Which heart chamber receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the vena cava? Right atrium Which blood vessel is unusual in carrying oxygenated blood? What is unusual about the pulmonary artery? How many times does blood pass through the heart on each circuit of the body? Twice (= double circulation) It carries deoxygenated blood What forces blood to enter the ventricles of the heart? Contraction of the atria Name the main blood vessel which takes oxygenated blood from the heart to the body. Aorta Give 2 structural differences between arteries and veins. Arteries = thick muscle and elastic in wall; vein = thin Arteries = no valves; veins = valves Pulmonary vein What stops the backflow of blood in the heart when the ventricles contract? Heart valves What is the name of the main blood vessel which returns deoxygenated blood to the heart from the body? Vena cava Which blood vessels supply the heart muscle with oxygenated blood? Coronary arteries. How can blocked arteries be treated? What may happen if a blocked coronary is not treated? Open with a stent. Heart attack (lack of O2 to heart muscle) Name the narrowed type of blood How are capillaries adapted? vessels. Thin walls (only 1 cell thick) = capillaries short diffusion path for rapid diffusion/exchange Name 2 substances that pass Name 2 substances that pass from capillaries into cells. from cells into blood capillaries. Glucose (sugar) + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + lactic acid Name the fluid part of the blood. Name 3 things (excluding cells) transported by blood plasma. plasma 1 carbon dioxide 2 urea 3 glucose (sugar)/amino acids Where is urea made? Where do the soluble products of digestion enter the blood? Liver Small intestine What is the role of red blood cells? Transport oxygen Describe the word equation for the main reaction that occurs inside red blood cells at the lungs. Haemoglobin + oxygen → oxyhaemoglobin Give 2 adaptations of red blood cells. 1 biconcave disc shape = large SA for fast diffusion 2 no nucleus = more space for haemoglobin Describe the word equation for the main reaction that occurs inside red blood cells at body organs (excluding lungs). oxyhaemoglobin → Haemoglobin + oxygen What is the role of platelets? Describe a platelet. Make blood clot A cell fragment without a nucleus What is the role of white blood cells? Which liquid can be given in emergencies to replace lost blood volume and stabilise blood pressure? Plasma or saline Defence against pathogens/microbes Which non-reactive chemicals can carry oxygen and act as artificial blood? Perfluorocarbons (PFC’s) Give 2 advantages of an artificial heart. No donor wait No tissue match No immunosuppressant drugs Give 2 disadvantages of an artificial blood. Some do not mix well with blood Often broken down quickly May carry less oxygen Which tissue transports water and minerals in a plant? xylem Which term is used to describe the movement of water from the roots, through the xylem and out of the leaves? Transpiration stream What advantage do perflurocarbaons (PFC’s) have over blood? No blood cells, so deliver oxygen to damaged/swollen tissues; keep long time; no disease; no blood matching Give 2 disadvantages of an artificial heart. Problems with blood clotting Complex = stay in hospital expensive Which type of blood vessels carry blood away from the heart? Arteries Which tissue transports dissolved sugars from leaves to growing regions + storage organs? Phloem