* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eating Healthy for your Heart and Soul Lesson 5
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Food studies wikipedia , lookup
Food coloring wikipedia , lookup
Dietary fiber wikipedia , lookup
Food politics wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity wikipedia , lookup
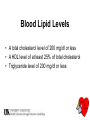
Eating Healthy for your Heart and Soul Lesson 5 Heart Health Pre-Test • Do you eat 5 or more fruits and vegetables each day? • Do you eat at least 6 servings of breads, cereals or other grain foods a day? • Do you include any whole grain foods? • Do you know your blood cholesterol level? Non-Modifiable Risk Factors • Age • Gender • Heredity Modifiable Risk Factors 90 80 70 60 50 KY Nation 40 30 20 10 0 Smoking Inactivity Obesity Diabetes No 5 A Day Heart Health Definitions • • • • • • • Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Blood Lipids Triglycerides Lipoproteins Cholesterol Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Blood Lipid Levels • A total cholesterol level of 200 mg/dl or less • A HDL level of at least 25% of total cholesterol • Triglyceride level of 200 mg/dl or less Dietary Guidelines for Americans Use the ABC’s: A= Aim for Fitness B= Build a Healthy Base C= Choose Sensibly The A-B-C’s • A= Aim for Fitness -Aim for a healthy weight -Be physically active each day • B= Build a Healthy Base -Let the pyramid guide your food choices -Choose a variety of grains daily, especially whole grains -Choose a variety of fruits and vegetables daily -Keep food safe to eat A-B-C’s continued….. • C= Choose Sensibly - Choose a diet that is low in saturated fat and cholesterol and moderate in total fat. -Choose beverages and foods low in sugar -Choose and prepare foods with less salt - If you drink alcoholic beverages, do so in moderation Use the Guidelines to Decrease Your Risk of CHD • Lose weight if you are overweight • Control high blood pressure • Lower high levels of blood cholesterol Choose a Diet Low in Fat, Saturated Fat and Cholesterol • This guideline tells us to have only 30 percent or fewer of our daily calories from fat. • Only 10% or fewer of those calories should come from saturated fats. • Saturated fats are made from substances including saturated fatty acids (SFA). • This type of fat in foods can increase blood cholesterol and lead to heart attacks. • Food fats that have a high amount of SFA are often solid at room temperature. Food Sources of SFA • Fats from animal sources such as beef, pork, lamb, and poultry skin. • Fats from whole milk, as well as other dairy foods such as butter, cheese, some yogurt, and ice cream. PUFA • Polyunsaturated Fats (PUFA) in general are not harmful to heart health and in fact, can be “good fats” when consumed in moderation. • 10% or fewer of fat calories should come from polyunsaturated fats. • Fats with a high amount of PUFA are liquids or soft products. Food Sources of PUFA • Fish such as Salmon, Lake Trout, Atlantic Mackerel, and Halibut. Taking fish oil supplements is not recommended for the general public. • Soybean, Corn, Sesame, Sunflower and Safflower Oil. MUFA • Monounsaturated Fats (MUFA), like PUFA, are not harmful when consumed in moderation. • 10% or fewer of fat calories should come from monounsaturated fat. • Fats with a high amount of MUFA are liquids or soft products. Food Sources of MUFA • Olive Oil • Canola Oil • Peanut Oil Trans Fatty Acids • Trans fatty acids are found in animal and plant foods. • Trans fatty acids are originally unsaturated the “good ones” which are changed to “bad ones” (saturated fat) through chemical changes including hydrogenation of oils. • Recent research suggests that trans fatty acids may increase the risk for heart disease. Food Sources of Trans Fat • Meats and Dairy Products (from naturally occurring chemical changes in the animal’s body as it digests food). • Plant oils that have been saturated (hydrogenated) Cholesterol • Cholesterol in food comes from animal sources only. • Cholesterol is also produced in our bodies. • Limit our dietary intake to no more than 300mg per day. Food Sources of Cholesterol • Meats, poultry, and shell fish • Whole milk and dairy products such as butter, cheese, some yogurt, and ice cream • Egg Yolks Choose a variety of grains daily, especially whole grains. Choose a variety of fruits and vegetables daily. • These guidelines focus on fiber. • Dietary fiber is the part of plant food that we cannot digest. • Healthy adults need 20-35 grams of total fiber per day. • There are two types of fiber in foods, soluble and insoluble. Soluble Fiber • Can contribute to heart health by lowering blood cholesterol. • Of the daily recommended amount of fiber, 6-10 grams should be soluble fiber. • Food sources of soluble fiber include: -oranges -bananas -carrots -apples -oats -dried beans - peas Insoluble Fiber • Insoluble fiber does not lower cholesterol, but helps the body in other ways, such as in good bowel function. • Food sources of insoluble fiber: -wheat products such as breads and cereals -wheat bran -beets -carrots -cabbage -cauliflower -apple skins Vitamins • Vitamins B6 and B12, and folic acid may play a role in preventing heart disease by keeping levels of homocysteine (an amino acid in the body) at the right level. • Vitamins C, E, and carotene (a form of Vitamin A) are antioxidants. They help prevent the oxidation of lipoproteins. This oxidation contributes to CHD. B-Vitamins B-Vitamin B6 B12 Folic Acid Recommended Daily Amount 1.3-1.5mg 2.4mcg 400 mcg Food Sources Fruits,vegetables,g rain foods,meat, fish Dairy products, meat, poultry,fish Fortified ready-to-eat cereal, dark green leafy vegetables, liver, legumes, citrus fruit Choosing Heart Healthy Foods • Read food package labels. • Understand health claims on food packages. Reading Labels • Food labels provide several types of information: -Total fat (SFA, PUFA, MUFA) -Cholesterol -Dietary Fiber -Vitamins Health Claims on Food Labels In order for a food product package to have a health claim, it must follow Food and Drug Administration regulations. -All Fats • Fat Free= less than .5 gms/serving and less than .5 gms trans fatty acids • Low Fat= 3 gms or less of total fat • Reduced or Less Fat= at least 25% less than the original product Saturated Fat Claims • Free= less than 0.5 gms/serving and less than 0.5 gms trans fatty acids • Low Saturated Fat= 1 gram or less/ serving and not more than 15% calories from saturated fatty acids. Cholesterol Claims • Free= less than 2 mg/serving • Low= 20 mg/serving Sodium Claims • Free= less than 5 mg/serving • Low= 140 mg or less/serving • Reduced= Sodium reduced by 25% of the original product’s sodium content Food Guide Pyramid Food Guide Pyramid Plan • In the tip, use fewer fats and choose oils and soft margarines. • In dairy and meat, make lean and low fat choices. Choose dry beans often. • In vegetables and fruits, get at least 5 a day, especially citrus fruits and green leafy vegetables. • In the base, look for whole grain foods rich in soluble fiber, folic acid, and other B vitamins. American Heart Association’s Heart Check Mark Certification • • • • • • Low fat (less than or= to 3 grams) Low saturated fat (less than or= to 1 gram) Low cholesterol (less than or= to 20mg) Sodium value of less than or=to 480mg Meats must meet the standard for extra lean Must contain at least 10% if the Daily Value of one or more of these nutrients: -Vitamin A -Vitamin C -Calcium -Iron or -Dietary Fiber